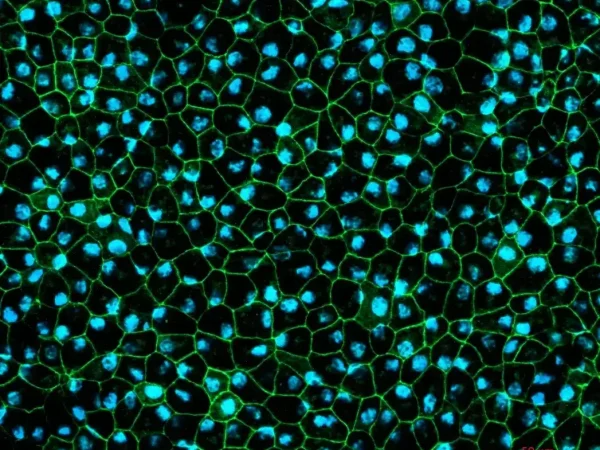
RPE cells displaying cobblestone morphology. Cells were immunolabeled with tight-junction ZO-1 marker (shown in green) and co-stained with nuclei marker, Hoechst (shown in blue). Image Credit: Newcells Biotech
For its services, Newcells utilizes a retinal pigment epithelial (RPE) cell model comprised of a monolayer of RPE cells. Derived from healthy donor iPSCs, its RPE cells uniquely have the same genetic background as retinal organoids, enabling parallel examination of RPE and neurosensory retina. Newcells can also create RPE cells from client-supplied iPSCs.
The 24-well Transwell® plates format enables dosing and analytical readout flexibility, including functional cell evaluation. Extensive RPE characterization comprises analysis of phagocytosis of photoreceptor outer segments, basal vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) secretion, morphology assessment, pigmentation, the polarity of apical pigment epithelium-derived factors (PEDF), RPE-specific expression at the protein level (BEST1, TYRP1), and trans-epithelial resistance (TEER).
Applications
- Gene therapy, including assessment of in vitro viral vectors
- Disease modeling
- Investigational drug safety and efficacy
Available analytical readouts for services provided with RPE
- Growth factor (VEGF, PEDF) secretion
- Flow cytometry
- Imaging
- mRNA quantification by RT-qPCR
- Transcriptomics by single-cell RNA sequencing
The extensive scientific knowledge and rigor of Newcells’ staff in the field of ophthalmology as well as their client goal-oriented thinking allowed us to advance quickly in our proof of concept.”
Dr Elke Vermassen, Sr. Product Development Manager, KiOmed Pharma
Model formats
- RPE cells cultured in 24-well Transwell® plates
Cell types
- Retinal pigment epithelial (RPE) cells
Origin
- Human iPSCs (healthy donor)
How to use the RPE model
Newcells’ team creates user experiments to provide a quick, dependable service addressing all questions asked. Customers can see results from gene therapy vector screening and efficacy testing in two to three months. State-of-the-art UK facilities are used to complete all custom projects.
Role of RPE in the retina
The RPE is a hexagonal-shaped layer of cells located between the back of the eye inside the blood vessels of the choroid and the retina. This cell layer is crucial to vision, decreasing light damage in the eye and regulating nutrient and waste product movement in and out of the retina. It also maintains blood vessels through growth factor secretion and is responsible for photoreceptor turnover.
As the RPE is critical to vision, it is important to evaluate how novel therapeutics impact it, and this task can be undertaken in vitro.
Retinal pigment epithelial cells characterization
Human iPSCs forming a two-dimensional layer generate in vitro retinal pigment epithelial cells, which are pigmented and display typical cobblestone morphology.
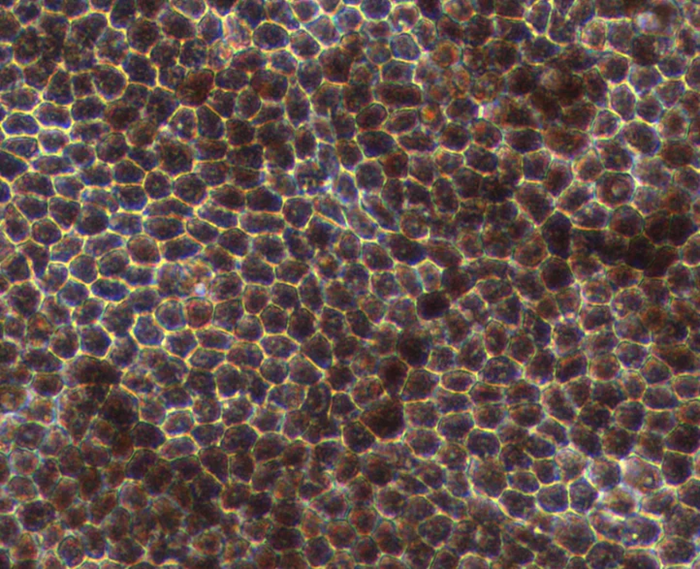
Hexagonal morphology and pigmentation typically observed in mature RPE cells. Image Credit: Newcells Biotech
The in vitro model closely recapitulates crucial functions found in vivo, including tight barrier formation and photoreceptor outer segment phagocytosis.
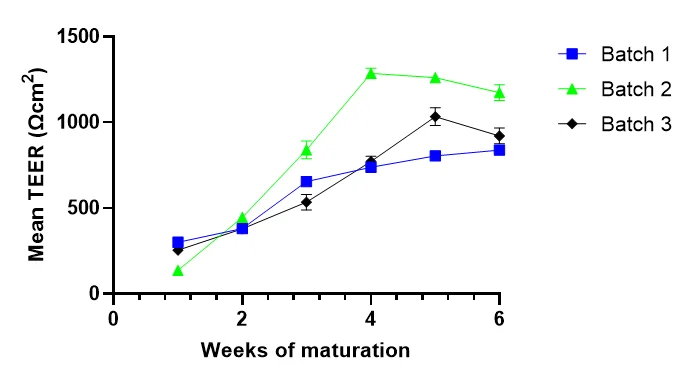
TEER measurements were carried out starting 7 days after seeding on the inserts. RPE reach maturation 4-6 weeks post-isolation when TEER starts to plateau. Image Credit: Newcells Biotech
High expression of the RPE markers BEST1, TYRP1, and PMEL17 in flow cytometry data indicates a highly pure, differentiated population.
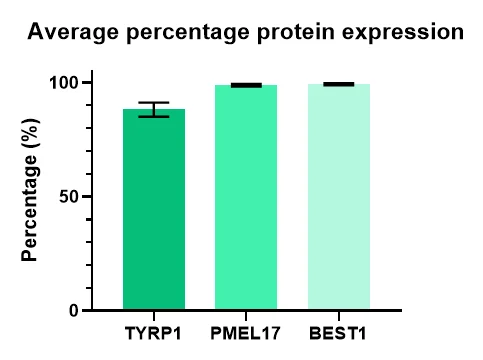
Expression of RPE markers, TYRP1, PMEL17 and BEST1. Image Credit: Newcells Biotech
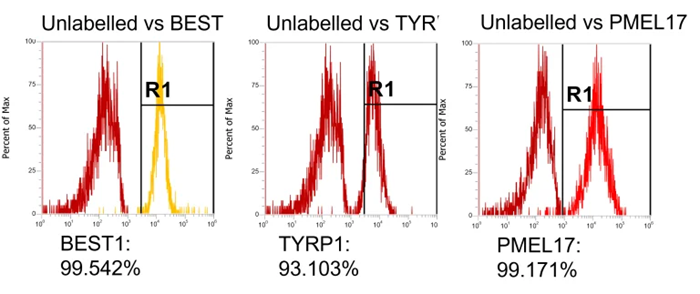
Protein expression of RPE cells using flow cytometry after TEER plateaued. PMEL17 – a protein which is expressed in melanosome precursors (>95% expression). TYRP1 – is expressed in mature RPE and is located in melanosomes (>85% expression). BEST1 – is a Ca2+-regulated chloride channel and is a critical for normal phagocytotic function (>98% expression). Image Credit: Newcells Biotech
Retinal pigment epithelial cells description
- Cell types: RPE cells
- Format: Monolayer, cultured in 24-well Transwell® plates
- Main characteristics: Cobblestone morphology, pigmentation, express RPE cells biomarkers, e.g., BEST1, TYRP1, and RPE65
- Other characteristics: Phagocytosis of photoreceptor outer segments and tight barrier formation
RPE cells origin: healthy, patient-derived or gene-edited cells
Differentiated from a healthy donor's fully-characterized iPSCs, RPEs can be developed from client iPSCs, either gene-edited or patient-derived. Newcells reprogram fibroblasts and peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) before RPE differentiation.
Catalogue reference
Source: Newcells Biotech
| Model |
Sku no. |
Format |
Species |
Readouts |
RPE disease
modelling |
RSD0000RPE |
24-well Transwell |
Human |
Brightfield imaging, Cell viability
(ATP/LDH), Quantitative IF, Gene
expression, Transmission (TEM)
and Scanning (SEM) electron
microscopy (optional),
Phagocytosis of photoreceptor
outer segment (optional) |
RPE gene therapy
assessment |
RSG0000RPE |
24-well Transwell |
Human |
Transduction efficiency of viral
vector, Cell viability assessment
(ATP/LDH), Therapy efficacy
using IF and Gene expression |
Test the novel therapeutics on two retina models RPE and organoids
Outsource experiments to Newcells Biotech
Newcells can evaluate compounds on RPE cells and organoids, which is especially relevant for disease modeling and viral vector analysis.
Gene therapy
Quick in vitro viral vector preclinical analysis for retinal therapy development.
Disease modeling
To create models of retinopathies, Newcells sources patient lines ethically or uses customer gene-edited lines.
RPE differentiation
Fibroblasts, iPSCs, and PBMCs provided by clients can be gene-edited or patient-derived and utilized as starting material to differentiate into RPE.