The COVID-19 pandemic has continued to spread globally since the discovery of SARS-CoV-2 in 2019, with a steadily rising number of global infections. During transmission, SARS-CoV-2 produces new variants of concern. Researchers have not abandoned their antiviral research in the face of these highly communicable variants.
Two key aspects of their research are vaccines and neutralizing antibody drugs. Vaccines encourage the body to produce antibodies against SARS-CoV-2, including neutralizing antibodies and immune cell responses preventing transmission. Neutralizing antibody drugs, on the other hand, can bind directly to viruses and hinder them from infecting cells.
What are neutralizing antibodies?
Neutralizing antibodies are a class of antibodies that bind to viruses and disable their infectivity. When a virus invades the body, plasma cells generate virus-specific antibodies, only a few being neutralizing antibodies.
The neutralizing mechanism is as follows:
- Altering the surface conformation of the virus;
- Binding to the virus epitope linked to adsorption and blocking its communication with receptors of the host cells;
- Developing immune complexes with the virus, which are readily cleared by macrophages;
- Triggering complement when the viral surface antigen binds to neutralizing antibodies, thereby resulting in viral lysis.
SARS-CoV-2 comprises an essential spike (S) protein, a trimeric transmembrane glycoprotein made of S1/S2 heterodimers, that identifies the angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2), host cell receptor, and mediates membrane fusion. A receptor-binding domain (RBD) on the S1 subunit has been directly involved in host receptor recognition and intercedes viral invasion.
The S protein, particularly the RBD, is considered a significant immunogenic component and the target of the majority of the neutralizing antibodies. Neutralizing antibodies prevent the binding of S1 or RBD to ACE2, thereby stopping the virus from invading host cells and eventually stopping viral infection (Figure 1). Therefore, S1 or RBD mutations might result in strong SARS-CoV-2 infectivity.
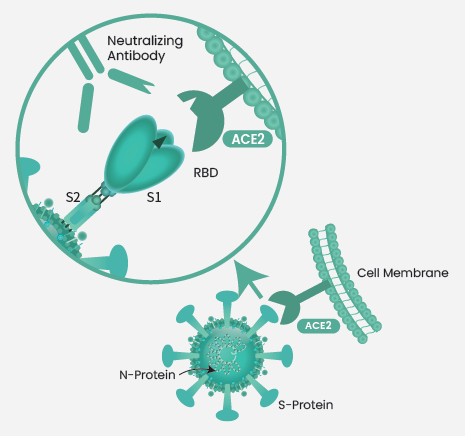
Figure 1. The neutralizing mechanism of SARS-CoV-2 RBD neutralizing antibody. Image Credit: Sino Biological Inc.
Why should we detect neutralizing antibodies?
The quantification of neutralizing antibodies is one of the significant indicators in clinical evaluation and vaccine development. A good vaccine must produce highly potent neutralizing antibodies.
The question of how long the vaccine’s safety lasts has to be answered by continuous tracking of neutralizing antibody levels. It is also questionable if it can produce efficient neutralizing antibodies against new SARS-CoV-2 variants.
Hence the detection of SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibodies is necessary to evaluate the herd immunity and track the vaccine efficacy against SARS-CoV-2.
How to detect neutralizing antibodies?
Neutralizing antibody detection tests consist of a neutralization test, a virus neutralization test, a pseudovirus virus neutralization test and a surrogate virus neutralization test.
The gold standard for neutralizing antibody detection is known to be the virus neutralization test. This primarily includes a plaque reduction neutralization test with the help of live viruses and a micro-neutralization test by almost detecting 50% cytopathic variables.
Both techniques utilize a quantitative number of live viruses mixed with corresponding amounts of serum at various dilutions and inoculated with pre-prepared monolayer cells. Neutralizing antibody titers are assessed depending on variations in cytopathic effects or plaque-forming units.
As a result of the manipulation of live viruses, such assays can just be executed in a biosafety level 3 laboratory. This significantly restricts the usage of plaque reduction neutralization tests and micro-neutralization tests.
Pseudovirus neutralization test
At present, more laboratories are making use of the pseudovirus neutralization test to detect neutralizing antibodies. The SARS-CoV-2 pseudovirus makes use of a non-pathogenic virus (like replication-deficient HIV-1) as a vector, substitutes the envelope protein of the vector virus with the S protein of SARS-CoV-2, and initiates detection signal molecules, like luciferase and GFP.
The pseudovirus utilizes the S protein RBD bound to ACE2, thereby simulating the process of viral invasion. Neutralizing antibodies can efficiently hinder SARS-CoV-2 pseudovirus from infecting host cells (Figure 2).
Neutralizing antibody titers are assessed by signal detection. As the pseudovirus can only be infected once and cannot replicate, this method could be operated in a biosafety level 2 laboratory.
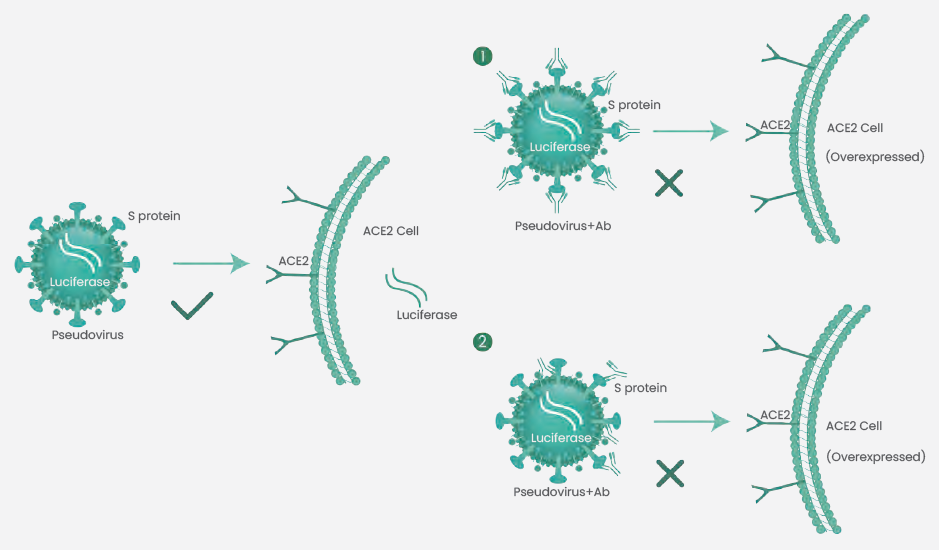
Figure 2. Schematic diagram of pseudovirus neutralization test. (1) Neutralizing antibodies directly block the binding of RBD and ACE2, preventing pseudovirus from infecting cells. (2) Neutralizing antibodies binding to Spike generates steric hindrance to inhibit RBD from binding to ACE2, or prevents cleavage of S1 and S2 subunits, thereby resulting in the failure of the pseudovirus to enter cells. Image Credit: Sino Biological Inc.
Sino Biological has been successful in packaging a novel SARS-CoV-2 pseudovirus (Figure 3) with the help of an HIV lentiviral vector. It expresses the SARS-CoV-2 S protein that spans numerous variants [Alpha (Cat: PSV006), Gamma (Cat: PSV007), Beta (Cat: PSV008), Delta (Cat: PSV011), Omicron (Cat: PSV016), D614G (Cat: PSV006)] and carries a luciferase reporter gene.
Neutralizing antibodies are detected by assessing the pseudovirus neutralization inhibition rate depending on comparative light units of luciferase reporters (Figure 3). The company can also offer pseudovirus packaging services and neutralization detection services.
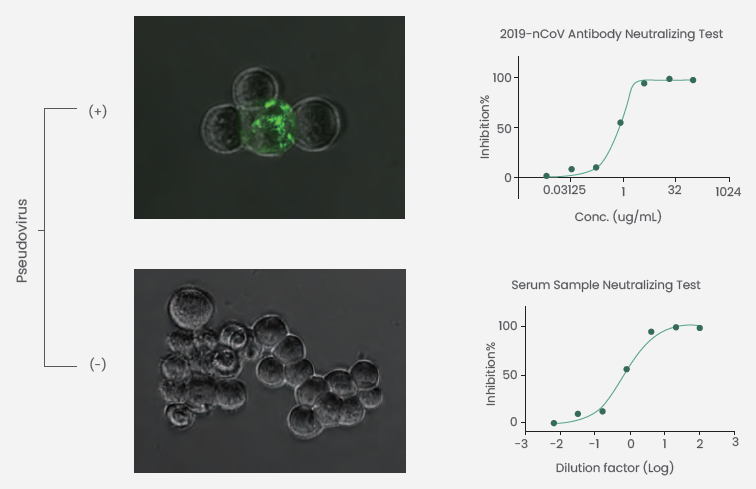
Figure 3. SARS-CoV-2 pseudovirus neutralization tests. Image Credit: Sino Biological Inc.
Surrogate virus neutralization test
The surrogate virus neutralization test relies on the principle of competitive enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and utilizes the binding interaction of recombinant RBD proteins with recombinant ACE2 proteins to imitate virus-cell interaction.
Neutralizing antibodies present in a sample could effectively impede the binding of RBD proteins to ACE2 proteins. In comparison to virus and pseudovirus neutralization tests, the surrogate virus neutralization test is simpler, safer, and less laborious to execute.
SinoBiological has developed a SARS-CoV-2 (2019-nCoV) Inhibitor Screening ELISA Kit (Cat: KIT001) that efficiently detects the neutralization abilities of antibodies (Figure 4). Neutralizing antibodies in samples compete with ACE2-His (Cat: 10108-H08B) to integrate with immobilized RBD. The signal color gets lighter as the content of neutralizing antibodies increases.
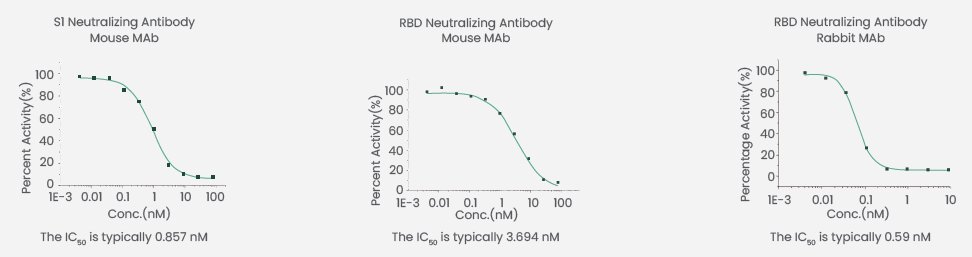
Figure 4. Neutralizing ability was detected by SARS-CoV-2 Inhibitor Screening ELISA Kit (Cat: KIT001) using competitive ELISA. Image Credit: Sino Biological Inc.
In this assay, immobilized SARS-CoV-2 spike RBD recombinant proteins are considered to be the core reagents. RBDs obtained from different variants could be utilized to detect neutralizing antibodies against the equivalent variants.
At present, the evaluation of the effectiveness of present vaccines against Delta and Omicron variants is an urgent task. These are, at present, the predominant strains, as their RBD proteins will play a vital role.
Sino Biological has come up with a series of high-quality RBD proteins spanning the wild type (Cat: 40592-V08B), Alpha variant (Cat: 40592-V08H82), Beta variant (Cat: 40592-V08H85), Gamma variant (Cat: 40592-V08H86), Delta variant (Cat: 40592-V08H90), Omicron variant (Cat: 40592-V08H121).
These RBD proteins were utilized to detect the neutralizing activities of neutralizing antibodies against various variants by surrogate virus neutralization test (Table 1). The outcomes displayed that these antibodies developed by Sino Biological possessed different neutralizing activities.
Table 1. Different RBD proteins were used to detect different neutralizing antibodies. Source: Sino Biological Inc.
| Neutralizing Antibodies |
RBD Proteins |
40592-V08B
Wild Type |
40592-V08H82
Alpha Variant |
40592-V08H85
Beta Variant |
40592-V08H86
Gamma Variant |
40592-V08H90
Delta Variant |
40592-V08H121
Omicron Variant |
| 40150-D001 |
++ |
+ |
++ |
++ |
++ |
- |
| 40150-D002 |
++ |
+ |
+ |
++ |
++ |
- |
| 40591-MM43 |
++ |
++ |
++ |
++ |
++ |
- |
| 40592-R001 |
+++ |
+++ |
- |
- |
+++ |
- |
| 40592-R118 |
+++ |
+++ |
- |
- |
+++ |
- |
| 40592-R117 |
+++ |
+++ |
- |
- |
- |
- |
| 40591-MM48 |
++ |
- |
- |
- |
+ |
+ |
| 40592-MM135 |
++ |
++ |
- |
- |
++ |
- |
| 40592-R0004 |
++ |
TBD |
TBD |
TBD |
+ |
+ |
| 40592-R831 |
++ |
+ |
+ |
+ |
++ |
- |
+: Neutralizing Capacity
Summary
New variants of SARS-CoV-2 virus are still emerging. The questions that now need answering are whether the present COVID-19 vaccines are still effective against the new variants, as well as how protective these vaccines are. These questions require an immediate answer.
Consequently, the demand for neutralizing antibody tests and recombinant proteins for new variants is growing. SinoBiological provides 290+ recombinant SARS-CoV-2 antigens that cover the majority of the variants, such as the present extensively disseminated Omicron variant (B.1.1.529, BA.1.1, and BA.2), thereby streamlining SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibody detection.
At the same time, the company has been active in tracking the status of the virus to make products up to date. It is possible for researchers to obtain products in a short span of time.
About Sino Biological Inc.

Sino Biological is an international reagent supplier and service provider. The company specializes in recombinant protein production and antibody development. All of Sino Biological's products are independently developed and produced, including recombinant proteins, antibodies and cDNA clones. Sino Biological is the researchers' one-stop technical services shop for the advanced technology platforms they need to make advancements. In addition, Sino Biological offers pharmaceutical companies and biotechnology firms pre-clinical production technology services for hundreds of monoclonal antibody drug candidates.
Sino Biological's core business
Sino Biological is committed to providing high-quality recombinant protein and antibody reagents and to being a one-stop technical services shop for life science researchers around the world. All of our products are independently developed and produced. In addition, we offer pharmaceutical companies and biotechnology firms pre-clinical production technology services for hundreds of monoclonal antibody drug candidates. Our product quality control indicators meet rigorous requirements for clinical use samples. It takes only a few weeks for us to produce 1 to 30 grams of purified monoclonal antibody from gene sequencing.
Sponsored Content Policy: News-Medical.net publishes articles and related content that may be derived from sources where we have existing commercial relationships, provided such content adds value to the core editorial ethos of News-Medical.Net which is to educate and inform site visitors interested in medical research, science, medical devices and treatments.