Therapeutic antibodies are among the best-selling drug classes in the pharmaceutical market. The introduction of antibody engineering and recombinant production significantly enhanced the collection of therapeutics against acute and chronic diseases.
Introduction
The engineering and production of antibodies are vital in drug discovery, offering effective and precise therapeutics and diagnostic/prognostic materials for numerous diseases.
Antibodies are proteins the immune system creates to react to foreign invaders, such as viruses or bacteria. They can bind to these invaders, neutralizing and inhibiting them from causing damage.
Over recent decades, scientists have developed techniques for engineering and producing antibodies that can be utilized as drugs. This article summarizes antibody engineering and production processes and their applications in drug discovery.
History
The history of engineering and production of antibodies in drug discovery began in the 1970s and 1980s when scientists initially explored the possibility of utilizing antibodies as therapeutics.1 The first-generation antibodies were obtained from natural sources, such as animal blood, and were used as diagnostic reagents.
One significant early milestone in the history of antibody engineering was the advancement of hybridoma technology by César Milstein and Georges Köhler in 1975.
This enabled the production of monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) by fusion of a B cell, which creates a single antibody type, with a myeloma cell that can divide indefinitely (see Figure 1). This made the production of large amounts of specific antibodies feasible.
However, the production of early mAbs was restricted by the availability of appropriate myeloma cell lines (typically rat or mouse) and the fact that hybridomas may be genetically unstable or low yielding.2
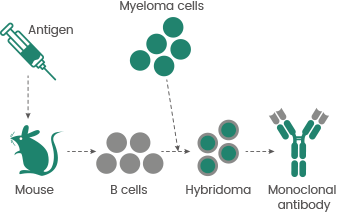
Figure 1. Hybridoma technology. Image Credit: Sino Biological Inc.
During the 1980s, scientists began developing techniques to create recombinant antibodies made using genetic engineering practices. These techniques enabled scientists to produce vast amounts of pure and consistent antibodies in a controlled environment.
This was a substantial development as it enabled the manufacture of antibodies on a large scale for utilization in preclinical and clinical trials.
Approximately one decade later, the development of display technologies (e.g., yeast display, phage display, and ribosome display) enabled the screening of large libraries of antibodies for specific binding properties. This accelerated the identification process of antibodies that bind to specific antigens.
This also enabled the optimization of the structure of antibodies to enhance their binding properties with mutant libraries. These display technologies, particularly phage display, are a significant driving force for discovering various antibodies that can be further engineered, optimized, and recombinantly produced.3
Phage display antibody library technology consists of several steps, such as constructing phage display antibody libraries, mAb identification, panning, and recombinant expression of positive clones (see Figure 2).
Sino Biological specializes in the production of recombinant proteins and the development of antibodies. Sino Biological offers efficient antibody discovery services due to its expertise in constructing and screening phage display antibody libraries.
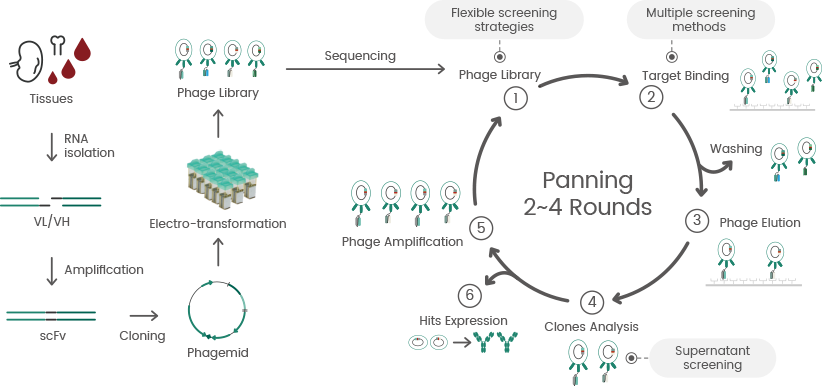
Figure 2. Technical route of phage display library construction and screening. Image Credit: Sino Biological Inc.
The first mAb drug to be licensed was muromonab-CD3 (1986). This is a hybridoma-derived antibody that was utilized for immunosuppression during organ transplantation. Rituximab (Rituxan) was approved by the FDA in 1997 and used for targeting CD20 protein in B-cell non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma.
This was a significant milestone in the antibody engineering and production field as it was the first antibody drug created with recombinant technology. Rituximab was also the first mAb approved for cancer treatment, along with a variety of other mAbs in the following years.
Since this milestone, approximately 170 antibodies and antibody-based therapeutics (including antibody-drug conjugates) have been approved by authorities globally.4,5
Antibody optimization
Aside from the ability to create vast amounts of antibodies with controlled quality, the advantages of recombinant antibody production include antibody engineering enabling the creation of different antibody structures and derivatives (Figure 3), such as Fc-fusion proteins and bispecific antibodies (bsAbs).
This enables the optimization of antibody structure, which can be carried out by introducing mutations into antibody genes to enhance the clinical efficacy of antibodies.
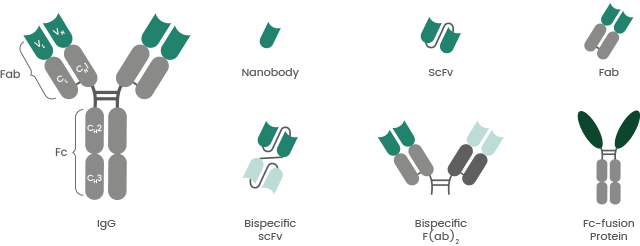
Figure 3. Examples of recombinant antibody formats. Image Credit: Sino Biological Inc.
BsAbs were designed to bind two different epitopes or antigens simultaneously. They have a broad range of applications, including blocking two different pathways and redirection of specific immune effector cells to tumor cells.
Fc-fusion proteins are comprised of the Fc region of IgG antibody and a desired linked protein, such as receptor extracellular domains, cytokines, enzymes, and active peptides. They have further valuable pharmacological and biological properties.
The main reason for fusing Fc with a biologically active protein of interest is that the Fc domain helps to extend the plasma half-life. Sino Biological has extensive experience in the production of recombinant antibodies in various formats and delivers a range of service packages to satisfy different research and drug discovery needs.
Antibody humanization is a key antibody optimization technology. Humanized antibodies represent a main type of antibody drug.
The clinical application of mouse mAbs is restricted by the human anti-mouse antibody (HAMA) response, which neutralizes these therapeutic antibodies in addition to leading to an allergic response in patients.
Humanization of mouse mAbs via genetic engineering can help to minimize the heterologous nature of mouse mAbs and maintain their affinity and specificity. Humanized antibodies better the therapeutic efficacy and safety of mAbs in clinical applications.
Sino Biological offers high-quality mAb humanization services utilizing computer-aided molecular modeling and complementarity-determining region (CDR) grafting technology (see Figure 4).
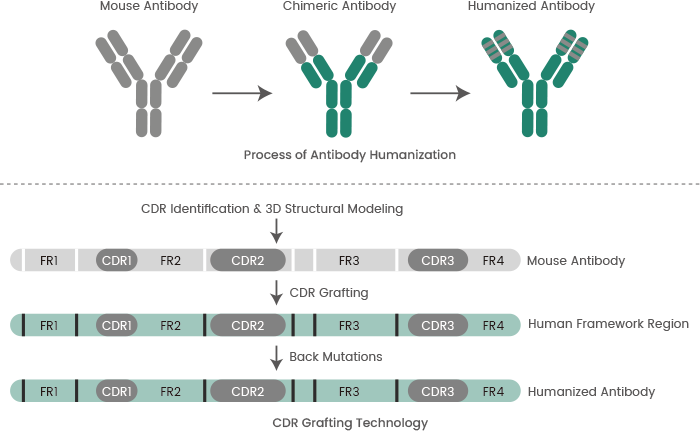
Figure 4. Process of antibody humanization and CDR grafting technology. Image Credit: Sino Biological Inc.
Alternative methods of optimization are developing as the field of antibody engineering and production continues to grow.
For example, scientists can optimize the manner in which an antibody binds to its antigen with the use of techniques, such as artificial intelligence (AI)-driven affinity maturation performed in silico, as opposed to relying on in vivo affinity maturation that involves animal use.
Sino Biological delivers an AI-driven affinity maturation service, which is an experimental and computational service targeted at improving the specificity and affinity of mAbs. This service utilizes machine learning algorithms to predict the impact of mutations on antibody-antigen binding and then validates the predictions in wet lab (see Figure 5).
This service is valuable for researchers in the process of developing mAbs for diagnostic or therapeutic applications, making their candidate antibodies more effective.
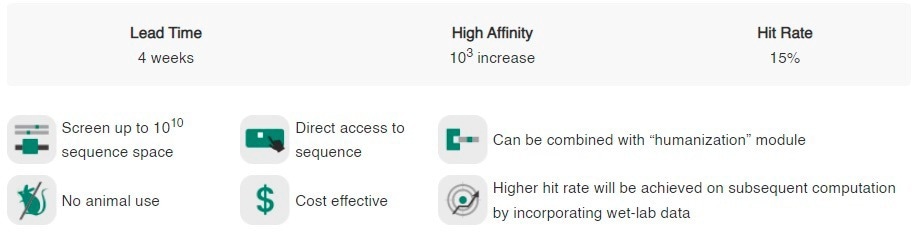
Figure 5. AI-powered affinity maturation platform advantages. Image Credit: Sino Biological Inc.
Production method
Once the required antibody sequences are attained, they must be manufactured in large amounts for use in drug development.
This is usually carried out by growing large quantities of cells, such as Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cells or Human Embryonic Kidney 293 (HEK293) cells, which have been genetically modified to generate the desired antibodies.
HEK293 and CHO cells are beneficial over other host cells, such yeasts and E. coli, because of their high capacity for post-translational modifications, which are crucial for the correct folding and activity of antibodies.
The cells are grown in large bioreactors and are fed with growth factors and essential. Subsequently, the antibodies are purified from culture media with several available purification methods and are ready to be utilized in in vitro, preclinical, and clinical studies.
Future perspectives
Antibodies are now one of the most effective classes of therapeutics used for treatment of various diseases, including autoimmune diseases, cancer, and infectious diseases. They are also vital tools for biomarker detection in the drug discovery process.
Researchers continue to work on improving the production process and developing novel ways of engineering and high-throughput (HTP) methods to manufacture antibodies that can be utilized during drug discovery.
Sino Biological is continuously developing new workflows and methods to decrease the cost and increase the efficiency of antibody production. Presently, Sino Biological offers HTP recombinant antibody production service, delivering the most cost-effective solution for the quick production of a vast quantity of antibodies.
In response to the fast-growing therapeutic requirements, Sino Biological combines its expertise in vector design, gene synthesis, and transient antibody expression technology to manufacture highly efficient antibodies in CHO and HEK293 cells in as little as two weeks (see Figure 6).
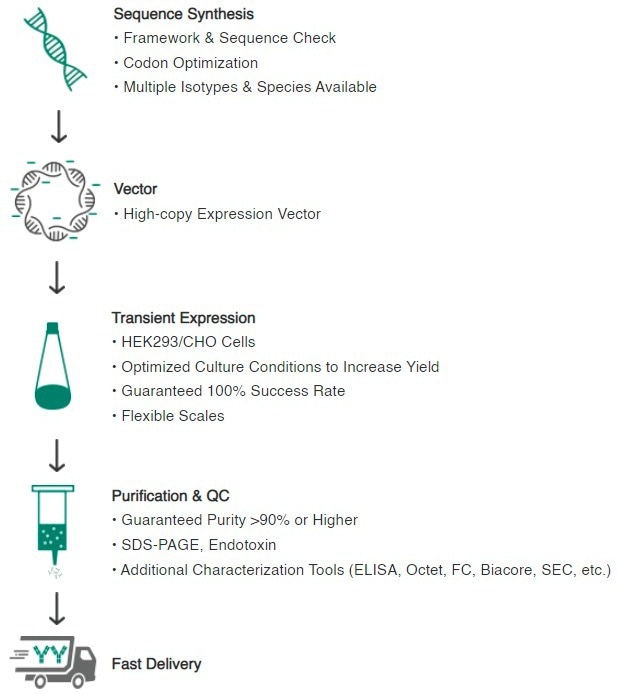
Figure 6. Technical workflow of Sino Biological high-throughput recombinant production platform. Image Credit: Sino Biological Inc.
The future of recombinant antibody production is anticipated to be driven by numerous factors, including the increased demand for therapeutics, the development of new technologies, and the need for more affordable and efficient production methods.
The field is expected to continue to expand and evolve, offering new opportunities for the development of more effective and accessible therapeutics.
References and further reading
- Marks L. (2012) The birth pangs of monoclonal antibody therapeutics: the failure and legacy of Centoxin. MAbs., 4(3), pp. 403-412. doi:10.4161/mabs.19909
- Liu JK. (2014) The history of monoclonal antibody development - Progress, remaining challenges and future innovations. Ann Med Surg (Lond)., 3(4), pp. 113-116. doi:10.1016/j.amsu.2014.09.001
- Geyer CR, McCafferty J, Dübel S, Bradbury AR, Sidhu SS. (2012) Recombinant antibodies and in vitro selection technologies. Methods Mol Biol., 901, pp. 11-32. doi:10.1007/978-1-61779-931-0_2
- Wang SS, Yan YS, Ho K. (2021;) US FDA-approved therapeutic antibodies with high-concentration formulation: summaries and perspectives. Antib Ther., 4(4), pp. 262-272. doi:10.1093/abt/tbab027
- The Antibody Society. Therapeutic monoclonal antibodies approved or in regulatory review. Available at: www.antibodysociety.org/antibody-therapeutics-product-data (Accessed on January 10, 2023)
About Sino Biological Inc.

Sino Biological is an international reagent supplier and service provider. The company specializes in recombinant protein production and antibody development. All of Sino Biological's products are independently developed and produced, including recombinant proteins, antibodies and cDNA clones. Sino Biological is the researchers' one-stop technical services shop for the advanced technology platforms they need to make advancements. In addition, Sino Biological offers pharmaceutical companies and biotechnology firms pre-clinical production technology services for hundreds of monoclonal antibody drug candidates.
Sino Biological's core business
Sino Biological is committed to providing high-quality recombinant protein and antibody reagents and to being a one-stop technical services shop for life science researchers around the world. All of our products are independently developed and produced. In addition, we offer pharmaceutical companies and biotechnology firms pre-clinical production technology services for hundreds of monoclonal antibody drug candidates. Our product quality control indicators meet rigorous requirements for clinical use samples. It takes only a few weeks for us to produce 1 to 30 grams of purified monoclonal antibody from gene sequencing.
Sponsored Content Policy: News-Medical.net publishes articles and related content that may be derived from sources where we have existing commercial relationships, provided such content adds value to the core editorial ethos of News-Medical.Net which is to educate and inform site visitors interested in medical research, science, medical devices and treatments.