Due to its profound impact on public health and well-being, obesity has become a critical research topic. The rising global prevalence of obesity has placed a tremendous burden on people, communities, and healthcare systems. By exploring the complex factors contributing to obesity, scientists aim to develop effective strategies to prevent and manage this global health crisis.

iNSiGHT. Image Credit: Scintica Instrumentation Inc.
Obesity is linked to several health problems, including cardiovascular diseases, type 2 diabetes, certain cancers, musculoskeletal disorders, and mental health issues. It is also associated with a reduced quality of life, increased healthcare expenses, and a shortened life expectancy.
Recognizing these harmful effects, researchers have increased efforts to uncover the underlying causes of obesity and develop effective prevention and treatment strategies.
Liraglutide and other glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) agonists have demonstrated considerable efficacy as anti-diabetic and anti-obesity drugs. It is currently marketed under the name Ozempic®, Victoza®, and Saxenda®. Although the metabolic impacts of liraglutide and semaglutide are well-established, their specific impact on various tissues has yet to be fully explored.
In this study, Park et al. investigated the metabolic profiles induced by liraglutide in diet-induced obese mice. This research focuses on uncovering the diverse metabolic changes induced by liraglutide treatment through comprehensive metabolomic analyses of the hypothalamus, plasma, liver, and skeletal muscle.
The study used the iNSiGHT DXA system to monitor lean and fat mass changes over time and observe bone mineral content and density.
GLP-1 is an incretin hormone that plays a critical role in insulin secretion, glucagon suppression, and appetite regulation through the GLP-1 receptor (GLP-1R). Liraglutide, a long-acting GLP-1 analog, has gained considerable attention in treating type 2 diabetes and obesity because of its extended half-life and therapeutic benefits.
Liraglutide works by suppressing appetite, reducing body fat and inflammation, regulating blood glucose levels, and promoting thermogenesis and browning of adipose tissue.
The study performed metabolomic analyses to explore the impacts of liraglutide on the metabolism of various tissues. The results revealed significant metabolic changes from liraglutide treatment compared to diet-induced obese or nonobese mice.
Liraglutide coordinated fatty acid metabolism in the hypothalamus and skeletal muscle, amino acid and carbohydrate metabolism in plasma and liver.
Through comparative analyses of metabolite dynamics, liraglutide treatment was shown to rewire inter-tissue metabolic correlations. These findings indicate that liraglutide's therapeutic effects influence metabolic pathways in multiple tissues, potentially facilitating communication and coordination between them.
Metabolomics, a powerful approach in surrogate diagnostics, is crucial for identifying biomarkers and elucidating mechanisms underlying metabolic disorders such as diabetes and obesity. By using metabolomics, scientists gain a deeper understanding of the effectiveness of anti-diabetes and anti-obesity drugs.
Although previous research has used metabolomics to explore the effects of other therapeutics, this study offers new insights into the metabolic changes induced by liraglutide treatment.
The study highlights the value of investigating the metabolic changes induced by liraglutide, a potent GLP-1 analog utilized to manage type 2 diabetes and obesity. Utilizing extensive metabolomic analyses, scientists discovered considerable alterations in metabolic profiles in various tissues after liraglutide treatment.
These results contribute to a better understanding of liraglutide’s therapeutic impacts and its effect on inter-tissue metabolic coordination. Additional research in this field could lead to the development of more precise and effective treatments for people with type 2 diabetes and obesity.
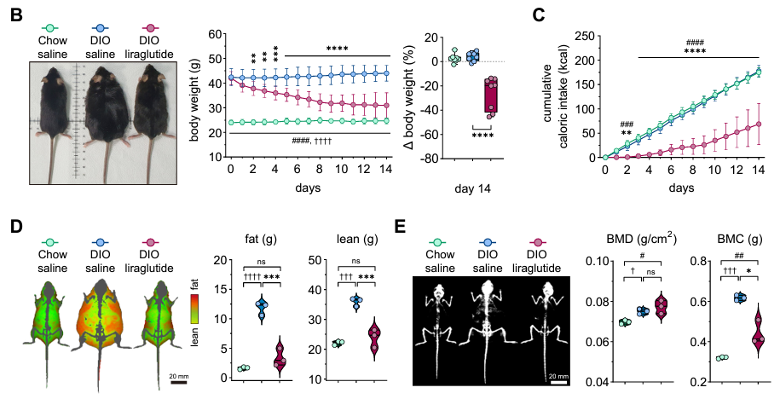
Image Credit: Scintica Instrumentation Inc.
References and further reading:
Park, S., Oh, S. and Kim, E. (2022). Glucagon-like peptide-1 analog liraglutide leads to multiple metabolic alterations in diet-induced obese mice. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 298(12), pp.102682–102682. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbc.2022.102682.
 About Scintica Instrumentation Inc.
About Scintica Instrumentation Inc.
Scintica Instrumentation Inc., a high value distributor of scientific medical equipment, was created as a joint venture between two companies, Indus Instruments and ONS Projects Inc., both with long standing experience in the medical device instrumentation field. Indus Instruments is an engineering and manufacturing company with excellence in designing and producing sophisticated products for both medical and other high-tech clients in aerospace, chemical and oil and gas industries. ONS Projects Inc. is a life science investment and marketing company built on the foundation of two other successful manufacturing companies in the laboratory instrumentation field,
The principals of the two companies each have more than 25 years of experience of manufacturing, selling and supporting scientists in their research around the world. Our team consists of scientists, applications experts, engineers and sales professionals from a cross section of backgrounds, who excel at simplifying transactions and ensuring that scientists have the best equipment for achieving research excellence.
At Scintica Instrumentation, we distribute for selected manufacturers from all over the world and represent them in multiple countries including the United States, Canada, and Europe, as well as in Asia through a network of authorized sub-distributors.
Sponsored Content Policy: News-Medical.net publishes articles and related content that may be derived from sources where we have existing commercial relationships, provided such content adds value to the core editorial ethos of News-Medical.Net which is to educate and inform site visitors interested in medical research, science, medical devices and treatments.