Sponsored Content by SartoriusReviewed by Maria OsipovaFeb 22 2024
How are biopharmaceutical companies able to bring groundbreaking biologics to market quickly? The secret behind powering innovation, speed, and compliance in biologics development are CROs, Contract Research Organizations. Below is an interview with BioOutsource, a CRO, regarding how they assist their clients in bringing life-saving biologics over the finish line.

Image Credit: Sartorius
The pivotal role of CRO expertise
CROs bring a depth of experience to the process of developing biologics, filling crucial gaps, reducing risks, and getting products to market quickly. This is of particular value to smaller biotech companies that may have less infrastructure or resources.
One realm where this type of specialized support is invaluable is in regulatory compliance. CROs can assist companies in navigating the maze of Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) and similar regulatory standards, making sure the company is aligned at each step.
Sartorius UK Ltd. recently spoke with Ben Tyrrell, Senior Scientist at BioOutsource (acquired by Sartorius in 2015), about biologics testing and compliance challenges. BioOutsource is a CRO that offers GMP-compliant cell bank manufacturing and testing services, including sterility, analytical, biosafety, and mycoplasma testing.
How can CROs like BioOutsource support biologics developers?
Meeting commercial release standards and biologics testing are complex challenges for drug developers. The best testing strategy for your molecule needs to be identified, and you need to have access to GMP-compliant labs that maintain exacting quality requirements.
At BioOutsource, we provide these resources and help our clients get the necessary data for drug approval. With a full spectrum of assays that includes ready-to-use and custom-developed options, we can help streamline the journey from lab to market.
What are the challenges in developing assays for biologics testing?
A methodical approach is required when developing assays for biologics testing, from proof of concept to qualification. The challenge of designing these assays in-house is made more complex by the requirement for advanced analytical technologies for cell and molecule analysis, like live-cell imaging, LC-MS, and high-throughput flow cytometry, and their incorporation into a GMP-compliant workflow. Quick implementation of this infrastructure is not typically possible for a newer company.
How about complex assays? How do they fit in cGMP biologics workflows?
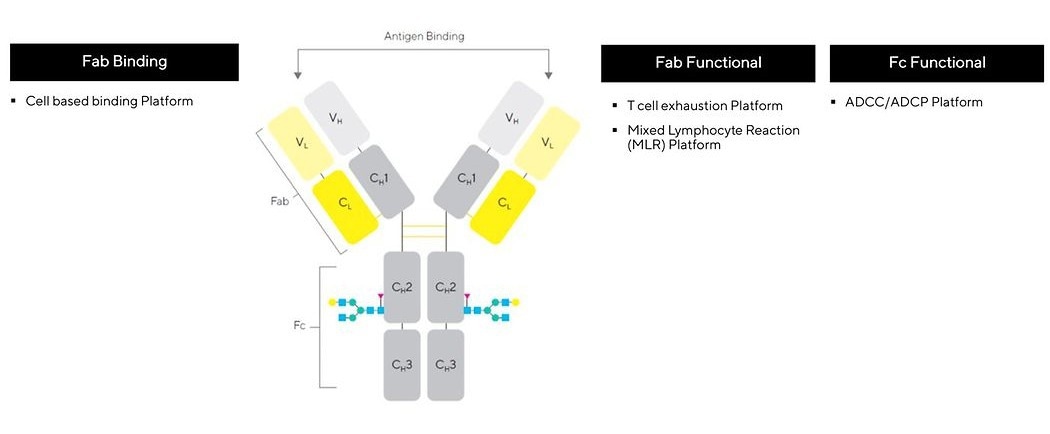
Complex assays, like Antibody-Dependent Cellular Phagocytosis (ADCP), offer critical information on a biologic’s efficacy and mechanism of action. However, conducting these assays to GMP standards is a limitation for some.
More sophisticated instrument capabilities are required, as well as extensive resources for complete system integration and documentation. Ensuring you are GMP-compliant requires detailed installation and operational qualifications (IQ/OQ) and specialized compliance-supporting software. CROs bring tremendous value in this area.
How do you make sure that your processes comply with regulatory requirements?
A fully compliant workflow needs to be built from the base level and can only happen with a wealth of expertise. A dedicated Quality Department and thorough training on crucial aspects like traceability and environmental controls are essential.
In addition, integrating digital systems like LIMS into workflows is very important for maintaining compliance; however, challenges are introduced here in terms of adoption and ongoing management. At BioOutsource, this is our bread and butter, as we can help alleviate this stress entirely.
Assays within the BioOutsouce immuno-oncology toolbox that utilize the iQue® Screener. Image Credit: Sartorius
What does it take to achieve GMP release of an instrument?
Traceability and data integrity are needed to get GMP clearance for an instrument. Traceability means a tamper-proof audit trail, digital confirmations for activities, and specific user access levels.
Incorporating the instrument into established workflows is essential for maintaining data integrity. This includes having a strong audit trail, reliable data export features, and software that safeguards against data loss. The development of more sophisticated instrument platforms is simplifying this process.
How are advanced systems and software simplifying compliance?
A significant regulation for compliance is 21 CFR Part 11, which is a US FDA regulation for electronic records.
The iQue® high throughput flow cytometer, a core instrument in the immuno-oncology toolbox, has recently introduced the 21 CFR Part 11 Software module to facilitate complete GMP validation. This addition aids in achieving complete GMP validation, streamlining a process that would typically depend on separate software suites or external IT services.
What are your thoughts on the future of outsourcing biologics testing?
CROs are still the key drivers in drug development pipelines throughout the industry as they provide expertise or, in some cases, additional capacity. The exciting push into cell and gene therapy fields happening across our industry is also influencing our offerings. For example, this year, BioOutsource launched an AAV testing portfolio with a range of GMP-compliant assays for AAV pipelines. We will continue to support our customers’ ambitions in developing these complex modalities.