Sponsored Content by SartoriusReviewed by Alex SmithMar 7 2022
The term ‘T cell exhaustion’ is commonly used to describe T cell dysfunction occurring as a result of chronic stimulation.
Exhausted T cells exhibit a distinct phenotype, such as overexpression of specific inhibitory markers, for example, LAG-3, PD-1, and TIM-3. These cells also display a notable impairment in terms of their ability to release pro-inflammatory cytokines (IFNγ and TNFα).
Exhaustion typically takes place in the tumor microenvironment in instances where T cells suffer a loss of their cytotoxic function, essentially rendering them unable to kill cancerous cells.
Significant research is ongoing which is looking to reverse or overcome the state of exhaustion. Much of this research is focused on CAR-T cell production, including checkpoint inhibitor antibodies.
The ability to simulate specific T cell exhaustion problem-solution scenarios has the potential to provide further insight into this phenomenon.
Assay concept
Using the iQue® Human T Cell Exhaustion Kit assay, it is possible to profile T cell phenotypes for the expression of three key exhaustion markers:
- PD-1 (early)
- LAG-3 (mid)
- TIM-3 (late)
The two effector cytokines (IFNg and TNFα) are quantified using 2-plex Qbeads via a sandwich immunoassay format. This is done in the same well. It is also possible to achieve simultaneous measurement of T cell proliferation or encoded target cells, should this be required.
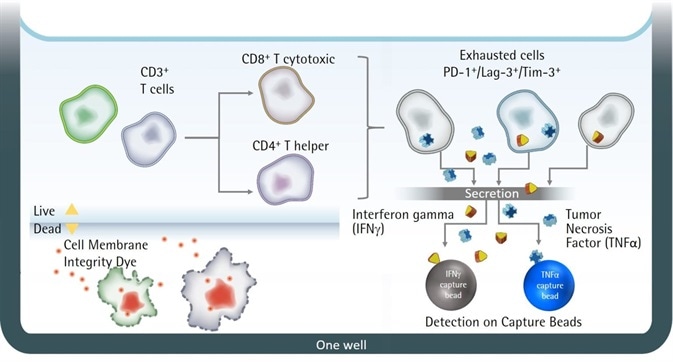
Figure 1. Illustration of iQue® Human T Cell Exhaustion Kit assay principles. Image Credit: Sartorius
Key advantages
This approach offers a number of advantages:
- The ability to simultaneously quantify surface protein and cytokine expression
- The ability to develop further biological insight into T cell exhaustion status in physiologically relevant models
- An accessible, easy to use and easy to interpret, pre-defined gating strategy
- Minimal sample manipulation is necessary – the process is low volume, requiring one wash and no dilution before mixing and reading.
Both pre-exhausted CD3+ T cells and non-exhausted CD3+ T cells with no prior stimulation were seeded at 200K/well.
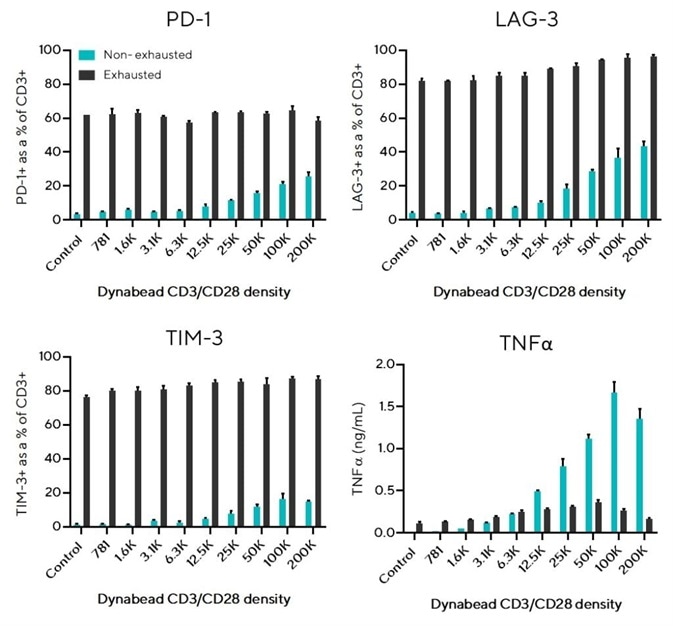
Figure 2. Exhausted T cells overexpress inhibitory receptors and produce low concentrations of effector cytokine TNFα. Image Credit: Sartorius
The pre-exhausted T cells had been stimulated using Dynabeads CD3/CD28 (1:1 bead-to-cell ratio) and then re-stimulated every 2-3 days (5 stimulations total) before seeding.
Varying densities of Dynabeads CD3/CD28 were used to induce in-well activation. Control wells that did not contain Dynabeads were also prepared. After 24 hours, 10 uL samples were analyzed with the iQue® Human T Cell Exhaustion Kit on the iQue® 3.
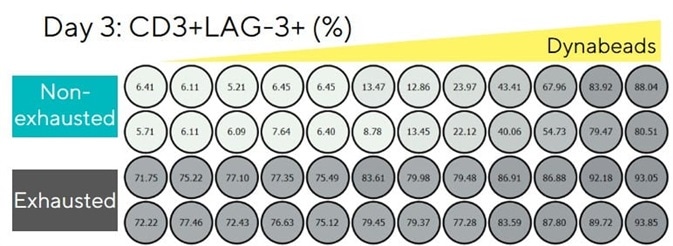
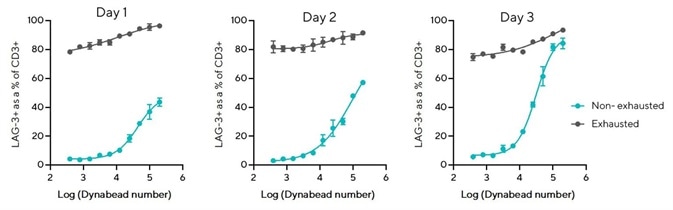
Figure 3. LAG-3 overexpression persists on exhausted T cells over 3 days. Image Credit: Sartorius
This approach made it possible to gain further biological insight into T cell activation status in a range of physiologically relevant models, thanks to its easy-to-use and interpret, pre-defined gating strategy.
The process was possible with minimal sample manipulation, requiring a low volume, one wash and no dilution. It should also be noted that the protocol involves both cells and supernatant being taken as one sample and that no labeling or compensation optimization steps were required.
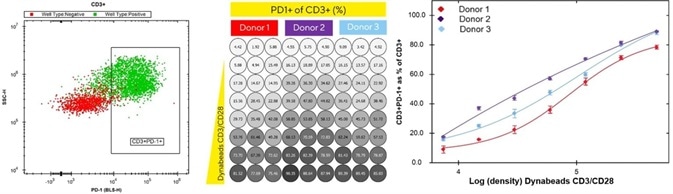
Figure 4. Pre-determined gates on iQue Forecyt® enable automatic phenotyping of exhausted T cell subsets. Image Credit: Sartorius
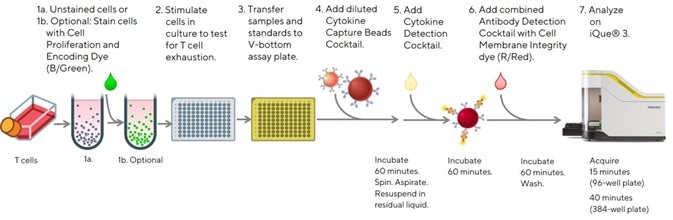
Figure 5a. Easy to follow protocol for the analysis of T cell phenotypes and cytokine release using the iQue® Human T Cell Exhaustion Kit. Image Credit: Sartorius
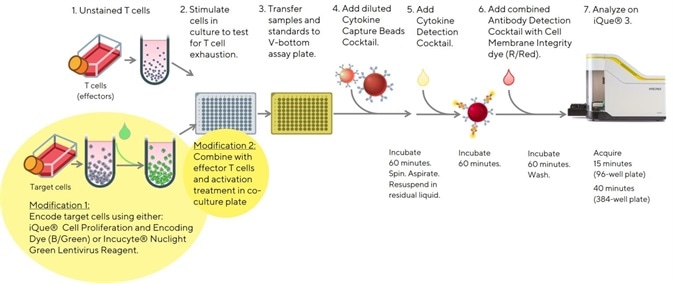
Figure 5b. Easy to follow modified protocol to allow the inclusion of target cells in the assay. Allowing the analysis of T cell phenotypes and cytokine release using the iQue® Human T Cell Exhaustion Kit. Image Credit: Sartorius
About Sartorius

Sartorius is a leading international pharmaceutical and laboratory equipment supplier. With our innovative products and services, we are helping our customers across the entire globe to implement their complex and quality-critical biomanufacturing and laboratory processes reliably and economically.
The Group companies are united under the roof of Sartorius AG, which is listed on the Frankfurt Stock Exchange and holds the majority stake in Sartorius Stedim Biotech S.A. Quoted on the Paris Stock Exchange, this subgroup is comprised mainly of the Bioprocess Solutions Division.
Innovative Technologies Enable Medical Progress
A growing number of medications are biopharmaceuticals. These are produced using living cells in complex, lengthy and expensive procedures. The Bioprocess Solutions Division provides the essential products and technologies to accomplish this.
In fact, Sartorius has been pioneering and setting the standards for single-use products that are currently used throughout all biopharmaceutical manufacturing processes.
Making Lab Life Easier
Lab work is complex and demanding: Despite repetitive analytical routines, lab staff must perform each step in a highly concentrated and careful way for accurate results.
The Lab Products and Services Division helps lab personnel excel because its products, such as laboratory balances, pipettes and lab consumables, minimize human error, simplify workflows and reduce physical workloads
Sponsored Content Policy: News-Medical.net publishes articles and related content that may be derived from sources where we have existing commercial relationships, provided such content adds value to the core editorial ethos of News-Medical.Net which is to educate and inform site visitors interested in medical research, science, medical devices and treatments.