B cells play a vital role in the immune system, given their key function in antibody production. Antibodies, also known as immunoglobulins, are glycosylated protein molecules that appear on the surface of B cells acting as antigen receptors, or they are secreted into the extracellular space where they can bind to and neutralize their target antigens.
Development of B-cells starts in the bone marrow and sequentially progresses through pro-B, pre-B and immature B cell stages with the expression of surface IgM, a mature B-cell receptor (BCR).
Each B cell generates a single species of antibody, each of which possesses a unique antigen-binding site. When an antigen binds to the B-cell surface, then B-cell maturity is initiated and separation into antibody-secreting effector cells, called plasma cells, takes place, which releases millions of antibodies into both the bloodstream and lymphatic system (Figure 1).
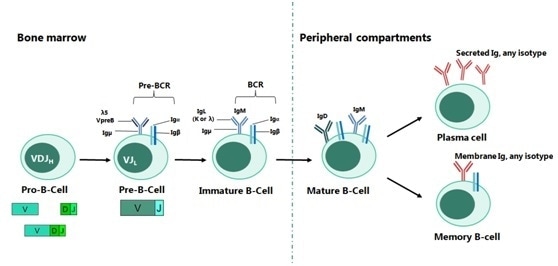
Figure 1. The Main Stages of B-cell Development. Image Credit: Sino Biological Inc.
Sino Biological uses a single B-cell sorting platform as leverage to produce single B-cell antibody production services, including single B cell isolation, culture, sequencing, cloning and screening of select single B-cell antibodies (Figure2).
Figure 2. Workflow of Sino Biological’s Single B-Cell Antibody Discovery Platform. Image Credit: Sino Biological Inc.
Isolation of single B-cells can be carried out by a selection of antigen-specific B-cells instrumentalizing antigen-coated magnetic beads and fluorochrome-labeled antigens by way of multi-parameter fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS), fluorescent foci methodology and the hemolytic plaque assay.
With FACS technology, cells can be classified and easily distinguished based upon the expression patterns of particular cell surface markers.
Generally, it is possible to sort B-cells at any stage, but class-switched memory B cells and antibody-secreting cells (ASCs, i.e., plasmablasts and plasma cells) are of particular interest in the acquisition of relevant monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) as they carry somatically mutated B-cell antigen receptors (BCRs) demonstrating significantly high affinities.
Memory B-cells can be stimulated polyclonally in vitro to prompt the secretion of detectable amounts of antibodies. Primarily, stimulation induction is completed using a mixture of the agonist and recombinant cytokines over several days.
Subsequently, screening of supernatants of the microwells is conducted using ELISA to detect the presence of antibodies of the preferred specificity followed by lysis of B-cells from selected wells.
Single-cell cDNA synthesis is generally conducted in 96-well plates with full-length Ig gene transcripts boosted by nested RT-PCR. Usually, forward primer mixes that complement the relative IgH and IgL V gene leader sequences and a single reverse primer specific to the constant region sequence are used for nested RT-PCR.
When appropriate, for example, when isotype-independent cell sorting is carried out, mixed reverse primers can be employed for the amplification of IgH chains with varying constant regions.
In the next round, nested primers or primer mixes are employed to boost sensitivity and specificity. Throughout this step, homologous arms for successive cloning steps can be integrated into the amplicons. Subsequently, linear expression cassettes can be transfected into mammalian cells directly for effective in vitro expression of monoclonal antibodies.
To establish the reactivity profile and biophysical characteristics of antibodies, target proteins have to be expressed, purified and antibodies tested on these targets in various assays.
The choices made most frequently for expression systems are transient and/or stable mammalian cell systems (e.g., HEK 293, CHO cells). In mammalian cells, antibody expression can persist in complete IgG format.
The COVID-19 pandemic caused by the SARS-CoV-2 virus has severely impacted global health care systems and economies and has challenged the development of vaccines, drugs and diagnostics.
Scientists at Sino Biological have been vigorously tracking the change and movement of the virus since the outbreak first began in order to develop potent anti-spike neutralizing antibodies from immunized animals.
This study was developed to identify anti-SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibodies from a rabbit immunized with the recombinant receptor-binding domain (RBD) domain of COVID-19. Employing high-throughput screening of antigen-specific B-cells from rabbit primordial bone marrow cells (PBMC)s led to the discovery of neutralizing antibodies.
Single-cell RT-PCR in combination with fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS) and B-cells activated in vitro facilitated the determination of antibody sequences in approximately two weeks.
This was achieved by conducting nested PCR on single antigen-binding memory B cells after single-cell sorting and cell culture. From 600 single B-cell supernatants, fifty-four antigen-binding B cell clones expressing antigen-specific antibodies were detected.
ELISA and bio-Layer interferometry (BLI) were employed to test the purified monoclonal antibodies for SARS-CoV-2 RBD/spike reactivity: 27 RBD-binding antibodies were identified.
Each of the ELISA-positive anti-SARS-CoV-2 mAbs was screened further for a capacity to neutralize using a SARS-CoV-2 pseudovirus system, which was created by co-transfection of HEK-293 T cells with plasmids encoding lentiviral packaging and luciferase reporters.
Four of the ELISA-positive anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibodies demonstrated excellent neutralization abilities with an IC 50 lower than 0.15μg/mL against SARS-CoV-2 pseudovirus (Figure 3). All four anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibodies demonstrated a firm bond to the RBD close to pM KD, exhibited by BLI (Figure 4).
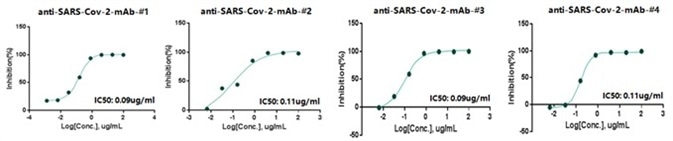
Figure 3. Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Monoclonal Antibody Neutralization with Pseudovirus. Image Credit: Sino Biological Inc.
Figure 4. Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Monoclonal Antibodies Affinity as Assessed by BLI. Image Credit: Sino Biological Inc.
T-cell immunoglobulin and mucin domain-3 (TIM-3), a key immune checkpoint, is known to impede cancer immunity. TIM-3 is principally expressed on immune cells, specifically on defective and exhausted T-cells, and engagement of TIM3 with its ligands promotes TIM-3-mediated T-cell inhibition.
Antagonistic ligand-blocking anti-TIM-3 antibodies exhibit the potential to abrogate T-cell inhibition, activate antigen-specific T-cells and improve anti-tumor immunity.
Sino Biological has developed anti-TIM-3 monoclonal antibodies derived from rabbits immunized with the His-tagged recombinant human TIM-3 extracellular domain (ECD) protein.
After B-cell sorting and proliferation, 200 antigen-specific antibodies were detected from 1100 single B-cell supernatants. The affinity and kinetics of 63 purified ELISA-positive anti-TIM-3 monoclonal antibodies were assessed using bio-Layer interferometry (BLI) technology.
Among the ELISA-positive antibodies, five of them demonstrated optimal affinity with a range between 10-11 and 10-12 M (Figure 5).
Figure 5. Anti-Tim-3 Monoclonal Antibody Affinity as Assessed with BLI. Image Credit: Sino Biological Inc.
To assess the full capacity of the five anti-TIM-3 monoclonal antibodies to impede the interplay of TIM-3 and its ligand phosphatidylserine (PtdSer), a bioluminescent reporter cell-based system was used to conduct a blocking assay.
Five anti-TIM-3 mAbs showed the ability to effectively impede the interaction between TIM-3 and PtdSer in a dose-dependent manner, with the IC50 of 0.070 ± 0.010 μg/mL, near to that of positive control (Figure 6).
Figure 6. Anti-Tim-3 Monoclonal Antibody Ligand- blocking Cell-based Assay. Image Credit: Sino Biological Inc.
About Sino Biological Inc.

Sino Biological is an international reagent supplier and service provider. The company specializes in recombinant protein production and antibody development. All of Sino Biological's products are independently developed and produced, including recombinant proteins, antibodies and cDNA clones. Sino Biological is the researchers' one-stop technical services shop for the advanced technology platforms they need to make advancements. In addition, Sino Biological offers pharmaceutical companies and biotechnology firms pre-clinical production technology services for hundreds of monoclonal antibody drug candidates.
Sino Biological's core business
Sino Biological is committed to providing high-quality recombinant protein and antibody reagents and to being a one-stop technical services shop for life science researchers around the world. All of our products are independently developed and produced. In addition, we offer pharmaceutical companies and biotechnology firms pre-clinical production technology services for hundreds of monoclonal antibody drug candidates. Our product quality control indicators meet rigorous requirements for clinical use samples. It takes only a few weeks for us to produce 1 to 30 grams of purified monoclonal antibody from gene sequencing.
Sponsored Content Policy: News-Medical.net publishes articles and related content that may be derived from sources where we have existing commercial relationships, provided such content adds value to the core editorial ethos of News-Medical.Net which is to educate and inform site visitors interested in medical research, science, medical devices and treatments.