What is erythropoietin?
Erythropoietin (EPO) is a 30.4 kDa glycoprotein comprised of one 165 amino acid residues chain with four glycosylation locations (Figure 1). The hormone is produced naturally in the kidneys, stimulating red blood cell creation.
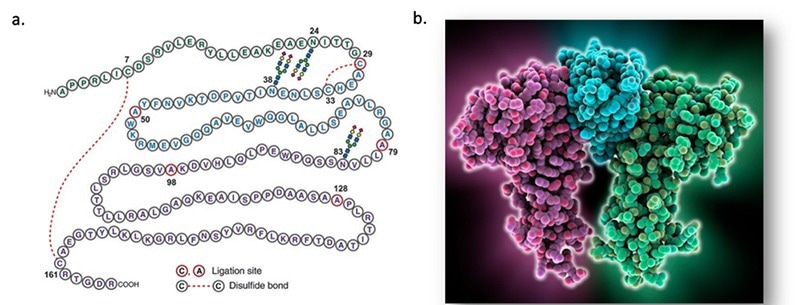
Figure 1. The structure of human EPO. a, the primary structure of EPO (ref 1 )(https://doi: 10.1126/sciadv.1500678); b, the 3D structure of EPO.
What are LNP-mediated mRNA drugs?
LNP-mediated mRNA drugs are therapeutic agents utilizing lipid nanoparticle (LNP) technology, delivering modified messenger RNA (mRNA) into cells. The innovation received significant notice in the biopharmaceutics field because of its adaptability in gene delivery, including:
- Vaccines: LNP-mediated mRNA technology has successfully developed mRNA vaccines like the Pfizer-BioNTech and Moderna COVID-19 vaccines. These vaccines utilize synthetic mRNA to direct cells to build a viral spike protein that instigates an immune response, resulting in extended protection from the virus.
- Gene Therapy: LNP-mediated mRNA delivers therapeutic gene-editing molecules that repair genetic deficiencies or encourage the creation of specified proteins.
- Protein Replacement Therapy: LNP-mediated mRNA drugs direct cells to replace missing or insufficient proteins. This allows medical intervention for some genetic disorders with misfolded protein creation or non-expressing genes.
What role does Human EPO play in LNP-mediated mRNA drug discovery?
LNPs are carriers for mRNAs in LNP-mediated drug development, keeping them from degrading and supporting ingress into targeted cells.
The lipid coating permits the LNPs to join with the cell membrane and release the mRNA into the cytoplasm.
Evaluating LNP-mediated mRNA delivery effectiveness and supposed pharmacologic effects of drugs in vivo / in vitro, the utilization of human EPO (hEPO) -encoding mRNA is necessary (Figure 2).
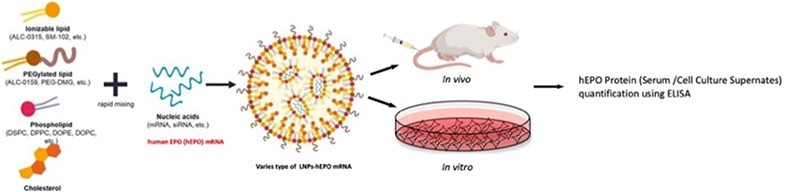
Figure 2. The mRNA delivery efficacy and pharmacology evaluation of mRNA-LNPs by modified mRNA encoding the protein for human erythropoietin. Image Credit: ACROBiosystems
EPO is the perfect molecule for evaluating mRNA delivery from LNPs. Researchers utilized LNPs (iLP171) filled with several quantities of modified hEPO-mRNA to transfect Huh7 cells and study the protein expression of mRNA-LNPs in vitro.
ELISA evaluates EPO produced by the cells to calculate the hEPO expression at specified time points. The results indicated that hEPO would be efficiently expressed by Huh7 cells in a dose and time-dependent manner (Figure 3).
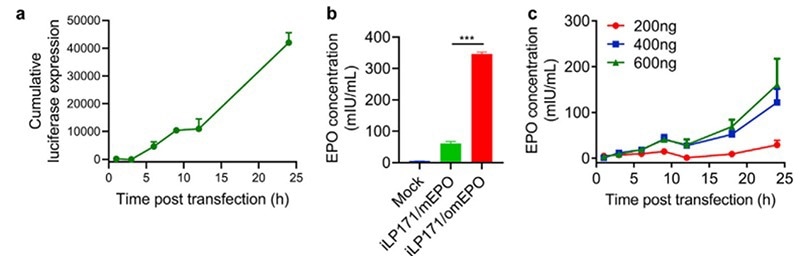
Figure 3. In vitro protein expression mediated by iLP171/mRNA. (ref 2 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bioactmat.2020.07.003)
In another study, researchers assessed the effectiveness of various lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) in delivering mRNA encoding a therapeutic protein in vivo. Mice were given separate types of LNPs with modified hEPO-mRNA.
Keeping to a designated timeframe, the concentration of hEPO in mouse serum was evaluated with the ELISA method (Figure 4). hEPO creation after the intravenous administration of 20% DODAP liver SORT LNPs peaked at six hours and was sustained for more than one week (ref 3).
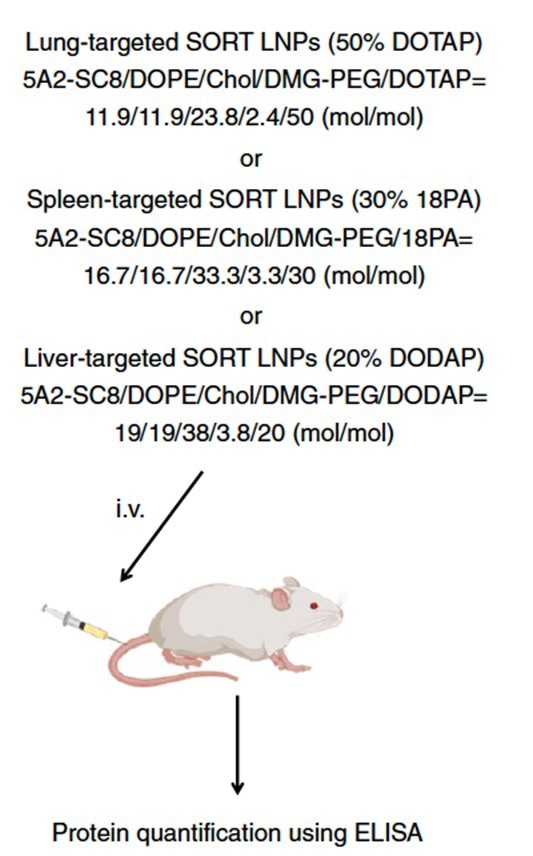
Figure 4. Scheme for mRNA delivery of secreted proteins in vivo. (ref 3 https://doi.org/10.1038/s41565-020-0669-6)
This allowed the assessment of mRNA transcription and protein expression contingent on LNPs in vivo but also included in vitro settings, using ELISA assays to calculate hEPO levels in cell supernatant, serum, and plasma.
The consistent and stable character of in vivo and in vitro Human EPO makes it an important secreted protein for evaluating mRNA delivery and the supposed pharmacologic effects of LNP-mediated mRNA drugs.
In addition, in rat and monkey species, the modified mRNA encoding hEPO had constant and reliable pharmacologic and toxicologic effects. Pharmacokinetic analysis completed after the first dose exhibited measured hEPO levels at the maximum six hours after the intravenous infusion and more than 100-fold the expected effective exposure (17.6 ng/ml) at the highest dose tested (ref 4 journals.sagepub.com/doi/10.1177/0300985817738095).
The studies reveal that EPO is a vital benchmark for the evaluation of the mRNA delivery effectiveness and pharmacokinetics profile using LNP-based delivery of therapeutic agents.
About ACROBiosystems
ACROBiosystems is a cornerstone enterprise of the pharmaceutical and biotechnology industries. Their mission is to help overcome challenges with innovative tools and solutions from discovery to the clinic. They supply life science tools designed to be used in discovery research and scalable to the clinical phase and beyond. By consistently adapting to new regulatory challenges and guidelines, ACROBiosystems delivers solutions, whether it comes through recombinant proteins, antibodies, assay kits, GMP-grade reagents, or custom services. ACROBiosystems empower scientists and engineers dedicated towards innovation to simplify and accelerate the development of new, better, and more affordable medicine.
Sponsored Content Policy: News-Medical.net publishes articles and related content that may be derived from sources where we have existing commercial relationships, provided such content adds value to the core editorial ethos of News-Medical.Net which is to educate and inform site visitors interested in medical research, science, medical devices and treatments.