The new Vi–Cell BLU Cell Viability Analyzer has recently been introduced by Beckman Coulter Life Sciences. The Vi–Cell BLU utilizes the chief performance components of the Vi–Cell XR but includes several design enhancements that have been requested by customers over the years.
Though a seemingly simple application, automated cell counting can be influenced by various conditions and variables originating from both the sample and instrument. Therefore, it is essential to guarantee that the instrument is operating to meet particular specifications so that any variability in the instrument can be removed from the sample measurements.
To establish the cell counting performance of the Vi–CELL BLU, Beckman Coulter Life Sciences modified the protocol framework by NIST (Sumona et al., 2017). Using a dilution series can enable assessment of instrument performance by determining the proportional cell count across the dilutions and replicate samples.
As well as using cells, Beckman Coulter Life Sciences also assessed the system utilizing standardized beads that are able to be used for Concentration, Viability and Size calibration and as cell-independent samples for evaluating instrument performance.

Image Credit: Beckman Coulter
Data comparisons of bead and cell counting
Sample materials used: 6602796 (lot 9747455F) Coulter CC L10 Standard, nominal 10 μm, Latex Particle (NIST Traceable), 1 x 15 mL
Cell type profile: BCI L10 beads
Bead analysis instrument settings
Table 1. Source: Beckman Coulter
| Cell Type Profile |
BCI L10 Beads |
| Minimum Diameter (µm) |
5 |
| Maximum Diameter (µm) |
15 |
| Images |
100 |
| Cell Sharpness |
22 |
| minimum Circularity |
0.5 |
| Decluster Degree |
Medium |
| Aspiration Cycles |
3 |
| viable Spot Brightness (%) |
50 |
| Viable Spot Area (%) |
1 |
| Mixing Cycles |
3 |
Data recorded as averages of 72 samples for each dilution from 3 replicate 96 well plates Control Bead Results Sample Type: L10 Size Beads Control (3 instruments with replicate plates)
Control bead results
Sample type: L10 Size Beads Control (3 instruments with replicate plates)
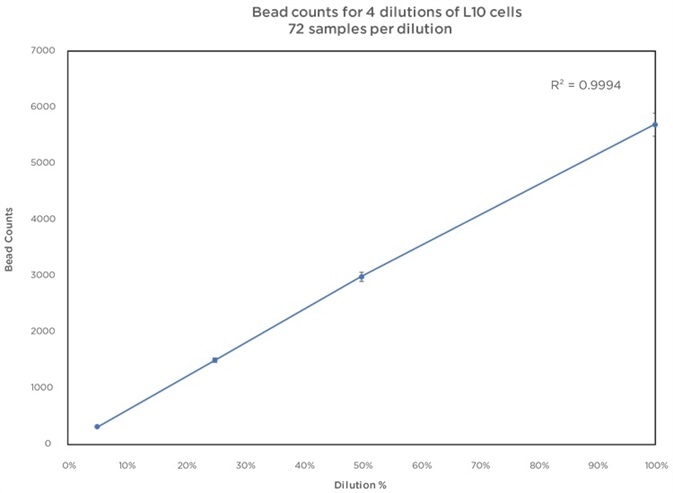
Image Credit: Beckman Coulter
Analysis of cell counting
Determination of instrument performance for Cell Counting was completed using standard cultured CHO cells. Preparation of the cells occurred in accordance with dilution guidelines described by NIST as displayed below and analysis of data was completed using standard Mammalian Cell Type. Cell type parameters for the protocols are shown below.
Cell Culture Analysis Instrument Settings:
Table 2. Source: Beckman Coulter
| Cell Type |
Mammalian |
| Minimum Diameter (µm) |
6 |
| Maximum Diameter (µm) |
30 |
| Images |
100 |
| Cell Sharpness |
7 |
| Minimum Circularity |
0.1 |
| Decluster Degree |
Medium |
| Aspiration Cycles |
3 |
| Viable Spot Brightness (%) |
55 |
| Viable Spot Area (%) |
5 |
| Mixing Cycles |
3 |
Cell count results
In order to test cell counting performance over varying ranges of concentration, a dilution protocol of 8 serial dilutions of CHO cells was established. The lower range concentrations were 9 replicate plates and were completed on 3 Vi–CELL BLU instruments; 3 plates for each instrument. Higher concentration ranges were completed as 3 sets of replicate samples of 10 tubes per dilution utilizing the carousel as a result of sample availability being limited.
Table 3. Source: Beckman Coulter
| Dilution |
Nominal Concentration (x10^6) cells/mL |
Nominal Concentration (x10^6) cells/mL |
| |
Low-Mid Range |
Mid-High Range |
| 100% |
5.50 |
13 |
| 80% |
4.40 |
10M |
| 60% |
3.30 |
8M |
| 50% |
2.75 |
6.5M |
| 40% |
2.20 |
5.2m |
| 30% |
1.62 |
3.9M |
| 20% |
1.10 |
2.6M |
| 10% |
0.55 |
- |
Results
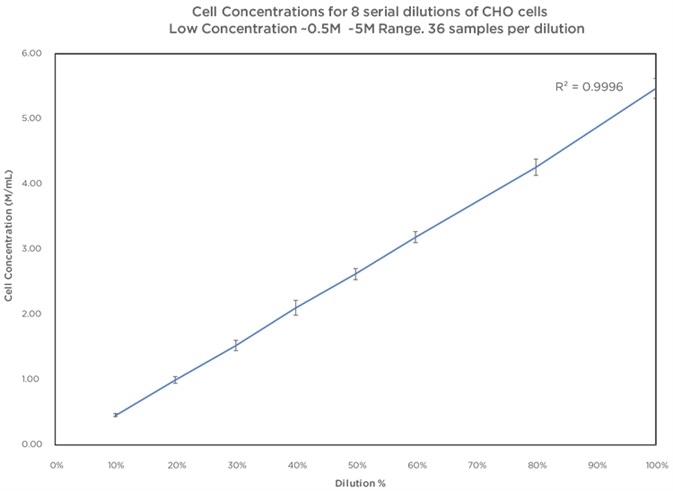
CHO Cells Low Concentration Range Dilution Series Data. Image Credit: Beckman Coulter
CHO Cells High Concentration Range Data. Image Credit: Beckman Coulter
Further sample plates were run utilizing a smaller dilution range to verify the instruments’ performance. Repetition of these occurred 3 times within a 16 hour time period utilizing the same stock supply of cells run on the same instrument. Throughout this time, an increase in cell population is thought to be minimal and the source material for analysis basically the same.
Three different Vi–CELL BLU instruments (9 plates total, n=864 samples) were used to run 3 plates in triplicate. The data underneath displays an average of 216 samples for every dilution. The data gathered from these runs was exposed to an ANOVA analysis to establish the degree of variability between the runs and within each run across sample replicates. The results display no statistical significance (p value >90) between all runs, across all instruments.
Table 4. Source: Beckman Coulter
| Dilution |
Nominal Concentration (x10^6) cells/mL |
| T100% |
2 |
| T50% |
1 |
| T15% |
0.5 |
| T10% |
0.2 |
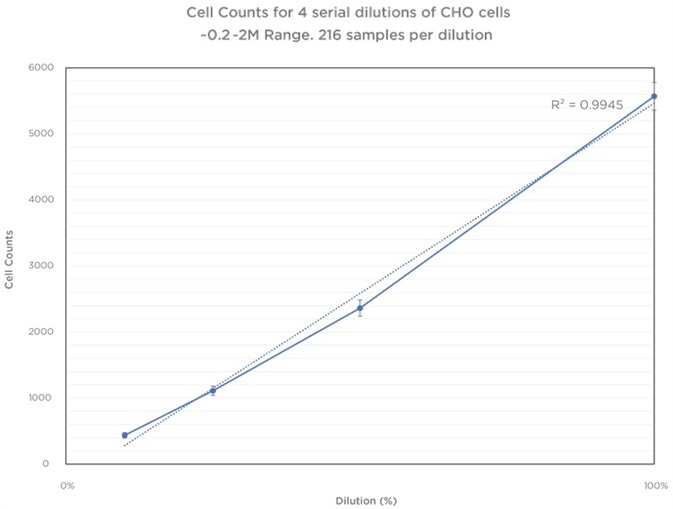
Dilution Series of CHO Cells, Multiple Replicates. Image Credit: Beckman Coulter
Conclusions
The Vi-CELL BLU’s counting performance displays brilliant linearity over many dilutions covering a range of 0.5 M–15 Million Cells per mL. As anticipated, cell counts under 0.5 M cells per mL do display an increased variability as a result of low overall numbers of cells per image frame. Although this is the case, the variability stays within allowable limits of 10% for instrument performance.
When utilizing standard L10 size beads, the variability in counts is significantly lower as a result of an increased uniform nature of the sample material. Employing the suggested NIST protocol means the proportional dilution acts as an internal control for cell count guaranteeing that the instrument is accurately counting over varying cell concentration ranges.
Correlation of the counts and concentration across dilutions has an R2 value of >0.99 displaying a constant counting performance across dilutions. It should be noted that it is possible to run a large number of samples on the Vi–CELL BLU which enables improved confidence in the cell counts and easier identification of anomalous results.
References
Evaluating the quality of a cell counting measurement process via a dilution series experimental design. Sarkar, Sumona et al. (2017) Cytotherapy, Volume 19, Issue 12 1509 – 1521.
About Beckman Coulter Life Sciences
Beckman Coulter Life Sciences is dedicated to empowering discovery and scientific breakthroughs. The company’s global leadership and world-class service and support delivers sophisticated instrument systems, reagents and services to life science researchers in academic and commercial laboratories, enabling new discoveries in biology-based research and development.
A leader in centrifugation and flow cytometry, Beckman Coulter has long been an innovator in particle characterization and laboratory automation, and its products are used at the forefront of important areas of investigation, including genomics and proteomics.
Primary activity / Product lines
- Flow Cytometry
- Centrifugation
- Particle Counting and Characterization
- Liquid Handling and Robotics
- Nucleic Acid Sample Preparation
Sponsored Content Policy: News-Medical.net publishes articles and related content that may be derived from sources where we have existing commercial relationships, provided such content adds value to the core editorial ethos of News-Medical.Net which is to educate and inform site visitors interested in medical research, science, medical devices and treatments.