Cancer is one of the leading causes of mortality worldwide. While therapeutic advances have increased the rates of survival, prevention is the most powerful tool to reduce the cancer burden, given that over two-thirds of premature deaths in 2020 were deemed preventable. Despite the availability of diverse digital resources for mediating cancer prevention, they are mostly unknown to target groups.
Conventional measures of prevention have become outdated, particularly among younger people who exhibit preferences for digital communication strategies. A study attributed 37% and 50% of cancer deaths among females and males, respectively, to modifiable risk factors, such as elevated body mass index (BMI), smoking, and alcohol consumption, underscoring the pressing need for awareness programs on these risks.
Research institutes struggle with translating their findings into actionable calls for the public, given that their competitors include powerful opponents, such as the tobacco and alcohol industry. As such, they must identify affordable measures to reach their target audience. Companies employ social media influencers to disseminate their messages and reach a broader audience base. However, partnering with influencers is expensive for research institutes.
About the study
In the present study, researchers explored the potential of AI-based social media influencers to disseminate cancer prevention messages. They used Midjourney as the generative AI tool to create content. A prompt was used to create a virtual influencer, “Wanda,” a young female with a light skin tone. The study ensured character consistency by refining the AI-generated outputs through iterative prompts and adding generated images as input references.
To raise awareness about five common risk factors of cancer, e.g., alcohol, human papillomavirus (HPV), unhealthy diet, tobacco, and sun exposure, one post was generated for each subject, comprising two AI-generated images and a caption with a preventive message. The researchers shared the content on Wanda’s Instagram profile for five consecutive days. Posts were boosted with €20 using automated and targeted advertising approaches.
In the automated approach, the target population was selected using Instagram’s algorithm based on the demographics of existing followers. The targeted approach selected target groups based on interests and age. The researchers noted that the targeted method was particularly effective in focusing on users with specific health interests and lifestyle behaviors. The targeted approach was implemented for the first two days after each post was uploaded, followed by automated targeting for two additional days. The campaign’s efficacy was evaluated by analyzing each post's reach, engagement metrics such as likes and comments, and age demographics.
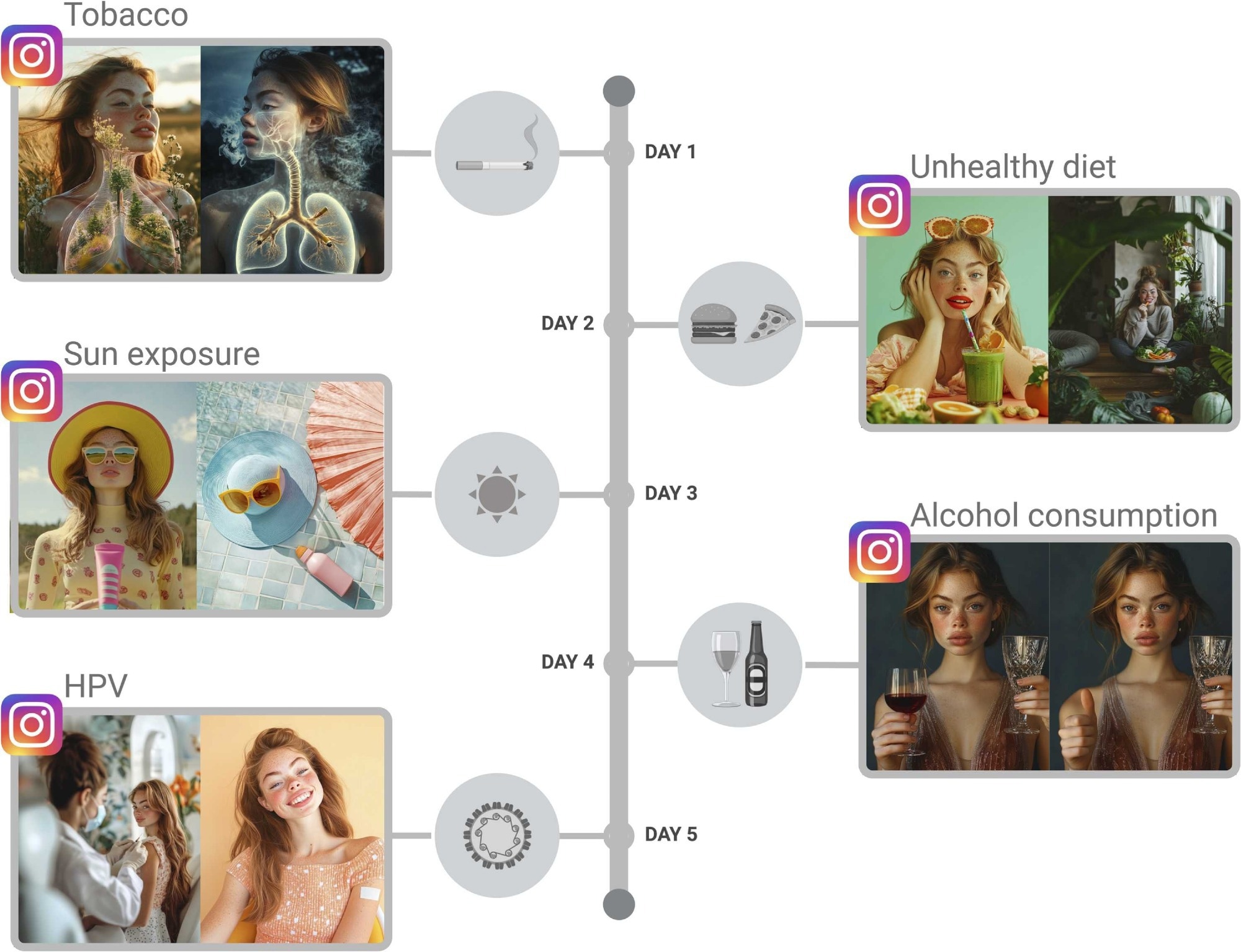 Content schedule for the Instagram campaign. Over five consecutive days, a post was published daily, each addressing one of the five leading risk factors for cancer: tobacco consumption, unhealthy diet, sun exposure, alcohol consumption, and HPV infection. The posts were designed using Midjourney.com as an exemplary GenAI platform and consistently featured the virtual persona “Wanda”. *Figure created with BioRender.com.
Content schedule for the Instagram campaign. Over five consecutive days, a post was published daily, each addressing one of the five leading risk factors for cancer: tobacco consumption, unhealthy diet, sun exposure, alcohol consumption, and HPV infection. The posts were designed using Midjourney.com as an exemplary GenAI platform and consistently featured the virtual persona “Wanda”. *Figure created with BioRender.com.
Findings
The team invested €100 in advertising, reaching 9,902 campaign recognitions within 10 days on Instagram. After all posts were advertised, 4,667 and 4,657 recognitions were reached through automated and targeted advertising approaches, respectively, indicating comparable efficacy in engagement. However, demographic data revealed differences in audience composition, with the targeted approach reaching a higher proportion of younger users.
The targeted approach increased the reach of posts on healthy diets and tobacco prevention. By contrast, the automated approach achieved a greater reach on other posts, especially among individuals aged ≥ 35 years. Individual posts reached up to 2,518 users, with posts on HPV reaching the most and those on sun exposure reaching the least. Notably, HPV-related content showed a high engagement rate, suggesting strong public interest in this topic.
The targeted approach was specific for people aged ≤ 34 years and effectively excluded people outside this age group. On the other hand, the automated approach consistently reached individuals over 34 years. The study also reported gender distribution data, indicating that female users were more likely to engage with prevention-related content. The proportion of users reached within target age groups ranged between 23% and 47.4%. The targeted approach had an average cost of €0.014 per reach; the automated approach had a comparable cost (€0.012). The study also highlighted that younger audiences were more cost-effective to reach through targeted strategies, particularly for topics related to healthy diet and tobacco use.
The tobacco prevention post (which had the highest reach) was the most economical intervention with the targeted approach, costing €0.006 per user. In contrast, the post on sun exposure had the highest cost (€0.029 per user). The researchers also noted a significant challenge in engaging audiences on sun-related cancer risks, suggesting the need for more creative approaches.
Conclusions
Together, the findings highlight the potential of AI-generated influencers as scalable tools for digital health communications. With an investment of €100 and five Instagram posts, the researchers reached over 9,900 recognitions. Both advertising strategies yielded similar reach overall, albeit there were differences in the age demographics of users. Notably, the study underscores the importance of tailoring AI-generated influencer content to resonate with different age groups and genders for maximum impact. As such, advertising to targeted audiences with specific demographics achieves comparable reach and increases thematic relevance.
Despite promising results, the study acknowledges challenges, such as audience trust and the perceived authenticity of AI-generated influencers, which could impact long-term engagement. Future research should explore integrating more interactive elements to enhance user connection with AI influencers.