Image Credit: Newcells Biotech
aProximateTM PTCs maintain high expression of key transporters involved in drug handling, including megalin and cubilin, making them ideal for studying drug transporters and drug interactions with small and large molecules. Transporters are crucial for the uptake and efflux of drugs across cell membranes, and drug interactions with these proteins are common.
These interactions can act as substrates or inhibitors, and identifying them early in drug development is essential for defining the absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion (ADME) profile. Leveraging our scientific expertise, Newcells offers transporter assays using the aProximateTM model to meet your specific needs and help identify potential drug interactions.
The model has been able to closely recapitulate human in vivo proximal tubule functionality and generated valuable insights regarding drug transport by primary human kidney cells. In my opinion, Newcells is the premiere provider of primary human renal cells with physiologically relevant functionality to support toxicity, renal clearance, and renal drug interaction screening.”
David Rodrigues, PhD, Senior Scientific Director, Pfizer
Service outputs
- Identification of transporter-mediated drug interactions
- High content imaging data
- Flux Assay: Apical to Basal (Jab) and Basal to Apical (Jba) flux
- Net transport measurements
- Uptake assays: measurement of intracellular drug and metabolite concentrations
Services
- Drug transporter assays
- Drug interactions
- Flux and net transporter measurements
- Measurement of intracellular drug and metabolite concentrations
Models
- Human, mouse, rat, and dog proximal tubule cells from the aProximateTM kidney
Timeline
How to use aProximate™ for the assessment of drug transporter interactions
Newcells' aProximateTM assay-ready plates are available for delivery to clients in the USA and Europe. Customers can utilize freshly isolated proximal tubule cells in their own lab, enabling an understanding of potential drug interactions. Available in 24- and 96-well Transwell® format, the assay-ready plates come with maintenance medium and user guide covering an in-depth protocol for cell recovery upon receipt.
Due to its constant supply of fresh kidney tissue, Newcells provides a rapid and reliable service. Experiments are designed collaboratively to answer all drug interaction queries. All information provided will offer crucial insights into compounds' ADME and pharmacokinetic profiles to enable streamlined lead optimization. Kidney experts undertake bespoke projects in the company's modern UK facilities.
Example 1: In vitro investigation of drug-drug interactions
The aProximateTM model has been assessed for its capacity to imitate the renal clearance of probenecid. Co-administration of other medications, such as para-aminohippurate (PAH), furosemide, cidofovir, or fexofenadine, significantly reduced the in vivo renal clearance of probenecid, suggesting drug-drug interactions via renal transporters, OAT-1 and OAT-3.
The in vivo interaction between probenecid and PAH is replicated in the aProximateTM model. As demonstrated below, when probenecid is present in aProximateTM PTCs, there is a notable decrease in PAH basolateral to apical flux (JBA) and net flux (JNet). As observed, aProximateTM accurately predicts renal drug-drug interactions and recapitulates proximal tubule function.
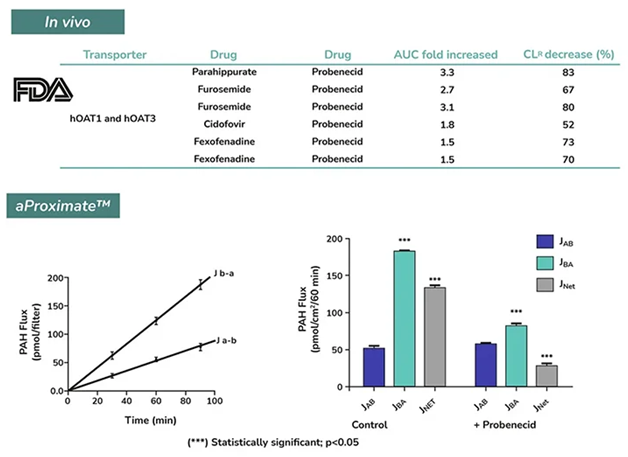
A reliable model to assess drug/drug interactions (DDI). In vivo renal clearance of drugs is reduced by the OAT inhibitor probenecid (upper panel). A similar effect is observed in vitro using the aProximate™ model (bottom panel). Image Credit: Newcells Biotech
Example 2: Mechanistic insights into drug renal clearance
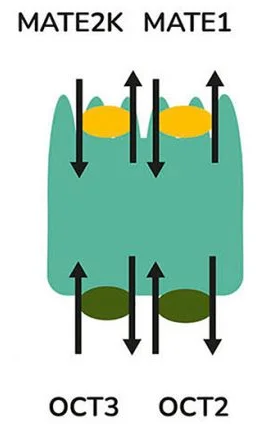
The same transporters transport several drugs and metabolites. Creatinine, an endogenous metabolite, and the immunomodulatory drug pyrimethamine are both basolateral OCT2 and apical MATE transporter substrates. OATs and MATEs transport organic anions like creatinine and organic cationic drugs such as metformin, a common treatment for type 2 diabetes.
Administering transporter inhibitors like cimetidine and pyrimethamine can block the excretion of creatinine. In vivo, these inhibitors also reduce the renal clearance of metformin by blocking OCT and MATE transporters.
Cimetidine interferes with metformin uptake into proximal tubule cells, while pyrimethamine blocks efflux. This results in a significant increase in systemic exposure to metformin and a decrease in its renal clearance, as metformin and pyrimethamine compete for efflux via MATE transporters.
This data demonstrates how this proximal tubule model can be used to investigate drug interaction mechanisms in the kidney.
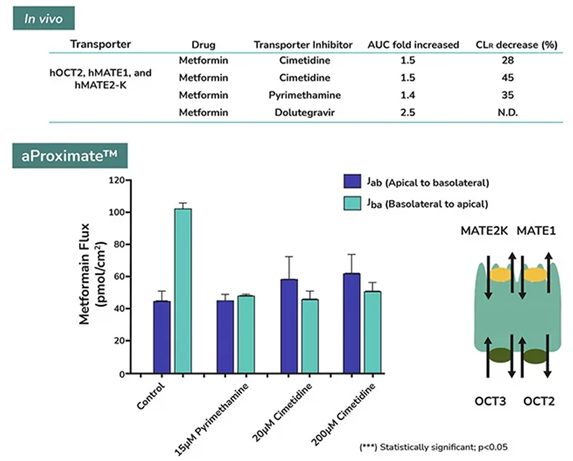
Predictions of drug/transporter interactions in aProximate™ showing a reduction in renal clearance of metformin upon inhibition of OCT and MATE transporters, comparable to that observed in vivo. Image Credit: Newcells Biotech
Service overview
aProximateTM PTCs show high expression of key transporters involved in drug absorption, excretion, and interactions, including OAT1 and OCT2 (Brown et al., 2008). Newcells' aProximateTM PTCs are available from various species, including humans, rats and dogs.
Substrate assessment and inhibition services using Newcells' transporter assay are performed quickly to generate data required to advance lead compounds to clinical development.
The data generated by the transporter assays was used for IND submissions to provide comprehensive drug metabolism, transporter, and drug interaction data using testing parameters that adhered to regulatory guidelines.
The project timelines are short due to the constant supply of fresh kidney tissue. The scientific experts’ robust data will give users confidence as they make key decisions during drug development.
Measurements of net transport and transepithelial flux in proximal tubule cells, particularly Apical to Basal (Jab) and Basal to Apical (Jba) flux, are examples of transporter drug interaction packages. Users can also measure the amount of intracellular accumulation across the apical and basolateral membranes. Three distinct biological donor kidneys from various species can be used to generate data.
Source: Newcells Biotech
| |
| Models |
aProximateTM primary isolated kidney proximal tubule cells |
| Assay format |
24-well Transwell® plates |
| Species |
Human |
| Mouse |
| Rat |
| Dog |
| Service readouts |
Flux measurements: Apical to Basal (Jab) and Basal to Apical (Jba) flux |
| Net transport measurements |
| Uptake assays: Measurement of intracellular drug and metabolite concentrations |
| High content imaging (HCI) |
| Species comparison |
| Time points and replicates |
0, 30, 60, 90, 120 minutes |
| Data points are usually performed in triplicates |
Models from this service
aProximate™ proximal tubule cells
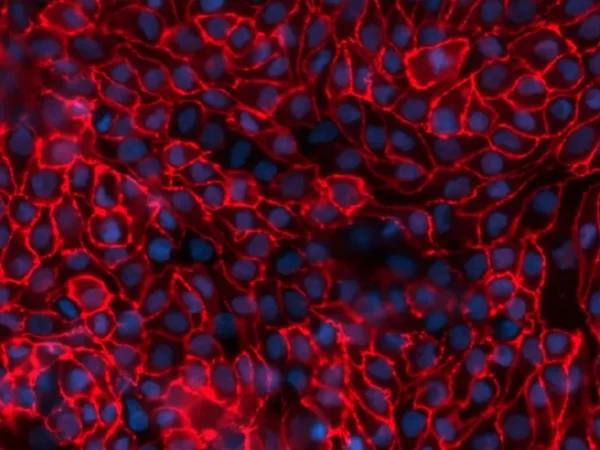
ZO-1 Staining of tight junctions between aProximateTM proximal tubule cells. Image Credit: Newcells Biotech
aProximateTM is a highly advanced, near-physiological in vitro kidney PTC model. aProximateTM PTCs are derived from fresh human kidney tissue and grown on Transwells®. They stay well differentiated as a polarized cell layer with tight junctions.