Cadherins, a group of transmembrane glycoproteins, play a vital role as mediators in calcium-dependent cell-cell adhesion, serving crucial functions in both normal physiological processes and the progression of various diseases.
This family includes CDH1 (E-Cadherin), CDH2 (N-Cadherin), CDH5 (VE-Cadherin), and others, contributing to tissue development, synaptic adhesion, and the maintenance of epithelial barrier function under healthy conditions.
Conversely, deviations in cadherin activity are associated with the advancement of cancer, vascular disorders, and other pathological conditions. In the realm of drug development, certain cadherins, such as CDH1, CDH2, CDH5, CDH13 (H-Cadherin), and CDH17 (LI-Cadherin).
All these have emerged as promising targets with potential applications in treating various cancers, including gastric, liver, colon, and metastatic tumors, as well as diseases like melanoma, fibrosis, carotid atherosclerosis, diabetic retinopathy, and infant respiratory distress syndrome.
Despite the absence of specific drugs targeting cadherins on the market, ongoing preclinical and clinical studies aim to leverage the therapeutic potential of these molecules. Recombinant cadherin proteins play a pivotal role in biomedical research, enabling significant discoveries and supporting investigations into diseases such as COVID-19, arrhythmogenic cardiomyopathy, and cancer.
These proteins advance the understanding of nanoscale cell-contact-guided and antibody-fragmentation technologies. Sino Biological provides an extensive selection of recombinant cadherin proteins and corresponding antibodies, including CDH1, CDH2, CDH3 (P-Cadherin), CDH4 (R-Cadherin), CDH5, CDH6 (K-Cadhedin), CDH8, CDH12, CDH13, CDH16 (Ksp-Cadherin), CDH17, and CDH18.
This comprehensive range provides valuable insights for the development of new cancer drugs, supporting innovative advances in cancer therapy and the treatment of other disease treatments.
Physiological and pathological roles
Cadherins play crucial roles in physiological processes and are equally pivotal in pathological conditions. In physiological contexts, these proteins act as mediators of cell-cell adhesion, facilitating tissue development, morphogenesis, and the maintenance of tissue integrity.
They play a vital role in the formation of tight and adherence junctions, which are necessary for epithelial barrier function. Furthermore, cadherins are critical in synaptic adhesion within the nervous system, affecting learning and memory processes.
Conversely, in pathological scenarios, changes in cadherin expression or function are linked to the progression of various cancers. Notably, CDH1 and CDH2 are implicated in cancer invasion and metastasis, particularly in gastric, colorectal, and breast cancers.
CDH5 plays a role in angiogenesis and vascular diseases, CDH13 is associated with atherosclerosis and various carcinomas, and CDH17 is involved in both liver development and carcinogenesis.
The dysregulation of these cadherins has the potential to disrupt tissue homeostasis, contributing to a range of diseases. This underscores their importance in both health and pathology.
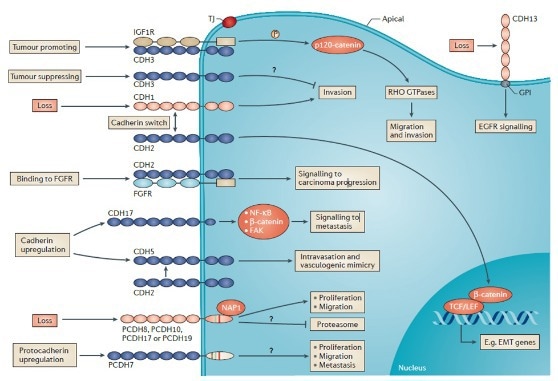
Interactions and biological activities of cadherins in cancer cells. Image Credit: doi.org/10.1038/nrc3647
From bench to bedside
Various cadherins have been subjects of scrutiny in the realm of drug discovery and development. Notably, CDH1 has been implicated in cancer development, invasion, and metastasis. CDH2 and CDH4 are associated with neural development and cancer progression.
CDH5 is deemed critical for vascular integrity and barrier permeability. CDH3 is linked to specific hereditary genetic disorders and cancers. CDH6 and CDH16 play roles in kidney development and associated diseases. CDH13 is associated with cardiovascular diseases. CDH17 is related to gastrointestinal and hepatocellular carcinoma. CDH11 is known to be implicated in musculoskeletal disorders.
Despite the crucial roles of cadherins in various disease conditions, there are currently no drugs on the market that specifically target these molecules. However, numerous ongoing preclinical and clinical studies are addressing this gap.
For example, the targeting of CDH1 and CDH17 is significant in treating various cancers, such as colon, gastric, and other metastatic tumors. CDH2 is closely linked to drug discovery efforts focused on fibrosis and melanoma. CDH5 targeting has prompted numerous clinical investigations related to infant respiratory distress syndrome, acute lung injury, and diabetic retinopathy.
Lastly, the targeting of CDH6 and CDH11 has been utilized in the treatment of solid tumors, including renal and kidney cancer, as well as other metastatic malignancies.
Table 1. Cadherins in preclinical and clinical studies. Source: https://www.pharnexcloud.com/
| Targets |
Drug Discovery |
Pre-clinical |
Clinical Application |
Phase I |
Phase II |
Phase III |
Conditions |
| CDH1 |
7 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
Gastric cancer, colon cancer and other metastatic tumors. |
| CDH2 |
3 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
Melanoma, fibrosis. |
| CDH5 |
1 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
Infant respiratory distress syndrome, acute lung injury, cardiovascular disease, diabetic retinopathy, and cancer et al |
| CDH6 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
Ovarian cancer, kidney cancer, and metastatic malignant tumor of kidney or renal pelvis. |
| CDH11 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
Metastatic malignant tumor, end-stage renal disease, fibrosis, rheumatoid arthritis. |
| CDH17 |
6 |
2 |
0 |
2 |
0 |
0 |
Cholangiocarcinoma, colorectal, gastric, neuroendocrine, pancreatic cancer et al. |
Application in research
Recombinant cadherin proteins play a crucial role in drug screening and diverse biomedical studies, spanning cell adhesion, cancer, and cardiovascular research.
Researchers leverage these proteins to investigate cell behavior, adhesion mechanisms, autoantibody-mediated cleavage, and virus-host interactions, thereby gaining valuable insights for therapeutic development.
For instance, Eftekharjoo et al. utilized soft silicone substrates coated with recombinant human CDH1-Fc (Cat#: 10204-H02H, Sino Biological) to establish a connection between actin-supported CDH1 adhesions and carcinoma properties, identifying two distinct CDH1 adhesion types.
In another study, Tabdanov et al. employed recombinant human CDH1-Fc protein (Cat#: 10204-H02H, Sino Biological) for nanoscale cell contact guidance investigations on anisotropic nano-grids.
Li et al. utilized recombinant human CDH2 (Cat#: 11039-H08H, Sino Biological) to develop human scFv phage display libraries and refine antibody fragment techniques. Yeruva et al. confirmed autoantibody-induced CDH2 cleavage in arrhythmogenic cardiomyopathy patients using recombinant CDH2 protein (Cat#: 11039-H03H, Sino Biological).
Shen et al. demonstrated GzmB’s role in a CDH5 cleavage assay employing recombinant mouse CDH5 (Cat#: 50192-M08H, Sino Biological)16. In a different study, Zhao et al. employed recombinant human CDH6 protein (Cat#: 10150-H08H, Sino Biological) and recombinant human CDH12 protein (Cat#: 10317-H08H, Sino Biological) to validate CDH6 and CDH12 as SARS-CoV-2 protease substrates, thereby advancing the understanding of 3CLpro functions.
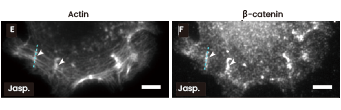
Immunofluorescence images displaying C2BBw cells cultured on CDH1 (Cat#: 10204-H02H, Sino Biological) substrates and exposed to a 1 nM jasplakinolide (an inducer of actin polymerization and stabilization), with staining for actin (depicted as 'E') and β-catenin (shown as 'F'). Irregular adhesions in cells are highlighted using white arrows in both images. Image Credit: doi.org/10.1021/acsbiomaterials.2c00253.
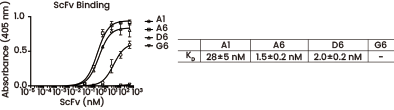
Four scFvs have been successfully expressed and purified (A1, A6, D6 and G6). The affinities of the anti-CDH2 scFvs were investigated by ELISA on immobilized CDH2 recombinant protein (Cat#: 11039-H08H, Sino Biological). Image Credit: doi.org/10.1093/protein/gzv024.

(B) CDH2 (N-CAD) cleavage assay was conducted in vitro, where CDH2 protein (Cat#: 11039-H03H, Sino Biological) was incubated with IgGs from AC patients and control IgG. (D) Upon the treatment with the respective IgGs, the binding frequency of CDH2 has been analyzed with cell-free atomic force microscopy. Image Credit: doi.org/10.1007/s00018-023-04853-1.
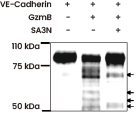
Assessment of GzmB-mediated cleavage of CDH5 (Cat#: 50192-M08H, Sino Biological) in vitro. Arrows indicate VE-cadherin cleavage fragments. The presence of Serpin A3N (SA3N) inhibits GzmB-mediated VE-cadherin cleavage. Image Credit: doi.org/10.1016/j.ajpath.2015.09.010.
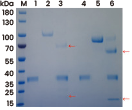
A cleavage analysis has been conducted to access the 3CLpro-mediated cleavage of CDH6 (Cat#: 10150-H08H, Sino Biological) and CDH12 (Cat#: 10317-H08H, Sino Biological). Red arrows in Lane 3 and Lane 6 indicate the 3CLpro-associated cleavage. Image Credit: doi.org/10.1016/j.jbc.2023.104831.
Featured recombinant cadherin proteins
Human CDH17 protein - (His & AVI tag)
(Cat#: 11360-H49H-B)
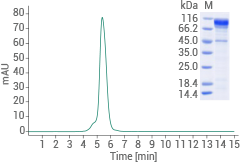
Image Credit: Sino Biological US Inc
Human CDH17 protein - (His tag)
(Cat#: 11360-H08H)
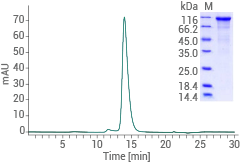
Image Credit: Sino Biological US Inc
Cynomolgus CDH17 protein - (His tag)
(Cat#: 90994-C08H)
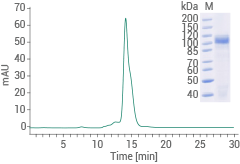
Image Credit: Sino Biological US Inc
More recombinant cadherin proteins (partial list)
Source: Sino Biological US Inc
| Molecule |
Product |
Cat# |
Citations |
| N-Cadherin/CDH2 |
Human CDH2 Protein (His Tag) |
11039-H08H |
3 Citations |
| E-Cadherin/CDH1 |
Human CDH1 Protein (His Tag) |
10204-H08H |
2 Citations |
| E-Cadherin/CDH1 |
Human CDH1 Protein (hFc Tag) |
10204-H02H |
1 Citation |
| VE-Cadherin/CDH5 |
Mouse CDH5 Protein (His Tag) |
50192-M08H |
1 Citation |
| K-Cadherin/CDH6 |
Human CDH6 Protein (His Tag) |
10150-H08H |
1 Citation |
| Cadherin12/CDH12 |
Human CDH12 Protein (His Tag) |
10317-H08H |
1 Citation |
| R-Cadherin/CDH4 |
Human CDH4 Protein (His Tag) |
10230-H08H |
|
| VE-Cadherin/CDH5 |
Human CDH5 Protein (hFc & His Tag) |
10433-H03H |
|
| Cadherin8/CDH8 |
Human CDH8 Protein (His Tag) |
10144-H08H |
|
| H-Cadherin/CDH13 |
Mouse CDH13 Protein (His Tag) |
51163-M08H |
|
| Ksp-Cadherin/CDH16 |
Human CDH16 Protein (His Tag) |
10915-H08H |
|
| LI-Cadherin/CDH17 |
Cynomolgus CDH17 Protein (hFc Tag) |
90147-C02H |
|
| Cadherin18/CDH18 |
Rhesus CDH18 Protein (His Tag) |
90149-C08H |
|
Featured anti-cadherin antibodies
Anti-E-cadherin/CDH1 antibody; Rabbit mAb
(Cat#: 10204-R032)
Applications: IHC-P, ICC/IF
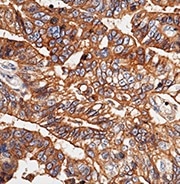
Immunochemical staining of human E-cadherin in human gastric cancer. Image Credit: Sino Biological US Inc
Anti-N-cadherin/CDH2 antibody; Rabbit mAb
(Cat#: 11039-R020)
Applications: WB, ELISA, FCM, ICC/IF
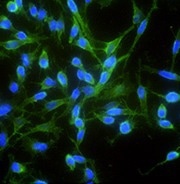
Immunofluorescence staining of human CDH2 in Hela cells. Image Credit: Sino Biological US Inc
Anti-VE-cadherin/CDH5 antibody; Rabbit mAb
(Cat#: 10433-R048-F)
Applications: FCM
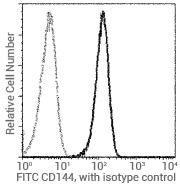
Flow cytometric analysis of human CD144 expression on HUVEC cells. Image Credit: Sino Biological US Inc
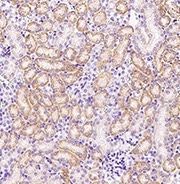
Anti-cadherin 17/CDH17 antibody; Mouse mAb
(Cat#: 11360-MM05)
Applications: IHC-P
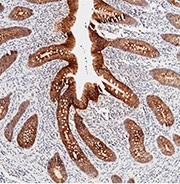
Immunochemical staining of human CDH17 in human appendix. Image Credit: Sino Biological US Inc
Anti-P cadherin/CDH3 antibody; Rabbit pAb
(Cat#: 107913-T08)
Applications: IHC-P
Hela whole cell lysate probed with anti-CDH13 rabbit polyclonal antibody. Image Credit: Sino Biological US Inc
Anti-H cadherin/CDH13 antibody: Rabbit pAb
(Cat#: 51163-T52)
Applications: WB, ELISA, IP
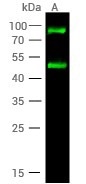
Hela whole cell lysate probed with anti-CDH13 rabbit polyclonal antibody. Image Credit: Sino Biological US Inc
More anti-cadherin antibodies (partial list)
Source: Sino Biological US Inc
| Antigen |
Product |
Cat# |
Applications |
| E-Cadherin/CDH1 |
Anti-CDH1 Antibody, Mouse mAb |
10204-MM12 |
ELISA |
| E-Cadherin/CDH1 |
Anti-CDH1 Antibody, Rabbit pAb |
50671-RP01 |
ELISA, IHC-P |
| N-Cadherin/CDH2 |
Anti-CDH2 Antibody, Rabbit mAb |
11039-R017 |
ELISA, ICC/IF |
| R-Cadherin/CDH4 |
Anti-CDH4 Antibody, Rabbit pAb |
10230-RP02 |
ELISA |
| VE-Cadherin/CDH5 |
Anti-CDH5 Antibody, Rabbit mAb |
10433-R048 |
ELISA, FCM, ICC/IF |
| VE-Cadherin/CDH5 |
Anti-CDH5 (FITC) Antibody, Mouse mAb |
10433-MM01-F |
FCM |
| K-Cadhedin/CDH6 |
Anti-CDH6 Antibody, Mouse mAb |
10150-MM09 |
ELISA |
| Cadherin8/CDH8 |
Anti-CDH8 Antibody, Rabbit mAb |
10144-R032 |
ELISA |
| Cadherin12/CDH12 |
Anti-CDH12 Antibody, Rabbit mAb |
10317-R403 |
ELISA |
| Ksp-Cadherin/CDH16 |
Anti-CDH16 Antibody, Mouse mAb |
10915-MM08 |
IHC-P |
| LI-Cadherin/CDH17 |
Anti-CDH17 Antibody, Rabbit pAb |
11360-T26 |
ELISA, IHC-P, ICC/IF |
Learn More About Cadherins