Throughout the world, confirmed cases of COVID-19 now surpass 6 million, scientists are driving forward with efforts to advance vaccines and treatments to curb the pandemic and mitigate the damage caused by the virus.
Already, globally there are hundreds of projects focused on the development of a vaccine for COVID-19. As of May 31st, eight candidate vaccines were entered into clinical trials.1 However, the reality is more likely that a vaccine will not be readily available until next year.
However, in contrast, the development cycle of neutralizing antibodies is comparatively short. Leading many experts to believe that the efforts of the companies advancing antibody drugs are considerably important in the fight against the disease. When compared to vaccines or antiviral drugs, what makes antibodies so unique is their capacity to treat and protect against viral infections. With the benefit of high specificity and being easily scaled-up, much attention is being paid to developing a neutralizing antibody around the world.
Recently, Sunney Xie’s group presented their work about the screening of the neutralizing antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 in the journal, Cell. This article will summarize the innovative approach in their work.
Xie’s group hypothesized that enriched B cell clonotypes would present a higher likelihood to yield high-affinity SARS-CoV-2 binding and neutralizing antibodies. Thus, they initially carried-out a high-throughput sequencing of single B cells from convalescent patients. However, they only received one RBD-binding mAb with a weak virus neutralization ability during their first attempt. To improve the method, they utilized RBD and S protein pre-coupled magnetic beads to enhance the RBD binding B cells (Fig. 1). Thereafter, a total of 169 ideal candidates were selected based on a set of specific criteria. Following further screening using ELISA and SPR, 149 S-binding mAbs were detected, among which 70 mAbs bind to the RBD.
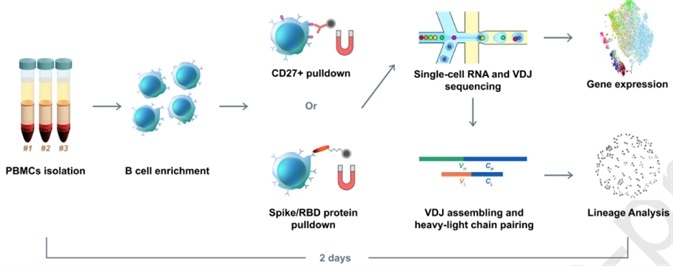
Figure 1. Illustration of RBD binding B cells enrichment using RBD and S protein pre-coupled magnetic beads.
Furthermore, they screened all ELISA-positive mAbs for neutralizing capabilities using a SARS-CoV-2 pseudovirus system and discovered that through all the neutralizing mAbs, seven of them displayed effective neutralization capability with an IC50 lower than 0.05 μg/mL (Fig. 2A). To authenticate their neutralization capacities against the authentic virus, they carried out the plaque reduction neutralization test and determined that BD-368-2 showed the greatest potency against the authentic virus with an IC50 of 15 ng/mL (Fig. 2B).
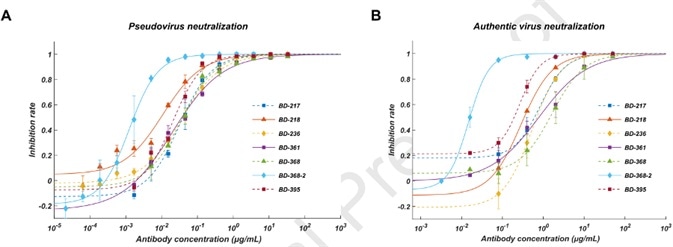
Figure 2. A. Pseudovirus neutralization result; B. Authentic virus neutralization result.
To assess whether the neutralizing mAbs identified could function as a therapeutic intervention and prophylactic protection against SARS-COV-2 in vivo, they assayed the neutralization efficacy of BD-368-2 on hACE2 transgenic mice contaminated with SARS-CoV-2. It was found that BD-368-2 displayed high therapeutic and prophylactic potency in vivo (Fig. 3).
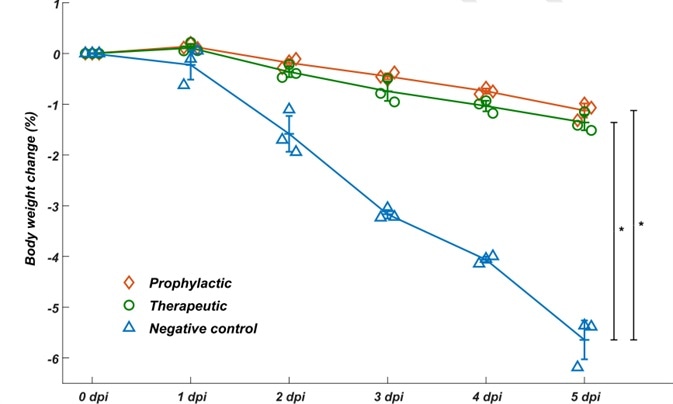
Figure 3. BD-368-2 exhibits high therapeutic and prophylactic efficacy in vivo.
According to the Cry-EM results illustrated below (Fig. 4), it can be seen that the S ectodomain adopts an asymmetric form with the RBD in one protomer (mol A) assumes an “up” position, while the other two RBDs (mol B and C) adopt “down” positions. Here, in this 3D reconstruction, a single BD23-Fab is found per S trimer, and it binds the “down” RBD in protomer B. Only the heavy chain variable domain of BD-23 is involved in binding to the RBD.
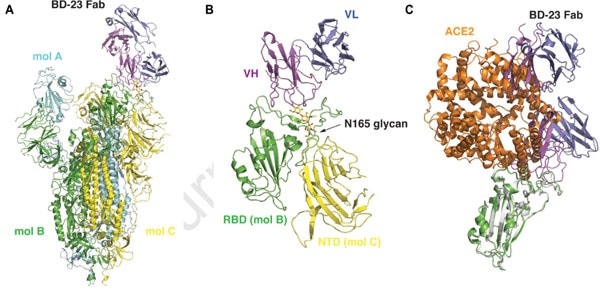
Figure 4. 3D reconstruction results of Cryo-EM.
Bioinformatic-based selection approaches were promoted further in the study and it was discovered that mAbs neutralizing antibodies sharing a CDR3H structure with great similarity to SARS-CoV demonstrated a high percentage of high neutralization potency for SARS-CoV-2. Otherwise stated as structure analysis can help improve the efficiency of the neutralizing antibody screening.
A key focus of this study is the utilization of the RBD and S protein pre-coupled magnetic beads to enrich the B cell clonotypes. Stating in a recent interview, Sunney Xie, the corresponding author of the paper featured in Cell, the pre-coupled magnetic beads can facilitate an increase of the efficiency of B cell enrichment by 20-fold.3
Closing the gap in the market, ACROBiosystems has advanced high-grade S1 protein and RBD protein pre-coupled magnetic beads. These pre-coupled magnetic beads will offer excellent benefits with reduced non-specific binding and validated protocols. This ready-made product could save significant time and eventually accelerate therapeutic antibody development.
Quantification of the pre-coupled RBD protein
Static adsorption experiments demonstrate that RBD protein-coupled magnetic beads can effectively capture the anti-SARS-CoV-2 S1 antibody, and the RBD load is higher than 40μg / mg magnetic beads.
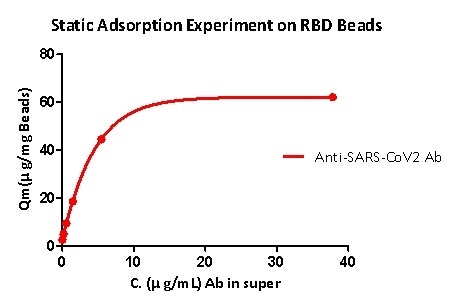
Figure 5. Static adsorption experiment on RBD beads.
Binding test of RBD pre-couple magnetic beads
Rigorous QC tests were performed to these pre-coupled beads. The short process is shown below: 0.1 mg beads were introduced to a tube. The supernatant was extracted after washing. 100 μL of the antibody or ACE2 protein (10 μg / mL ~ 0.039 μg / mL) was then added to the beads for incubation totaling 1-hour. A fluorescent-labeled secondary antibody was utilized for detection.
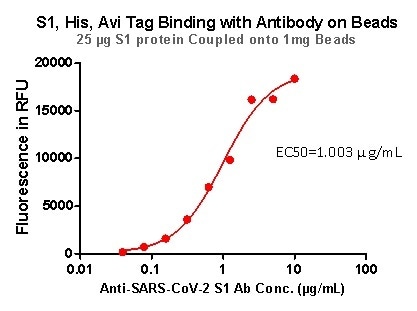
Figure 6. S1,His, Avi Tag Binding with Antibody on beads.
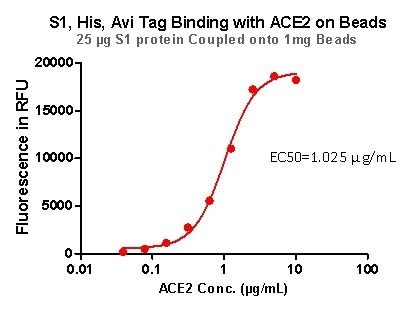
Figure 7. S1,His, Avi Tag Binding with ACE2 on Beads.
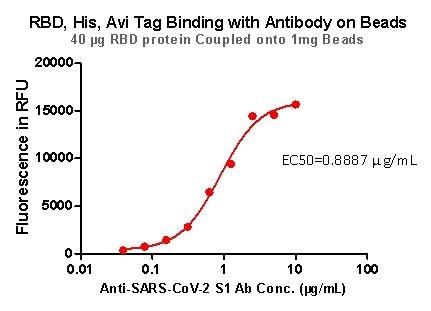
Figure 8. RBD,His, Avi Tag Binding with Antibody on beads.
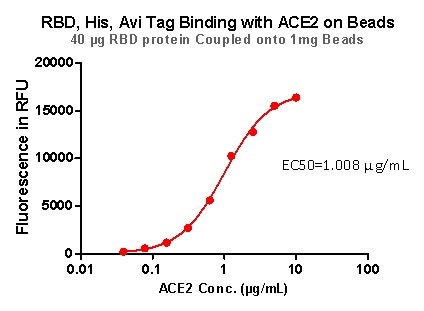
Figure 9. RBD,His, Avi Tag Binding with ACE2 on beads.
Pre-coupled magnetic beads can be employed for sample enrichment, immunocapture, and screening as well as biopanning. The quality of both the microsphere and the coupled protein is what is important to the performance of the pre-coupled beads product. ACROBiosystems is dedicated to improving and developing enhanced, high-grade products for the pharmaceutical industry.
Product list.

References and Further Reading
- https://www.raps.org/news-and-articles/news-articles/2020/3/covid-19-vaccine-tracker
- Cao, Y., et al., Potent neutralizing antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 identified by high-through put single-cell sequencing of convalescent patients’ B cells, Cell (2020), doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2020.05.025.
- https://finance.sina.com.cn/wm/2020-05-21/doc-iirczymk2863827.shtml?cre=tianyi&mod=pcpager_focus&loc=1&r=9&rfunc=61&tj=none&tr=9
About ACROBiosystems
ACROBiosystems is a cornerstone enterprise of the pharmaceutical and biotechnology industries. Their mission is to help overcome challenges with innovative tools and solutions from discovery to the clinic. They supply life science tools designed to be used in discovery research and scalable to the clinical phase and beyond. By consistently adapting to new regulatory challenges and guidelines, ACROBiosystems delivers solutions, whether it comes through recombinant proteins, antibodies, assay kits, GMP-grade reagents, or custom services. ACROBiosystems empower scientists and engineers dedicated towards innovation to simplify and accelerate the development of new, better, and more affordable medicine.
Sponsored Content Policy: News-Medical.net publishes articles and related content that may be derived from sources where we have existing commercial relationships, provided such content adds value to the core editorial ethos of News-Medical.Net which is to educate and inform site visitors interested in medical research, science, medical devices and treatments.