Influenza (also known as flu) is an acute respiratory illness caused by the influenza viruses A, B, C and D. Amongst them, influenza A, B and C affect humans (Table 1).
Table 1. Classification of Influenza Virus. Source: Sino Biological Inc.
| |
Influenza A |
Influenza B |
Influenza C |
| Hosts |
Humans, waterfowl, poultry, pigs, horses, sea mammals, bats |
Humans, seals |
Humans, pigs, dogs |
| Gene Segments |
8 |
8 |
7 |
| Proteins |
11 |
11 |
9 |
| Clinical Features |
Moderate to severe illness |
Milder disease than Influenza A |
Largely subclinical |
| Epidemiological Features |
Causes pandemics |
Less severe epidemics than Influenza A; no pandemics |
Does not cause epidemics or pandemics |
Influenza A and B viruses exhibit the potential to cause epidemic (interpandemic or seasonal) influenza, and influenza A viruses can also be responsible for pandemics.
Influenza virus structure
Influenza A viruses consist of eight negative-sense, single-stranded viral RNA (vRNA) gene segments that encode 10 viral proteins (Figure 1).
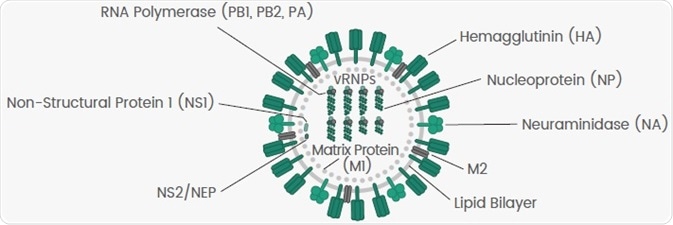 Figure 1. Diagram of Influenza Virus. Image Credit: Sino Biological Inc.
Figure 1. Diagram of Influenza Virus. Image Credit: Sino Biological Inc.
With the help of the nucleoprotein (NP), the eight genome segments are encapsulated loosely. Polymerase complexes consisting of three polymerase proteins, PB1, PB2 and PA, are situated at the ends of nucleocapsids.
Such helical capsids have been encircled by the matrix protein 1 (M1) and a host-derived lipid bilayer envelope in which the viral surface glycoprotein hemagglutinin (HA), the matrix protein 2 (M2) and neuraminidase (NA) are embedded.
HA, NA and NP are known as the three significant antigens of the influenza virus, which play crucial roles in the lifecycle of a virus (Table 2). Their recombinant proteins find extensive use in fundamental research, vaccine development, therapeutics and diagnosis.
Table 2. Classification of Influenza Virus. Source: Sino Biological Inc.
| Antigens |
Functions in Lifecycle |
Applications |
| HA |
Binding to sialic acid receptors on the surface of the host cell membrane, helping the interfusion of the viral envelope with the host cell membrane. |
Basic research; Vaccine development; Anti-hemagglutinin antibody development; Detection reagents development |
| NA |
Mediating the release of nascent viral particles assembled in the host cells by cleaving sialic acid groups from glycoproteins. |
Antiviral drug development; Basic Research; Vaccine development; Antibody development; Detection reagents development |
| NP |
A major component of the ribonucleoprotein complex, engaging in viral gene replication, transcription, and translation. |
Antiviral drug development; Basic Research; Antibody development; Detection reagents development |
Influenza pandemics and strains
In the past, influenza pandemics were caused by the influenza A viruses. This could be additionally divided into different subtypes based on HA and NA differences.
Four influenza pandemics happened in the past 10 decades: the H1N1 Spanish flu pandemic (1918–1920), the H2N2 Asian influenza pandemic (1957–1958), the H3N2 Hong Kong flu pandemic (1968–1969), and the H1N1/09 swine flu pandemic (2009–2010) (Table 3).
Table 3. Four Influenza Pandemics in the Past 100 Years. Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Influenza_pandemic
| Name |
Date |
Subtype |
Infected (est.) |
Deaths |
Case Fatality Rate |
| Spanish Flu |
1918-1920 |
H1N1 |
500 million or >1 billion |
17–100million |
2–3%, or ~4%, or ~10% |
| Asian Flu |
1957-1958 |
H2N2 |
>500 million |
1–4 million |
<0.2% |
| Hong Kong Flu |
1968-1969 |
H3N2 |
>500 million |
1–4 million |
<0.2% |
| Swine Flu |
2009-2010 |
H1N1/09 |
0.7–1.4 billion |
151,700–575,400 |
0.01% |
The strains accountable for the four pandemics, H1N1 (swine flu and Spanish flu), H2N2 (Asian flu), and H3N2 (Hong Kong flu), have gained increased attention. In the last two decades, several potential pandemic strains have appeared with various zoonotic influenza events (Figure 2).
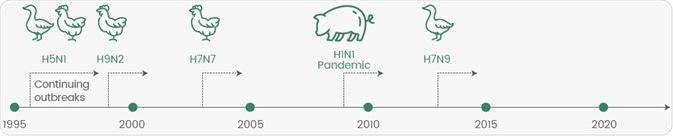 Figure 2. Emerging Potential Pandemic Strains in the Last 20 Years. Image Credit: Sino Biological Inc.
Figure 2. Emerging Potential Pandemic Strains in the Last 20 Years. Image Credit: Sino Biological Inc.
Sino Biological has come up with a panel of antigen proteins and antibodies for influenza pandemic strains (Table 4). It has been designed to be utilized for numerous biochemical assays, like antigen detection, antibody titer and antigenic characterization assays.
Table 4. Influenza Pandemic Strains. Source: Sino Biological Inc.
| Subtype |
Strain |
Year |
Antigen Proteins |
Antigen Antibodies |
| H1N1 |
A/Brevig Mission/1/1918 |
1918 |
HA, HA1, M1, NP |
HA |
| H1N1 |
A/California/04/2009 |
2009 |
HA, HA0, HA1, NA |
HA, NA |
| H2N2 |
A/Guiyang/1/1957 |
1957 |
HA, HA1 |
|
| H3N2 |
A/Hong Kong/1/1968 |
1968 |
HA, HA1, NP |
NP |
| H5N1 |
A/Hong Kong/483/97 |
1997 |
HA, HA1 |
HA |
| H7N7 |
A/Netherlands/219/2003 |
2003 |
HA, HA1, NA |
HA, NA |
| H7N9 |
A/Shanghai/1/2013 |
2013 |
HA, HA1, HA1+HA2, NA, NP |
HA |
| H9N2 |
A/Hong Kong/35820/2009 |
2009 |
HA, HA1 |
|
Flu prevention and control
Early diagnosis and vaccination are significant methods to avoid and control the flu. Early diagnosis and treatment can efficiently reduce the duration of the illness, relieve symptoms and regulate the spread of the virus. The World Health Organization (WHO) suggests annual vaccination to prevent seasonal influenza.
Immunodetection
A common method used to diagnose flu is Immunodetection. Antibodies that target NP proteins are generally utilized for immunodetection in different assays. This includes lateral flow assay, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and direct fluorescent antibody tests.
As a result of the high frequency of antigenic drift or shift present in several influenza strains, broad-spectrum influenza antibodies are preferred specifically for diagnosing flu. Sino Biological has determined six pan-antibody pairs each against the NP protein of influenza A and B (Table 5).
Table 5. Pan Antibody Pairs for NP Detection. Source: Sino Biological Inc.
| Pair No. |
Capture Ab |
Detection Ab |
Pair No. |
Capture Ab |
Detection Ab |
| PanA-1 |
40205-MM16 |
40208-R014 |
PanB-1 |
40438-R004 |
40438-MM10 |
| PanA-2 |
40205-R063 |
40205-MM18 |
PanB-2 |
40438-R036 |
40438-MM10 |
| PanA-3 |
40208-R117 |
40205-MM18 |
PanB-3 |
40438-MM05 |
40438-R036 |
Such matched pairs have the ability to detect broad-spectrum strains inside the target subtype in the absence of any cross-reactivity along with other subtypes (Figure 3).
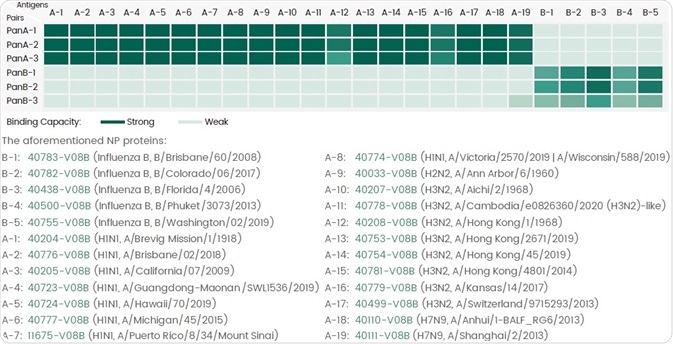 Figure 3. Six Pan antibody pairs each against the NP protein can detect different NP proteins of influenza A or B virus by ELISA assay. Image Credit: Sino Biological Inc.
Figure 3. Six Pan antibody pairs each against the NP protein can detect different NP proteins of influenza A or B virus by ELISA assay. Image Credit: Sino Biological Inc.
Vaccine development
Flu, particularly seasonal flu, is a universal threat to human health. Vaccination is an efficient method to avoid the spread of infection. Annually, numerous different flu strains are chosen as vaccine strains depending on the surveillance data of the recent isolates and their performance in the early season.
Over the last few years, the majority of the vaccines are either trivalent or quadrivalent, such as one H1N1, one H3N2 and Yamagata and/or Victoria-type flu B.
Sino Biological has liberated a panel of recombinant antigen products spanning all WHO-recommended vaccine strains in recent years (Table 6). The products include NA, HA, as well as NP and have been developed for vaccine development.
Table 6. Antigens for 2015-2022 Vaccine Strains. Source: Sino Biological Inc.
| Strains |
HA |
NA |
NP |
Year |
| A/Brisbane/02/2018 (H1N1) |
40719-V08H |
40767-V08B |
40776-V08B |
2019-2020 |
| A/California/7/2009 (H1N1) |
11085-V08B |
|
40205-V08B |
2016-2017, 2015-2016 |
| A/Cambodia/e0826360/2020 (H3N2) |
40789-V08H
40789-V08H1 |
40784-V08B |
40778-V08B |
2021-2022 |
| A/Guangdong-Maonan/SWL1536/2019 (H1N1) |
40717-V08H |
|
40723-V08B |
2020-2021 |
| A/Hawaii/70/2019 (H1N1) |
40717-V08H |
|
40724-V08B |
2020-2021 |
| A/Hong Kong/2671/2019 (H3N2) |
40721-V08H |
|
40753-V08B |
2020-2021 |
| A/Hong Kong/45/2019 (H3N2) |
40765-V08H |
|
40754-V08B |
2020-2021 |
| A/Hong Kong/4801/2014 (H3N2) |
40555-V08B |
40569-V08B |
40781-V08B |
2017-2018, 2016-2017 |
| A/Kansas/14/2017 (H3N2) |
40720-V08H |
40766-V08B |
40779-V08B |
2019-2020 |
| A/Michigan/45/2015 (H1N1) |
40567-V08H1 |
40568-V08B |
40777-V08B |
2018-2019, 2017-2018 |
| A/Singapore/INFIMH-16-0019/2016 (H3N2) |
40580-V08H |
|
40779-V08B |
2018-2019 |
| A/Switzerland/9715293/2013 (H3N2) |
40497-V08B |
|
40499-V08B |
2015-2016 |
| A/Victoria/2570/2019 (H1N1) |
40787-V08H
40787-V08H1 |
40785-V08B |
40774-V08B |
2021-2022 |
| A/Wisconsin/588/2019 (H1N1) |
40787-V08H
40787-V08H1 |
40785-V08B |
40774-V08B |
2021-2022 |
| B/Brisbane/60/2008 |
40016-V08B |
40203-VNAHC |
40783-V08B |
2017-2018, 2016-2017, 2015-2016 |
| B/Colorado/06/2017 |
40581-V08H |
|
40782-V08B |
2019-2020, 2018-2019 |
| B/Phuket/3073/2013 |
40498-V08B |
40502-V07B |
40500-V08B |
2021-2022, 2020-2021, 2019-2020, 2018-2019, 2017-2018, 2016-2017, 2015-2016 |
| B/Washington/02/2019 |
40722-V08H |
40790-V08B |
40755-V08B |
2021-2022, 2020-2021 |
Summary
Regardless of the ongoing coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic, influenza occurs every year. This leads to substantial mortality and morbidity. Several relevant studies are in progress to help control the influenza virus.
The sophisticated tools designed by Sino Biological consist of a library of antiviral antibodies and a huge collection of recombinant virus proteins. Such reagents could be utilized extensively for vaccine development and immunodetection for the influenza virus.
About Sino Biological Inc.

Sino Biological is an international reagent supplier and service provider. The company specializes in recombinant protein production and antibody development. All of Sino Biological's products are independently developed and produced, including recombinant proteins, antibodies and cDNA clones. Sino Biological is the researchers' one-stop technical services shop for the advanced technology platforms they need to make advancements. In addition, Sino Biological offers pharmaceutical companies and biotechnology firms pre-clinical production technology services for hundreds of monoclonal antibody drug candidates.
Sino Biological's core business
Sino Biological is committed to providing high-quality recombinant protein and antibody reagents and to being a one-stop technical services shop for life science researchers around the world. All of our products are independently developed and produced. In addition, we offer pharmaceutical companies and biotechnology firms pre-clinical production technology services for hundreds of monoclonal antibody drug candidates. Our product quality control indicators meet rigorous requirements for clinical use samples. It takes only a few weeks for us to produce 1 to 30 grams of purified monoclonal antibody from gene sequencing.
Sponsored Content Policy: News-Medical.net publishes articles and related content that may be derived from sources where we have existing commercial relationships, provided such content adds value to the core editorial ethos of News-Medical.Net which is to educate and inform site visitors interested in medical research, science, medical devices and treatments.