The definition of a buffy coat can vary depending on context. From a research laboratory perspective, a buffy coat is not the same as the buffy coat produced by a donor center or blood bank.
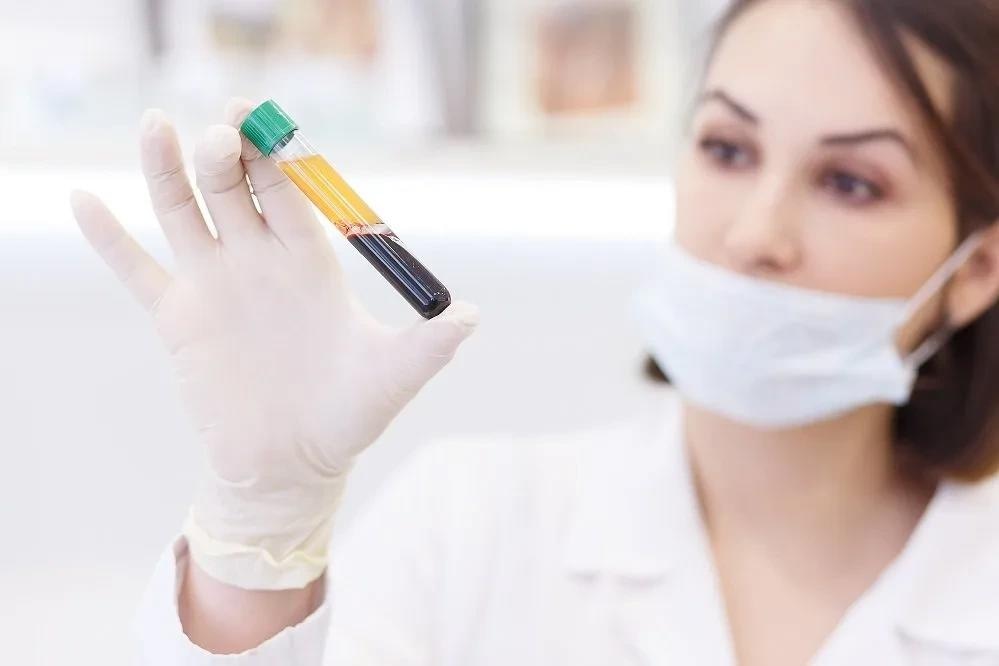

Image Credit: BioIVT
The terms PBMCs (peripheral blood mononuclear cells) and buffy coat are often used interchangeably. However, the products differ in terms of cell subset composition. PBMCs refer to the isolated mononuclear fraction of white blood cells, whereas buffy coat usually describes the entire white blood cell layer after centrifugation.
A white blood cell “buffy coat” layer is separated when peripheral whole blood is centrifuged. The buffy coat layer consists of monocytes, lymphocytes, and granulocytes (as shown in Figure 1).
However, a clean PBMC layer is separated when whole blood is layered on a density gradient and centrifuged. The PBMC layer predominantly contains monocytes and lymphocytes, with low levels of granulocyte contamination due to differences in density (as shown in Figure 2).
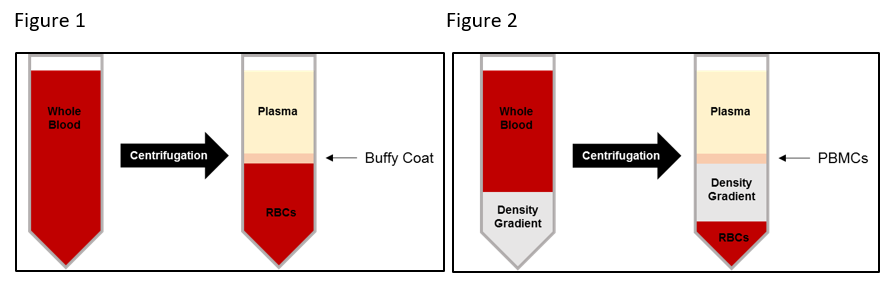
Image Credit: BioIVT
In a donor center or blood bank setting, a buffy coat is processed from a whole unit of blood, which is centrifuged in the original collection bag after donation. The centrifuged unit is then positioned on an expressor, which separates and transfers the buffy coat, plasma, and RBC (red blood cell) components into individual bags in a sterile, closed system (as shown in Figure 3).
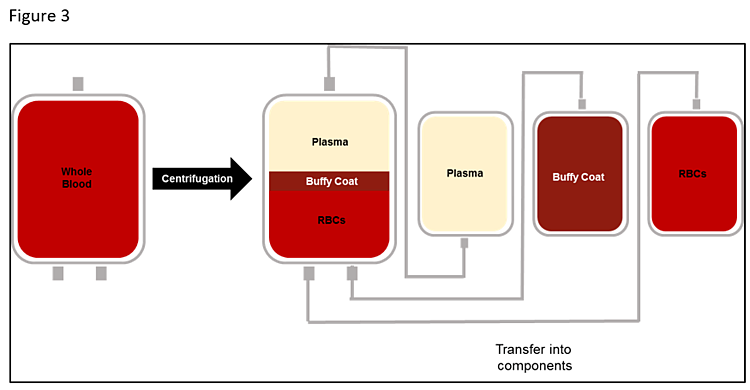
Image Credit: BioIVT
Buffy coat bags hold about 75-100 mL and resemble whole blood due to the low levels of RBCs. The bagged buffy coat comprises monocytes, lymphocytes, and some granulocytes.
The end application plays a crucial role in determining whether an isolated PBMC product or a buffy coat is appropriate. In most cases, researchers require isolated PBMCs, rather than buffy coats, due to the high purity of mononuclear cells (monocytes and lymphocytes).
BioIVT offers isolated PBMCs that have been quality control tested for both purity and viability to ensure high-quality cells to accelerate research. BioIVT supports its customers by providing a range of blood-derived immune cell products, offering both buffy coats isolated from whole blood units and isolated PBMCs.
About BioIVT
BioIVT, formerly BioreclamationIVT, is a leading global provider of high-quality biological specimens and value-added services. We specialize in control and disease state samples including human and animal tissues, cell products, blood, and other biofluids. Our unmatched portfolio of clinical specimens directly supports precision medicine research and the effort to improve patient outcomes by coupling comprehensive clinical data with donor samples.
Our Research Services team works collaboratively with clients to provide in vitro hepatic modeling solutions. And as the world’s premier supplier of ADME-Tox model systems, including hepatocytes and subcellular fractions, BioIVT enables scientists to better understand the pharmacokinetics and drug metabolism of newly discovered compounds and the effects on disease processes. By combining our technical expertise, exceptional customer service, and unparalleled access to biological specimens, BioIVT serves the research community as a trusted partner in ELEVATING SCIENCE®.
Sponsored Content Policy: News-Medical.net publishes articles and related content that may be derived from sources where we have existing commercial relationships, provided such content adds value to the core editorial ethos of News-Medical.Net which is to educate and inform site visitors interested in medical research, science, medical devices and treatments.