Variety of tetrazole derivatives, including antihypertensive pharmaceutical agent Irbesartan, are produced using alkali metal azides (MeN3). Azides or hydrazoic acids (HN3) are extremely lethal when inhaled or consumed. Therefore, industries that use or manufacture azide need to implement stringent control measures.
Spectrophotometry, gas chromatography, and capillary electrophoresis are some of the widely used analytical techniques for determination of azide ions. However, these methods have their own drawbacks. For instance, gas chromatography and capillary electrophoresis involve elaborate derivitization steps, while lack of sensitivity is the shortcoming in the case of the spectrophotometric method.
Direct-injection ion chromatography (IC) is the analysis method prescribed by the US Pharmacopeia. In this method, a transfer solution containing an IC eluent and appropriate organic solvents is used for extraction of the pharmaceutical from the analytical column. The IC analysis method is not only laborious and time intensive, but also suffers from the inability to be automated.
A simple, fast, and accurate ion chromatographic method equipped with suppressed conductivity detection is described in this article. In conjunction with previous matrix elimination, this improved IC method eliminates the drawbacks pertaining to selectivity, sensitivity and analysis time.
Instrumentation
The precise IC method was used for the analysis of azide ions in Irbesartan to demonstrate its applicability in the determination of trace amounts of inorganic impurities in pharmaceuticals. The instrumentation setup (Figure 1) used for the IC analysis consisted of the following instruments:
- Professional IC 850 Anion – MCS – Prep 2
- Professional Sample Processor 858 – Pump – Injector
- Metrosep A Trap 1
- Metrosep A PCC 1
- Metrosep A Supp 10 – 250
- Metrosep RP Guard
The trace concentrations of toxic azides up to the sub-ppb range in pharmaceutical formulations can be precisely detected using isocratic IC method equipped with the Metrohm Inline Matrix Elimination and suppressed conductivity detection.

Figure 1. Experimental setup for IC analysis
Matrix Elimination
The presence of interfering Irbesartan components in pharmaceutical products increases the complexity of ultratrace azide analysis. In order to overcome the influence of such ingredients, a transfer solution is used for rinsing an anion pre-concentration column for 6 minutes after pre-concentrating the azide in the column but before the chromatographic separation step. The pre-concentration column holds back the azide anions, while the transfer solution composed of 70% methanol and 30% ultrapure water removes the interfering pharmaceutical matrix. Typical problems caused by the interfering excipients, such as nitrate anions, are eliminated by the analytical setup through the generation of a well-defined azide peak. The process flow is shown in Figure 2.
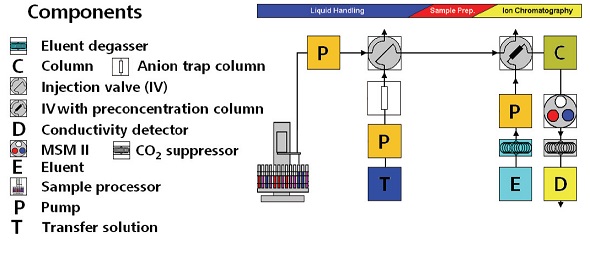
Figure 2. Process flow of the improved IC method
The chromatographic conditions are the same for all chromatograms illustrated in this article:
|
Column
|
Metrosep A Supp 10 – 250
|
|
Column temperature
|
60°C
|
|
Eluent
|
5mmol/L sodium carbonate and 5 mmol/L sodium hydrogen carbonate
|
|
Transfer solution
|
Methanol/water: 70/30
|
|
Rinsing time
|
6 minutes
|
|
Flow
|
1.0mL/min
|
|
Loop
|
1000μL
|
Results
The separation performance is illustrated in Figure 3. As shown in Figure 3, the azide peak can be clearly distinguished from the peaks of the excipient anions.
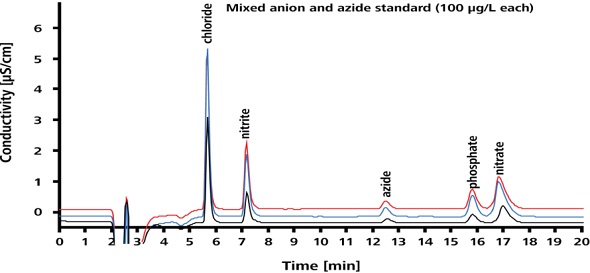
Figure 3. Separation performance
Linearity
Figure 4 shows sodium azide standards in sample matrix, and Figure 5 shows the azide calibration curve. Over the 5-80ppb range, calibration based on azide standards is linear, yielding a coefficient of determination of 0.9995.
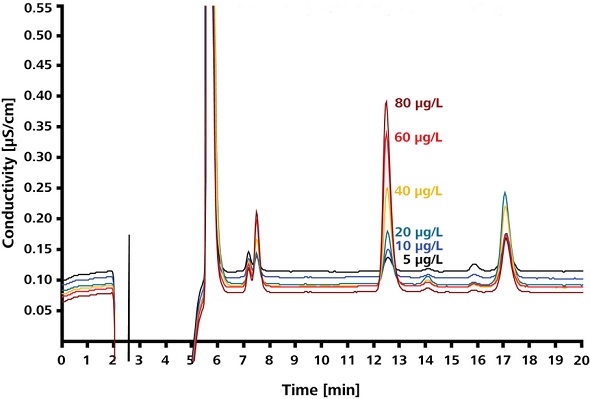
Figure 4. Sodium azide standards in sample matrix.
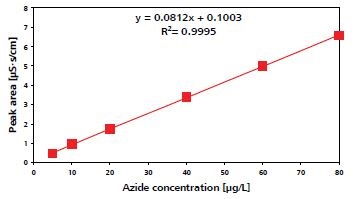
Figure 5. Azide calibration curve.
Precision and Spike Recoveries at LOD/LOQ
Limit of quantitation (LOQ) of azide in Irbesartan and limit of detection (LOD) of azide in Irbesartan were found to be 30μg/L and 5μg/L, respectively. The spike recoveries and precision at the LOQ and LOD are shown in Figures 6 and 7, respectively. The corresponding results are summarized in Table 1. The relative standard deviations (RSD) for peak area, peak height and retention time are less than 3.9%.
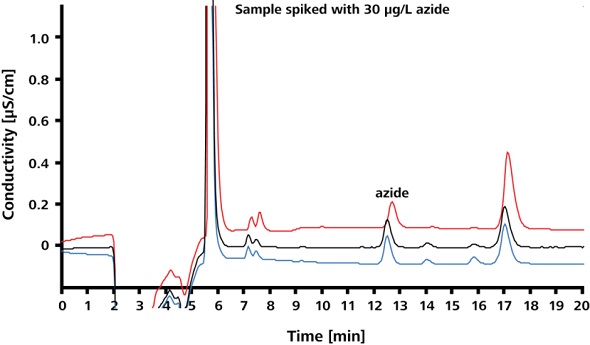
Figure 6. Spike recoveries at LOQ
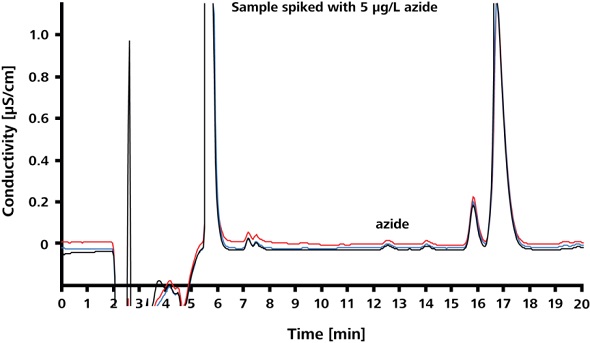
Figure 7. Spike recoveries at LOD
Table 1. Statistical Derivations based on analysis
|
5μg/L spike
|
30μg/L spike
|
|
|
|
Area [μS·s
/cm]
|
Height [μS
/cm]
|
RT [min]
|
Recovery [%]
|
Area [μS·s
/cm]
|
Height [μS
/cm]
|
RT [min]
|
Recovery [%]
|
|
| |
|
1
|
0.41343
|
0.02094
|
12.5624
|
99.58
|
2.57938
|
0.12448
|
12.7078
|
103.26
|
|
|
2
|
0.42990
|
0.02070
|
12.5604
|
103.54
|
2.57259
|
0.13384
|
12.5214
|
103.33
|
|
|
3
|
0.42350
|
0.02076
|
12.5627
|
102.00
|
2.57423
|
0.13221
|
12.5228
|
103.54
|
|
|
Mean
|
0.42228
|
0.02080
|
12.5618
|
101.71
|
2.57540
|
0.13018
|
12.584
|
103.38
|
|
|
SD
|
0.0083
|
0.0001
|
0.0013
|
1.9962
|
0.0035
|
0.0050
|
0.1072
|
0.1425
|
|
|
RSD
|
1.96%
|
0.60%
|
0.01%
|
1.96%
|
0.14%
|
3.84%
|
0.85%
|
0.14%
|
|
Method Robustness
The robustness of the transfer solution was tested by varying the column oven temperature and the transfer solution concentration, as shown in Figures 8 and 9, respectively. The RSDs obtained in terms of peak area were less than 2.8% and 3.1%, respectively.
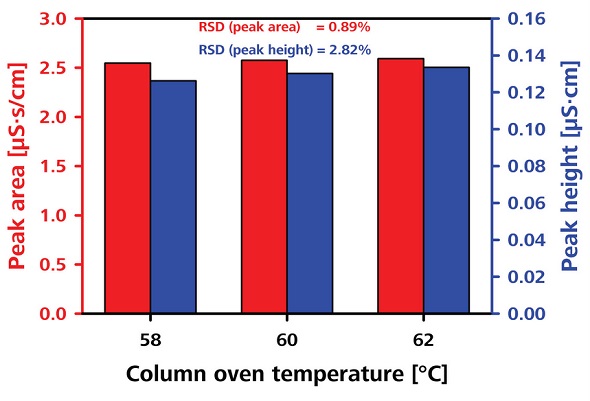
Figure 8. Testing the robustness by varying the column oven temperature.
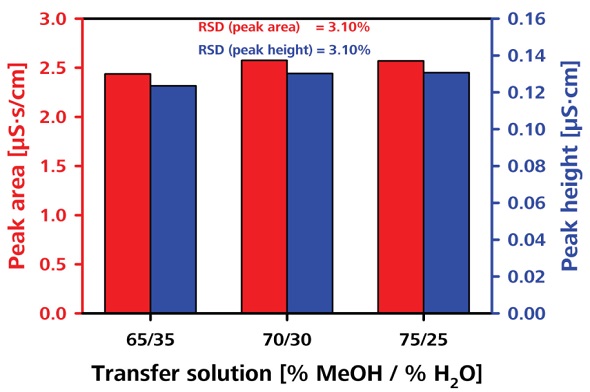
Figure 9. Testing the robustness by varying the composition of transfer solution
Validation
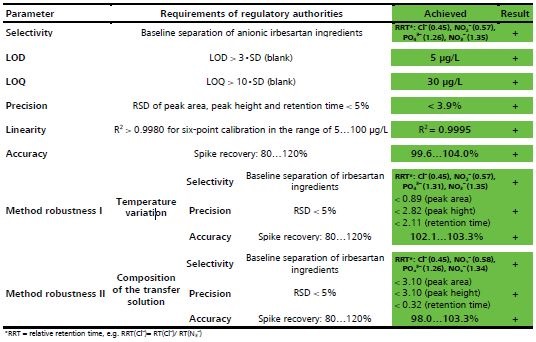
The various regulatory requirements laid down by authorities for different parameters are listed in Table 2.
Table 2. Regulatory requirements of analysis parameters
Acknowledgements
Produced from materials authored by N. Harihara Subramanian1 and A. Wille2 from:
1Micro Devices Metrohm Ltd., 1st Avenue, Indira Nagar, Adyar, Chennai 600020, India
2Metrohm AG, International Headquarters, Herisau, Switzerland.
About Metrohm
At Metrohm is one of the world’s most trusted manufacturers of high-precision instruments for chemical analysis. Metrohm was founded in 1943 by engineer Bertold Suhner in Herisau, Switzerland. Today, Metrohm is represented in 120 countries by subsidiaries and exclusive distributors. The global Metrohm Group also includes the Dutch companies Metrohm Applikon and Metrohm Autolab, manufacturers of online analyzers and instruments for electrochemical research, respectively. Recently, the Metrohm Group was joined by Metrohm Raman, a leading manufacturer of handheld Raman spectrometers.
Metrohm is the global market leader in analytical instruments for titration. Instruments for ion chromatography, voltammetry, conductivity, and stability measurement make the Metrohm portfolio for ion analysis complete. Instruments for Near-infrared and Raman spectroscopy are another, strongly growing segment of the Metrohm portfolio.
Metrohm is a problem solver, both in the laboratory and within the industrial process. To this end, the company offers their customers complete solutions, including dedicated analytical instrumentation as well as comprehensive application know-how. More than 30% of the company’s employees at the Metrohm international headquarters in Herisau work in R&D.
Metrohm has been owned 100% by the non-profit Metrohm Foundation since 1982. The Metrohm Foundation, which does not exert any influence on the company’s business operations, sponsors gifted students in the natural sciences, supports charitable and philanthropic purposes and, above all, ensures the independence of the company.
Sponsored Content Policy: News-Medical.net publishes articles and related content that may be derived from sources where we have existing commercial relationships, provided such content adds value to the core editorial ethos of News-Medical.Net which is to educate and inform site visitors interested in medical research, science, medical devices and treatments.