OsteoSys’ iNSiGHT dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA) scanner (with a 25-second scan time) can successfully deliver reproducible data for measuring global and local alterations in rat and mouse body composition. The system also precisely evaluates excised tissue.

iNSiGHT. Image Credit: Scintica Instrumentation Inc.
This research assessed the precision of the iNSiGHT DXA scanner in measuring bone mineral content (BMC), total fat mass, total lean mass, and total weight using chemical carcass analysis, ashing, and scale weight. In grams (g), the mean r values for BMC, total fat mass, lean mass, and total weight ranged from 0.8342 to 0.9996.
The DXA measurements vs. gravimetric/chemical extraction/ashing/scale weight were strongly correlated.
The iNSiGHT DXA scanner is the only one that has been properly validated against chemical carcass evaluation, ashing, and scale weight.
Objective
This research aimed to assess the accuracy of the iNSiGHT DXA scanner in measuring actual weight, total fat mass, and BMC using chemical carcass analysis, ashing, and scale weight.
Research approaches and procedures
Forty-eight C57BL/6 mice were separated into four groups.
Table 1. Study Design/Treatment Groups. Source: Scintica Instrumentation Inc.
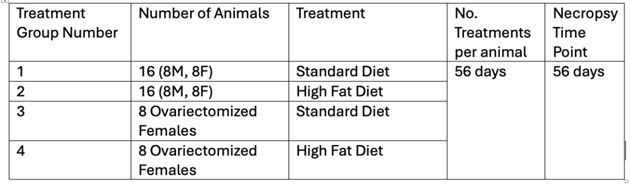
Mice were fed either a standard diet provided by Purima Lab Diet (#5001 Laboratory Rodent Diet) ad libitum or a high-fat diet provided by Diet-Induced (DIO) Rodent Diet with 45 % energy from fat, dyed red (Scott Pharma #58125) ad libitum.
On day 56, the animals were euthanized by either carbon dioxide suffocation or an overdose of isoflurane (an inhaled anesthetic) in compliance with accepted AVMA protocols. After euthanasia, they were placed in the prone position on the center of the DXA scanner’s measuring plate (16.5 x 25.5 cm scan area).
The animals’ spines were straightened, and their paws were positioned away from their bodies. A 25-second dual energy scan was performed with a 60 kV low energy and an 80 kV high energy setting at 0.8 mA. The X-ray exposure time was 5 seconds at every energy level, with an additional 15 seconds necessary for data and image processing.
The resulting images included an X-ray image, a bone mineral density (BMD) image, and a color image (lean mass in green, fat mass in red) for each animal (Figure 2). These measurements were repeated in triplicate to ensure precision.
The animals were then weighed on an electronic scale with 10 mg precision. Gravimetric and chemical extraction techniques (Soxhlet) were used as criterion methods to determine body composition, and ash content was measured by burning at 600 °C for 8 hours.
A Pearson’s two-tailed correlation was then performed to compare the values obtained via gravimetric/chemical extraction/ashing/scale weight with the DXA measurements.
Results
The iNSiGHT DXA scanner demonstrates a superior correlation to actual body composition, underlining the accuracy of both the dual-energy scan and its algorithms. Pearson’s two-tailed correlation demonstrated a high correlation between gravimetric/chemical extraction/ashing/scale weight and DXA measurements for total weight, BMC, fat mass, and lean mass (Figure 1).
In grams (g), the mean r values were 0.9996 (P< 0.0001) for total weight, 0.8342 (P< 0.0001) for bone mineral content (BMC), 0.9872 (P< 0.0001) for total fat mass, and 0.9360 (P< 0.0001) for lean mass. The DXA measurements vs. gravimetric/chemical extraction/ashing/scale weight were determined to be highly correlated.
This is the only scanner on the market that offers this full set of correlated values with a proper cross reference in ashing, chemical carcass, and weight analysis.
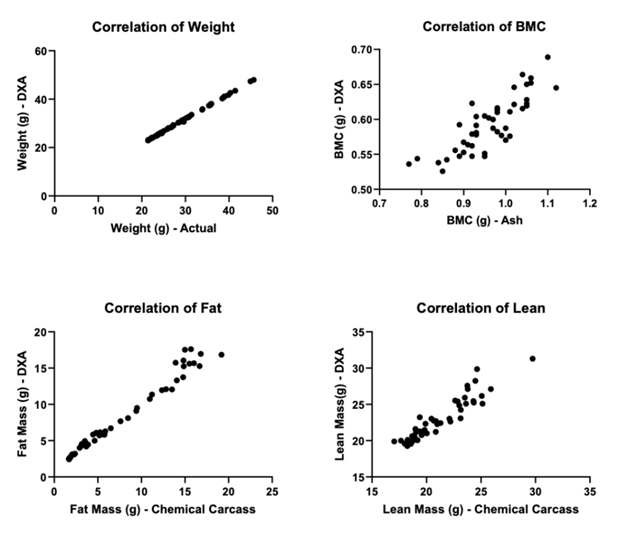
Figure 1. Correlated Values between DXA measurements and Chemical Carcass/Ashing Analysis. Image Credit: Scintica Instrumentation Inc.
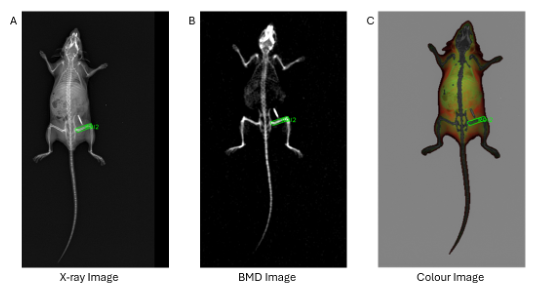
Figure 2. Example mouse images from study. Mouse 38 (Female, C57BL/6, Normal Diet). A) X-ray image. B) BMD Image. C) Colour image (lean mass in green and fat mass in red). Image Credit: Scintica Instrumentation Inc.
Conclusion
In this research, gravimetric/chemical extraction/ashing/scale weight and DXA measurements were strongly correlated for total weight, BMC, fat mass, and lean mass in mice. This represents cross-validation of the DXA measurements against the gold standard chemical carcass and ashing evaluation.
OsteoSys’ iNSiGHT DXA scanner is the only scanner currently on the market that can accurately measure alterations in body composition in small animal models.
 About Scintica Instrumentation Inc.
About Scintica Instrumentation Inc.
Scintica Instrumentation Inc., a high value distributor of scientific medical equipment, was created as a joint venture between two companies, Indus Instruments and ONS Projects Inc., both with long standing experience in the medical device instrumentation field. Indus Instruments is an engineering and manufacturing company with excellence in designing and producing sophisticated products for both medical and other high-tech clients in aerospace, chemical and oil and gas industries. ONS Projects Inc. is a life science investment and marketing company built on the foundation of two other successful manufacturing companies in the laboratory instrumentation field,
The principals of the two companies each have more than 25 years of experience of manufacturing, selling and supporting scientists in their research around the world. Our team consists of scientists, applications experts, engineers and sales professionals from a cross section of backgrounds, who excel at simplifying transactions and ensuring that scientists have the best equipment for achieving research excellence.
At Scintica Instrumentation, we distribute for selected manufacturers from all over the world and represent them in multiple countries including the United States, Canada, and Europe, as well as in Asia through a network of authorized sub-distributors.
Sponsored Content Policy: News-Medical.net publishes articles and related content that may be derived from sources where we have existing commercial relationships, provided such content adds value to the core editorial ethos of News-Medical.Net which is to educate and inform site visitors interested in medical research, science, medical devices and treatments.