The coronavirus disease-19 (COVID-19) is caused by the novel coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2), a positive-sense single-stranded RNA virus that frequently mutates during the replication step.
While most mutations have minus impact on the characteristics of the virus, some mutations may affect the severity of the associated diseases, its transmissibility, the effectiveness of treatments and vaccines and decrease the efficacy of diagnostic detections.
The SARS-CoV-2 variants are classified as variants under monitoring (VUM), variants of interest (VOI) and variants of concern (VOC). VOCs are the mutants that have been proven to negatively impact the current therapeutics, vaccines and diagnostics or increase disease severity or transmissibility.
VOIs are designated as emerging SARS-CoV-2 variants with similar epidemiological potential to pose apparent epidemiological impacts and affect virus characteristics. Meanwhile, the variants that lack the evidence to affect virus characteristics but may pose a future risk requiring enhanced monitoring and repeat assessment are known as VUMs.
A WHO expert team has developed several criteria to evaluate and monitor the existing risks of mutant strains in real-time due to the evolution of SARS-CoV-2, and the influence of the new variant strains on public health.
Additionally, scientists have established Pango, Nextstrain and GISAID nomenclature systems to track and study the changes in SARS-CoV-2. The WHO also recommends using Greek alphabets, such as Alpha, Beta, Gamma and Delta to label the mutants to make it easier for the public to discuss the variants.
Tables 1 and 2 show the five VOCs and two VOIs currently designated by WHO according to the variant risk. These variants are given higher priority for global COVID-19 research and monitoring.
Table 1. Variants of Concern designated currently by WHO. Source: Sino Biological Inc.
| WHO label |
Lineages |
Earliest documented samples |
| Alpha |
B.1.1.7 |
United Kingdom, Sep-2020 |
| Beta |
B.1.351 |
South Africa, May-2020 |
| Gamma |
P.1 |
Brazil, Nov-2020 |
| Delta |
B.1.617.2 |
India, Oct-2020 |
| Omicron |
B.1.1.529 |
Multiple countries, Nov-2021 |
Table 2. Variants of Interest designated currently by WHO. Source: Sino Biological Inc.
| WHO label |
Lineages |
Earliest documented samples |
| Lambda |
C.37 |
Peru, Dec-2020 |
| Mu |
B.1.621 |
Colombia, Jan-2021 |
While monitoring and performing grading for the mutant strains of SARS-CoV-2, it is also necessary to conduct scientific research on the pathogenicity, transmissibility and other characteristics of the mutant strains.
It is just as important to evaluate the detection accuracy of existing diagnostic approaches, the risk of reinfection of the population and the effectiveness of current treatment methods and vaccines.
Having a sufficient and high-quality supply of readily available raw materials and reagents are critical prerequisites to attaining these scientific goals. Sino Biological is an international service and reagent supplier that independently manufactures and develops all of its products.
Sino Biological has established a comprehensive SARS-CoV-2 Reagent Bank with a suite of advanced core technologies, including antibody titer assay kits, neutralizing/inhibitor assay kits, antigen detection antibodies, neutralizing antibodies, pseudoviruses, recombinant antigens and variants, antigen detection kits, genes and peptide.
These are widely used in various researches on SARS-CoV-2 and its variants.
Research on pathogenicity and transmissibility of SARS-CoV-2 variants
Transmissibility and pathogenicity are important parameters for the evaluation of the SARS-CoV-2 variants and epidemic surveillance. A common feature of current VOCs has increased transmissibility.
Mutation site analysis revealed that N501Y (Cat#: 40592-V08H82), sited in the spike receptor binding domain (RBD), could significantly increase the binding affinity of SARS-CoV-2 to ACE2. This can be found in Alpha, Beta, Gamma, and Omicron variants (Figure 1).
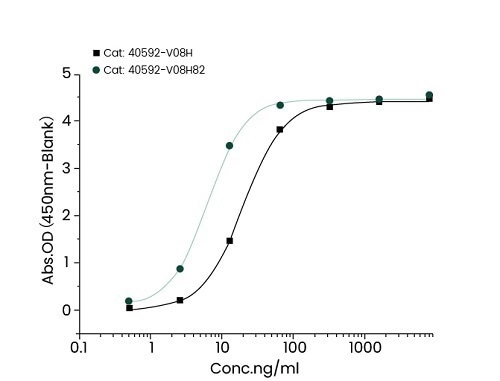
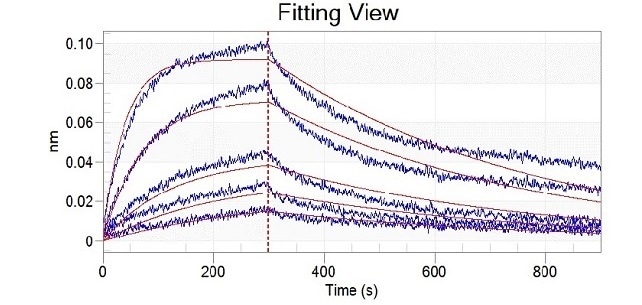
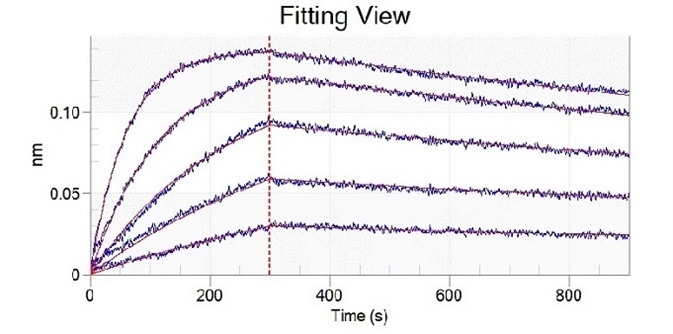
Figure 1. Recombinant RBD (N501Y) developed by Sino Biological (cat: 40592-V08H82) showed a stronger binding capacity than WT by ELISA and BLI. Image Credit: Sino Biological Inc.
P681 mutation may increase the cleavage of spike protein; it is closed to the furin restriction site and also present in Alpha, Delta and Omicron. Increased transmissibility of VOCs may partly be caused by these mutations.
Researchers have verified in both animal model test and cellular level assay that some early found mutations, like D614G (Cat#: 40591-V08H3), could lead to increased transmissibility of SARS-CoV-2.
As well as mutations in spike protein, G204R and R203K mutations (Cat#: 40588-V07E1) present in the nucleocapsid of Omicron and Alpha variants may be associated with increased viral RNA expression and viral load, which can increase virulence and transmissibility.
With the exception of Omicron, which needs further evaluation, there is the potential that VOCs will increase the risk of hospitalization in infected individuals. However, evidence has shown that Omicron could increase the risk of patient reinfection.
Evaluate the impact of SARS-CoV-2 variants on vaccine development
While SARS-CoV-2 mutates very quickly, it is essential to evaluate the efficacy of existing vaccines. One of the indicators for vaccine performance is the neutralizing activity of antibodies derived from convalescent or vaccinated serum.
The evaluation assay can be done using recombinant proteins, pseudovirus, isolated virus, pseudovirus and recombinant proteins. The COVID-19 vaccine showed decreased protective efficacy against Beta, Delta and Omicron variants according to preliminary laboratory results based on serum neutralizing antibody activity.
A study was published in Cell Research that dissected the immunity response to Beta variant using neutralizing antibody, recombinant vaccine and inactivated vaccine from recovered patients by virus neutralization experiments, high-throughput single-cell sequencing and cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) assay.
It was revealed through pseudovirus neutralization tests that more than half of the anti-RBD neutralizing antibodies had substantially decreased the neutralizing activity against the K417N/E484K/N501Y mutant. The substantial reduction in neutralizing activity was shown through Cryo-EM, which is attributable to charge reversal caused by the E484K mutation.
Antibody titer assay kit (KIT004/KIT002), pseudovirus (PSV016), recombinant variant proteins (Cat#:40591-V08H10, 40591-V08H3) and other reagents from Sino Biological have provided readily available support for those studies, as shown in Figure 2.
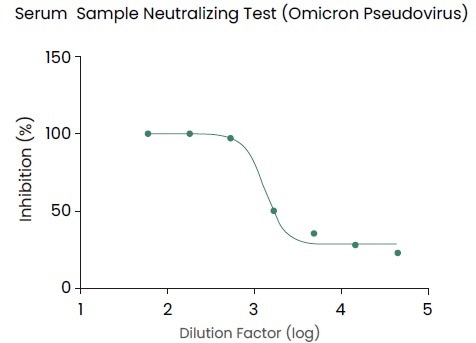
Figure 2. Pseudovirus (Omicron Spike pseudovirus, Cat. No.: PSV016) for the evaluation of neutralizing capacity in mouse serum after immunization. Image Credit: Sino Biological Inc.
The influence of SARS-CoV-2 variants on the development of antibody drugs
The RBD region of SARS-CoV-2 is what most neutralizing antibody drugs have been developed against. The high mutation frequency in the RBD region of emerging variants is highly likely to result in the failure of therapeutic antibody drugs.
A review published in Cell describes the effects of several variants on antibody drugs that are in clinical development or are urgently authorized and their effectiveness.
The Alpha variant has minimal effect on existing neutralizing antibody drugs, while the efficacy of some antibody drugs is adversely impacted by beta, gamma and delta variants (Figure 3).

Figure 3. Neutralization of a selection of VOCs/VOIs by clinical-stage mAbs. Source: Cell. 2021 Jun 10; 184 (12): 3086-3108. Image Credit: Sino Biological Inc.
Fifteen mutant sites have been found in the RBD region of Omicron, with the latest variant first detected in southern Africa. It has a very concerning impact on the efficacy of neutralizing antibody drugs.
It was revealed in an article published in Nature that only two neutralizing antibody drugs have shown satisfactory neutralizing activity against Omicron pseudovirus after analyzing nine monoclonal antibody drugs, where the remaining drugs’ neutralizing activity was reduced.
It was revealed in the study that six single point mutations in Omicron (G496S, Q493K, E484A, G446S, N440K, K417N) are one of the major contributing causes of immune escape.
Pseudovirus are applied to evaluate the neutralizing capacity of different antibody drugs in this study, while the detection of the recognition capacity of neutralizing antibodies to variants is done using recombinant variants (Omicron RBD, cat#40592-V08H121).
The evaluation results on mAbs using the pseudovirus (Omicron Spike pseudovirus, Cat. No.: PSV016) are shown in Figure 4.
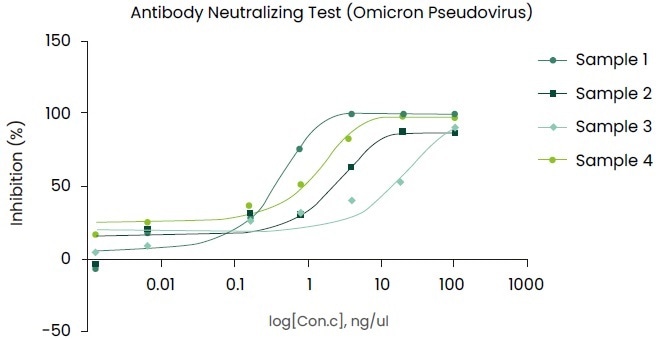
Figure 4. Using the pseudovirus (Omicron Spike pseudovirus, Cat. No.: PSV016) to evaluate Neutralizing antibody. Image Credit: Sino Biological Inc.
The influence of SARS-CoV-2 variants on the development of diagnostic reagents
Immunodiagnostic kits are essential for controlling COVID-19 outbreaks as they can get test results quickly and are easy to use. Under the emergence of new mutant strains, it is essential to establish whether there is a risk of off-target effects or missed detection in the shortest time.
Diagnostic reagents are essential for controlling COVID-19 outbreaks. A minimum of time is required to understand whether there is a risk of missed detection or off-target effects when a new mutant strain emerges.
Currently, antibodies that can recognize the N protein are the most commonly used raw material reagents for COVID-19 immunodiagnostic approaches.
As a leading supplier of raw materials for COVID-19 diagnostic reagents worldwide, Sino Biological has been actively tracking the status of the virus to make products “up to date.” The most divergent SARS-CoV-2 variant is the Omicron (B.1.1.529) strain.
Re-evaluating the effectiveness of the current diagnostics is critical. Recombinant Omicron Spike and Nucleocapsid proteins have been developed by Sino Biological, who have also validated all available antibodies against the Omicron proteins.
As a leading supplier of raw materials for COVID-19 diagnostic reagents, Sino Biological has always managed to recognize mutant strains via raw material antibodies at the very first outbreak of new strains.
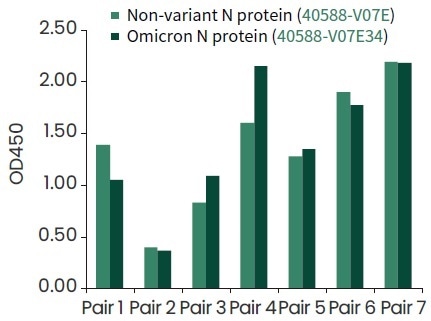
Seven top pairs of antibodies for the detection of Omicron nucleocapsid protein (Cat#40588-V07E34) have been identified by Sino Biological, as shown in Figure 5.
| Antibody Pairs |
Capture Ab |
Detection Ab |
| Pair 1 |
40143-MM08 |
40143-MM05 |
| Pair 2 |
40143-MM08 |
40143-R004 |
| Pair 3 |
40143-R004 |
40143-R040 |
| Pair 4 |
68097-MM180 |
40588-RB89 |
| Pair 5 |
40588-MM162 |
40588-RA84 |
| Pair 6 |
40143-R004 |
40588-MM124 |
| Pair 7 |
40143-MM05 |
40588-R001 |
Figure 5. The COVID-19 antibody pairs developed by Sino Biological can recognition of Omicron N protein (Cat#40588-V07E34) by ELISA binding assay. Image Credit: Sino Biological Inc.
Reference
- Tracking SARS-CoV-2 variants (who.int)
- CDC | Science Brief: Omicron (B.1.1.529) Variant
- DOI: 10.1038/s41586-021-03361-1
- DOI: 10.1038/s41422-021-00514-9
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2021.05.005
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/d41586-021-03796-6
About Sino Biological Inc.

Sino Biological is an international reagent supplier and service provider. The company specializes in recombinant protein production and antibody development. All of Sino Biological's products are independently developed and produced, including recombinant proteins, antibodies and cDNA clones. Sino Biological is the researchers' one-stop technical services shop for the advanced technology platforms they need to make advancements. In addition, Sino Biological offers pharmaceutical companies and biotechnology firms pre-clinical production technology services for hundreds of monoclonal antibody drug candidates.
Sino Biological's core business
Sino Biological is committed to providing high-quality recombinant protein and antibody reagents and to being a one-stop technical services shop for life science researchers around the world. All of our products are independently developed and produced. In addition, we offer pharmaceutical companies and biotechnology firms pre-clinical production technology services for hundreds of monoclonal antibody drug candidates. Our product quality control indicators meet rigorous requirements for clinical use samples. It takes only a few weeks for us to produce 1 to 30 grams of purified monoclonal antibody from gene sequencing.
Sponsored Content Policy: News-Medical.net publishes articles and related content that may be derived from sources where we have existing commercial relationships, provided such content adds value to the core editorial ethos of News-Medical.Net which is to educate and inform site visitors interested in medical research, science, medical devices and treatments.