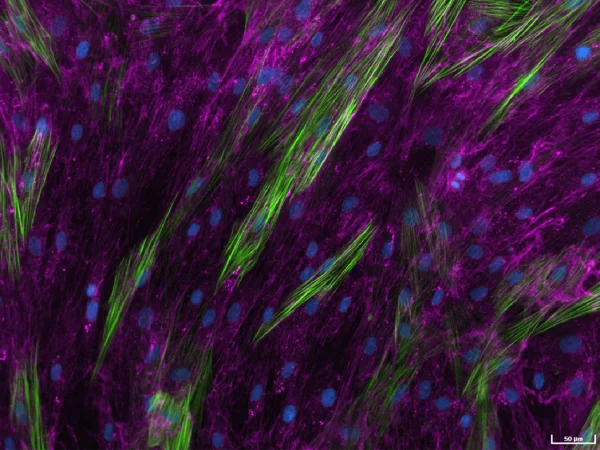
Human lung fibroblasts stimulated with TGF-β1 to detect extracellular collagen I (pink), alpha-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA) (green), and cell nuclei (blue) as a measure of matrix production and fibroblast activation, respectively. Image Credit: Newcells Biotech
The high-throughput, high-sensitivity fibroblast-to-myofibroblast transition (FMT) assay was created to precisely and quickly investigate a compound's capacity to inhibit lung fibroblast activation and decrease the deposition of extracellular matrix proteins after stimulation with the well-known fibrotic mediator TGF-β1.
The assay setup enables advanced testing of small molecule drugs at varying concentrations.
This FMT assay uses multiplexed detection to accurately measure changes in cell count, α-SMA expression, α-SMA strand perimeter, and extracellular collagen I deposition, which can aid in drug discovery programs.
Using fibrosis-related marker readouts, the fast, high-throughput high-sensitivity FMT assay service uses the most advanced imaging suite capabilities to precisely assess anti-fibrotic medications' effectiveness. Data quality objectivity is guaranteed by automatic quantification and analysis.
- 384-well format
- 4 parameter readout
- High sensitivity
FMT Assay service outputs
- Automated quantification and analysis of α-SMA expression
- Automated quantification and analysis of α-SMA strand perimeter
- Cell count
- Automated quantification and analysis of extracellular collagen I deposition
Assays
Models
- Primary human lung fibroblasts from healthy donors
- Human primary lung fibroblasts from patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
Timeline
Outsource experiments to Newcells Biotech
Utilize the expertise and state-of-the-art technology to acquire accurate data indicative of in vivo activity. In-house lung experts collaborate with users to design hypothesis-driven experiments that are carried out in modern facilities.
Newcells' fast and dependable high-throughput, high-sensitivity FMT assay service, combined with the state-of-the-art imaging suite, yields study data that offers insights into how well anti-fibrotic drugs can lower lung fibroblast activation and matrix deposition in vivo.
Service overview
The FMT assay simulates how fibroblasts react to TGF-β1 after pre-incubating with test articles.
Assay Design. Source: Newcells Biotech
| Assay Design |
| Cell Type |
Primary lung fibroblasts |
| Species |
Human |
| Assay Format |
Cell count |
| Quantification of extracellular collagen I deposition |
| Quantification of α-SMA expression |
| Quantification of α-SMA strand perimeter |
| Biological Variation |
N = 3 validated healthy donors and N=2 validated diseased IPF patients lung fibroblasts |
| Technical Replicates |
N = 6 technical replicates per condition |
| Assay Treatment Window |
72 hours |
Functionally validated assay
- The assay’s functional validation demonstrates
- Increased expression of α-SMA
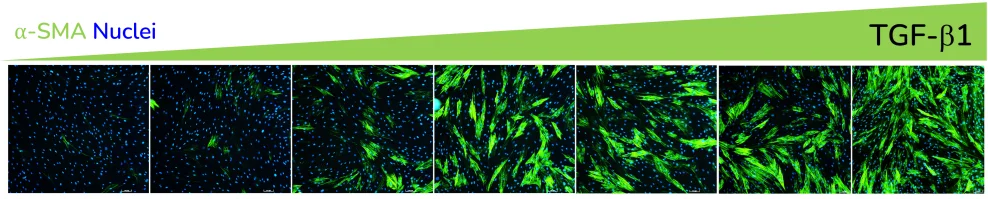
α-SMA expression in response to dose-dependent treatment with TGF-β1. Images were acquired using the ImageXpress Confocal HT.ai imaging system. Image Credit: Newcells Biotech
- Increased α-SMA strand perimeter
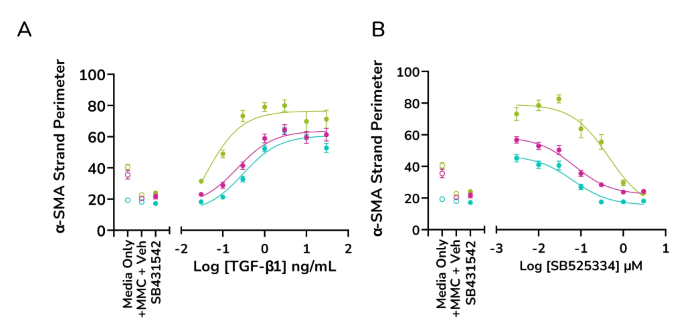
TGF-β1 dose-dependently increases α-SMA strand perimeter indicating increased contractile potential of activated fibroblasts, while ALK5 inhibitor SB525334 shows a decreasing trend (A&B) Data for α-SMA strand perimeter from three healthy human lung fibroblast donors. Image Credit: Newcells Biotech
- Increased extracellular collagen I deposition
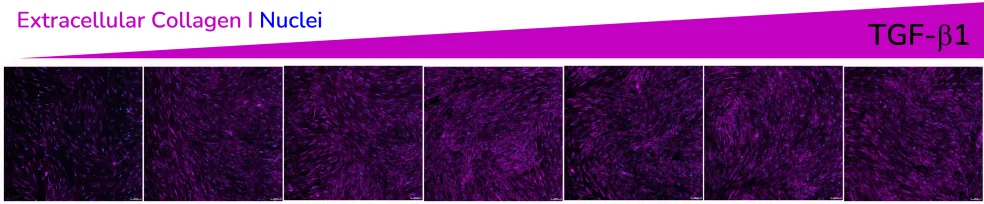
Extracellular collagen I deposition in response to dose-dependent treatment with TGF-β1. Images were acquired using the ImageXpress Confocal HT.ai imaging system. Image Credit: Newcells Biotech
Exposure to ALK5 inhibitors SB431542 and SB525334 reduces the effect of TGF-β1 at pathophysiologically relevant concentrations.
Controlled cell proliferation and optimal assay sensitivity
- The addition of a macromolecular crowder (MMC) agent to the culture medium creates a more in vivo-like environment and encourages the deposition of secreted extracellular collagen I, increasing signal sensitivity
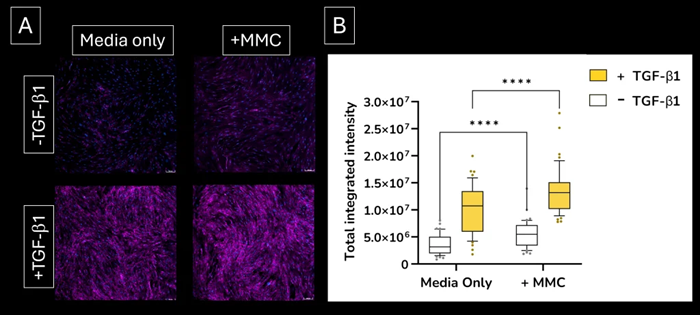
Increased sensitivity. Addition of the macromolecular crowding (MMC) agent to the lung fibroblast culture medium increases the deposition of extracellular collagen I protein. (A) extracellular collagen I deposition. Images were acquired using the ImageXpress Confocal HT.ai imaging system (B) quantified expression levels of extracellular collagen I deposition. Image Credit: Newcells Biotech
- The FMT assay minimizes the effect of changes in cell number on the expression levels of α-SMA and extracellular collagen I by using lower serum concentrations and optimized culture conditions that regulate cell proliferation even in the presence of different doses of TGF-β1
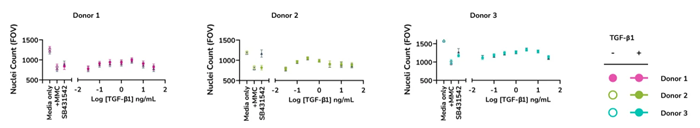
Controlled cell proliferation. Optimized assay culture conditions minimize the effects of TGF-β1 on nuclei count. Human lung fibroblasts from three healthy donors were stimulated with TGF-β1 and stained for cell nuclei. Image Credit: Newcells Biotech
Enhanced sensitivity and rapid screening
When assessing the effectiveness of anti-fibrotic drugs, the HTHS FMT assay is extremely sensitive to detecting subtle variations in the expression of fibrotic markers. Compared to LED-based imaging, laser-based α-SMA expression imaging and quantification produces a "steeper" dose-response curve with a larger area under the curve, resulting in an assay with higher overall sensitivity.
- Compared to LED-based imaging, laser-based imaging has a higher sensitivity and can detect more subtle changes in the expression of fibrotic markers
- Faster imaging and reduced analysis times allow for the quick screening of numerous compounds
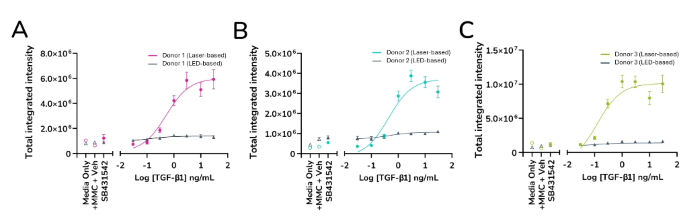
Quantified expression levels of α-SMA from ImageXpress Confocal HT.ai vs ImageXpress Pico. Data from three healthy human lung fibroblast donors (A, B & C). Image Credit: Newcells Biotech
The HTHS assay has been demonstrated to produce a more sensitive dose-response curve for measuring extracellular collagen I deposition and other ECM proteins, much like it does for measuring α-SMA expression. This makes it possible to screen for anti-fibrotic compounds using more predictive datasets.
Catalogue reference
Source: Newcells Biotech
| Offering |
Sku code |
Format |
Species |
Readout |
HTHS
Lung FMT
assay |
LSFMT0000H |
384-wells |
Human |
Cell count along with dose-response
curve for a-SMA expression, a-SMA
strand perimeter and extracellular
collagen I deposition |
Images
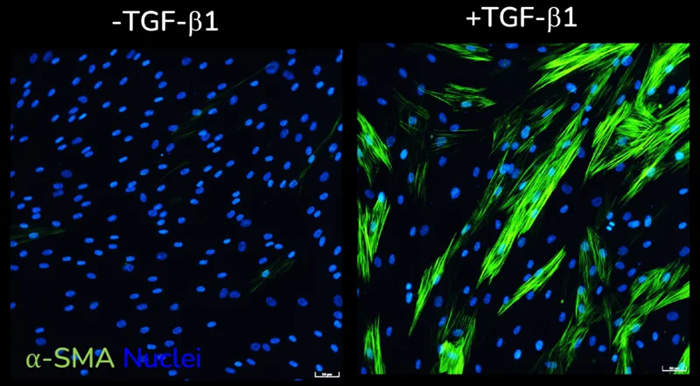
α-SMA expression without (left) and with (right) TGF-β1 stimulation of primary HLFs acquired using ImageXpress Confocal HT.ai imaging system, Scale bar: 50 µM. Image Credit: Newcells Biotech
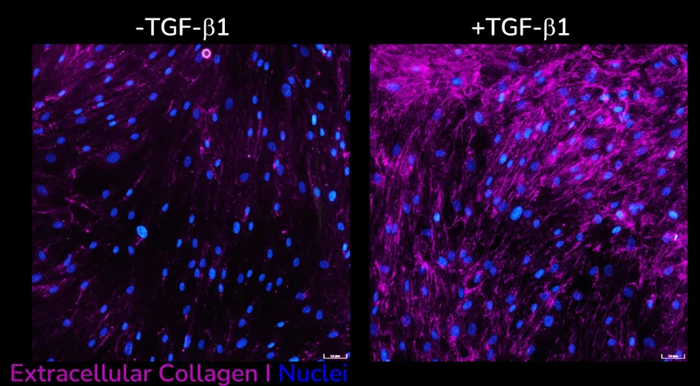
Extracellular collagen I deposition without (left) and with (right) following TGF-β1 stimulation of primary HLFs acquired using ImageXpress Confocal HT.ai imaging system, Scale bar: 50 µM. Image Credit: Newcells Biotech
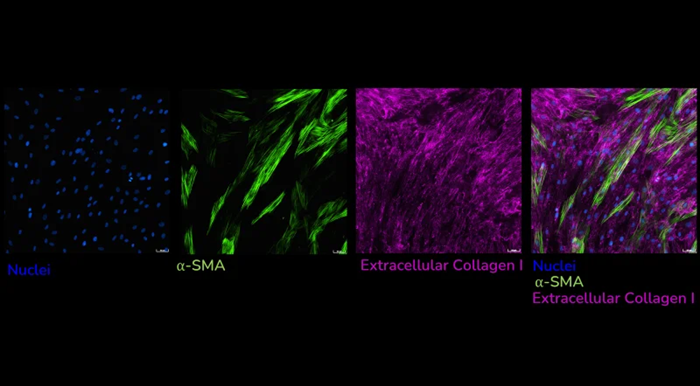
Human lung fibroblasts stimulated with TGF-β1 and immunostained to detect extracellular collagen I (pink) and α-SMA (green) as a measure of matrix production and fibroblast activation, respectively. Images captured using ImageXpress Confocal HT.ai imaging system, Scale bar: 50 µM. Image Credit: Newcells Biotech
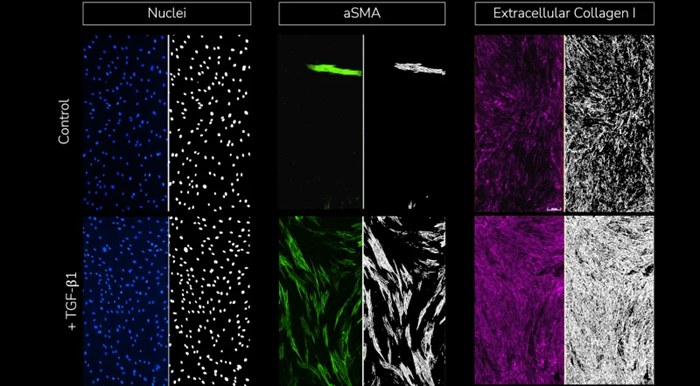
Split view images with fluorescent staining of cell nuclei, α-SMA, and extracellular collagen I (left) and respective segmentation analysis masks (right) for each stained marker under control (un-stimulated, top) and TGF-β1 stimulated conditions (bottom). Image Credit: Newcells Biotech
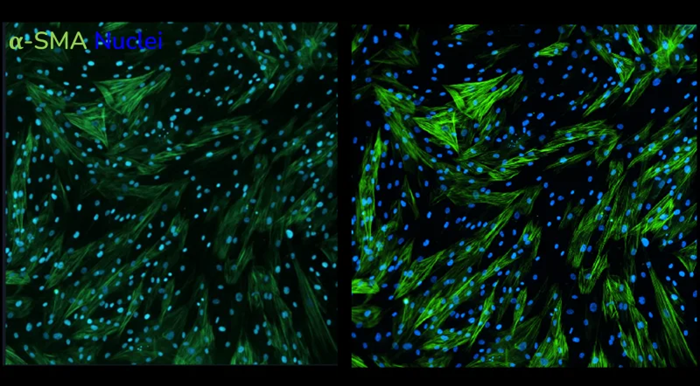
Increased resolution of laser-based acquisition. α-SMA staining following stimulation of human lung fibroblasts with TGF-β1 captured using LED-based imaging (left) vs. laser-based imaging (right). Images taken at 20x magnification. Image Credit: Newcells Biotech