T cell activation plays a key role in the immune response. Its activation, proliferation and differentiation necessitate dual stimulation signals. The initial signal is made up of a combination of TCR/CD3 and antigen-presenting cell (APCs) surface-specific MHC molecule antigen-peptide complexes.
The next signal is a non-specific co-stimulatory signal, which is triggered by the interaction of several pairs of co-stimulatory molecules on the exterior of APCs and the relative receptors of T cells (such as CD28, CTLA-4 and CD80, CD86, 4-1BB and 4-1BBL, CD40 and CD40L, PD-1 and PD-L1, etc.).
CD28 is considered to be the main co-stimulatory molecule, and the second signal has the ability to activate T cells, secrete cytokines, and express cytokine receptors. Studies have demonstrated that in vitro activation and proliferation of T cells have a critical role in research fields such as cell therapy and immune checkpoints.
Cell therapy
Currently, there is an emphatic focus on CAR-T and TCR-T therapy regarding research into adoptive immune cell therapy. Whether it is CAR-T or TCR-T cell culture in vitro, T cells must be activated prior to conducting any subsequent operations.
Therefore, it is crucial that a suitable T cell activation reagent is selected as a raw material when developing cell therapy drugs.
At present, the primary in vitro activation methods of T cells on the market are:
- Application of soluble antibodies, such as Anti CD3/CD28 antibodies, in combination with cytokines such as IL-2 for stimulation;
- Using antibodies attached to solid-phase carriers, such as CD3/CD28 antibody-coupled magnetic beads, the suitable T cell activation method can be chosen based on the strength of the activation and subsequent residual detection considerations.
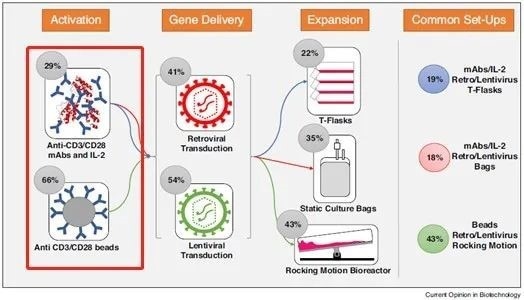
Figure 1. Activation of T cells during cell therapy development. Image Credit: ACROBiosystems
Immune checkpoint research
Currently, immune checkpoint drugs are under the spotlight in tumor immunotherapy due to their exceptional clinical efficacy, specifically their antibody targeting immune checkpoints, a key area in immunotherapy: a factor that has emerged at the forefront of the competition among pharmaceutical giants.
The main areas of antibody development are not just any functional effects, but also activity assays in vitro play a key role as they offer early data support for functional in vivo. Presently, the in vitro activity research methods for immune checkpoint antibodies predominantly focus on the activation activity of T cells.
For instance, PBMC culture plates can be coated with CD3 antibodies, and CD28 soluble antibodies can be introduced to the supernatant to activate T cells or by CD3 /CD28 antibody paired with magnetic beads to activate.
Subsequently, the content of cytokines in the culture supernatant, which contained the immune checkpoint drug, was identified to reflect the activation of the drug on T cells.
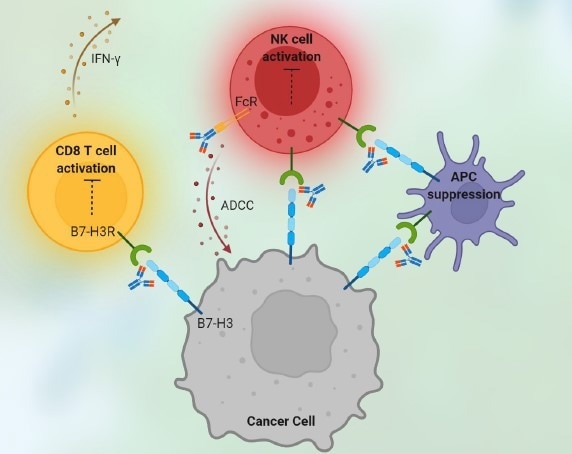
Figure 2. Immune checkpoint drugs killing tumor cells. Image Credit: ACROBiosystems
Recommended products
Anti-CD3/CD28 antibody-coupled magnetic beads
- 5.5 μm size, can better simulate APC and stimulate T cells
- Strong magnetism, simple separation, magnetic beads easy to separate
- Ultra low endotoxin (< 2 EU/mg), no T Cell damage
- Validated by cell-based assay, it can effectively activate and expand T cells
Cytokines ELISA Kits
- Both RUO and ClinMax versions are available to meet the demands of R&D and clinical trials
- Kit standards are calibrated by WHO standard NIBSC/WHO (87/586)
- Low matrix interference tested by cells culture medium and real samples of serum
- Strictly controlled sensitivity, specificity, accuracy, linearity and inter-/intra-assay precision
Immune checkpoint proteins
- High batch to batch consistency by strict QC tested
- High bioactivity validated by ELISA/SPR/FACS, etc.
- High purity validated by MALS or HPLC
T cell culture
T cells are completely activated by the first and second signal stimulation, which are contingent on a range of various cytokines (IL-1, IL-2, IL-4, IL-6, IL-10, IL-12, IL-15 and IFN-γ, etc.) for further proliferation and activation.
On the other hand, activated T cells are not able to proliferate and differentiate, which results in apoptosis. Therefore, it is important that media supplements such as IL-15, IL-7, and IL-21 and other cytokines are introduced as reagents for the proliferation and differentiation of T\NK immune cells.
Both the FDA and CDE have appropriate regulations when using these crucial materials. The FDA, CMC advises the use of FDA-approved or clinical-grade materials.
For Chinese Pharmacopoeia regulations, preference should be given to using low-risk materials, including GMP grade materials, rather than non-GMP grade materials. Therefore, safe, effective, and compliant cytokines are vital for the success of R&D applications and processes of immune cell therapy drugs.
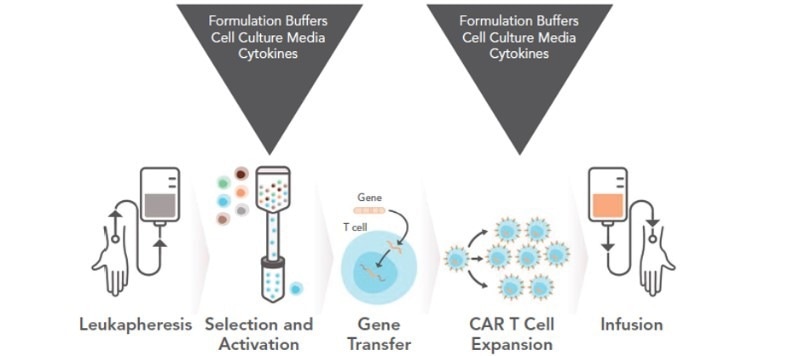
Figure 3. The development of CAR-T requires cytokines and other culture materials. Image Credit: ACROBiosystems
Recommended products
GMP-grade Cytokines such as IL-15, IL-7, IL-21
- Comprehensive regulatory support files
- Exceptional safety profile (tested for sterility, mycoplasma, endotoxin, and residual impurities)
- High stability and batch-to-batch consistency
- Stringent quality control standards
Summarize
As a key immune cell, T cells have a central role in the development of immune cell therapy culture. With a wide range of T cell culture-related reagents on the market, ensuring the safe and compliant selection of the appropriate products is vital for drug development and regulatory approval.
To meet the demands of the market, ACROBiosystems has developed a range of related products for T cell activation and culture that have been released under stringent quality standards to expedite the drug development process.
Product list
Anti-CD3/CD28 Ab-coupled magnetic beads
Table 1. Source: ACROBiosystems
| Product |
Size |
Amount |
| Anti-CD3/CD28 Antibody-coupled Magnetic Beads (recommended for human T cell activation & expansion) |
2.5 mg |
2.5 × 107 beads |
| 10 mg |
1 × 108 beads |
GMP-grade Cytokines
Table 2. Source: ACROBiosystems
| Molecule |
Cat.No. |
Product description |
Preorder/Order |
| IL-15 |
GMP-L15H13 |
GMP Human IL-15 |
Order |
| IL-7 |
GMP-L07H24 |
GMP Human IL-7 |
Order |
| IL-21 |
GMP-L21H25 |
GMP Human IL-21 |
Preorder |
Cytokine ELISA Kit
Table 3. Source: ACROBiosystems
| Molecule |
Cat. No. |
Product Description |
Preorder/Order |
| IFN-γ |
CRS-A001 |
Human Interferon-γ(IFN-γ) ELISA Kit |
Preorder |
| IL-2 |
CRS-A003 |
Human Interleukin-2(IL-2) ELISA Kit coming soon |
Inquiry |
| IL-4 |
CRS-A004 |
Human Interleukin-4(IL-4) ELISA Kit coming soon |
Inquiry |
| IL-6 |
CRS-A005 |
Human Interleukin-6(IL-6) ELISA Kit coming soon |
Inquiry |
| IL-8 |
CRS-A007 |
Human Interleukin-8(IL-8) ELISA Kit coming soon |
Inquiry |
| IL-10 |
CRS-A008 |
Human Interleukin-10(IL-10) ELISA Kit coming soon |
Inquiry |
| IL-1beta |
CRS-A012 |
Human Interleukin-1beta(IL-1beta) ELISA Kit coming soon |
Inquiry |
| GM-CSF |
CRS-A013 |
Human Macrophage Colony Stimulating Factor 2(GM-CSF) ELISA Kit coming soon |
Inquiry |
Anti-CD3/CD28 antibody-coupled magnetic beads can effectively expand T cells and have a higher expansion ability than that of other competitors
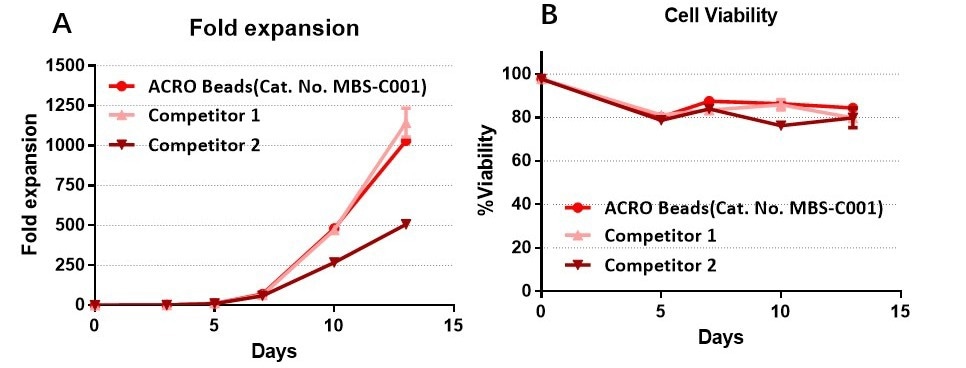
The purified human T cells were stimulated using Anti-CD3/CD28 Antibody-coupled Magnetic Beads (Cat. No. MBS-C001) and competitor’s beads respectively. Cells were expanded in T cell culture medium supplemented with 4 ng/mL of rhIL-2 Protein (Acrobiosystems, Cat. No. IL2-H4113). Activated Cells were expanded for up to 13 days (A) with high cell viability (B). Image Credit: ACROBiosystems
GMP human IL-15 (GMP-L15H13) has high batch-to-batch consistency
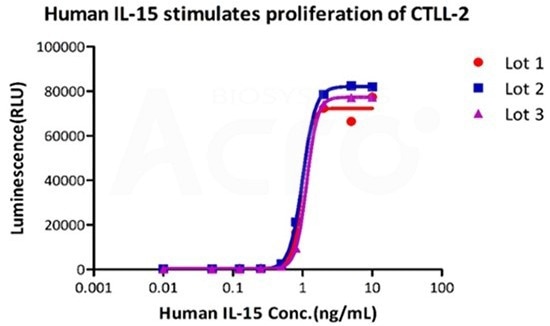
Image Credit: ACROBiosystems
References
- Kay, J.E., 1991. Mechanisms of T lymphocyte activation. Immunology Letters 29, 51 – 54
- Trickett A, Kwan YL. T cell stimulation and expansion using anti-CD3/CD28 beads. J Immunol Methods. 2003Apr 1;275(1-2):251-5.
- Kalos M, Levine BL, Porter DL, KatzS, Grupp SA, Bagg A, June CH: T cells with chimeric antigen receptors have potent antitumor effects and can establish memory in patients with advanced leukemia. Sci Transl Med 2011, 3:95ra73.
- Hollyman D, Stefanski J, PrzybylowskiM, Bartido S, Borquez- Ojeada O, Taylor C, Yeh R, Capacio V, Olszewska M, HoseyJ et al.: Manufacturing validation of biologically functional T cells targeted to CD19 antigen for autologous adoptive cell therapy. J Immunother 2009, 32:169-180.
- https://www.chromatographyonline.com/view/physicochemical-methods-for-vectors-and-ancillary-materials-in-cellular-and-gene-therapies
About ACROBiosystems
ACROBiosystems is a cornerstone enterprise of the pharmaceutical and biotechnology industries. Their mission is to help overcome challenges with innovative tools and solutions from discovery to the clinic. They supply life science tools designed to be used in discovery research and scalable to the clinical phase and beyond. By consistently adapting to new regulatory challenges and guidelines, ACROBiosystems delivers solutions, whether it comes through recombinant proteins, antibodies, assay kits, GMP-grade reagents, or custom services. ACROBiosystems empower scientists and engineers dedicated towards innovation to simplify and accelerate the development of new, better, and more affordable medicine.
Sponsored Content Policy: News-Medical.net publishes articles and related content that may be derived from sources where we have existing commercial relationships, provided such content adds value to the core editorial ethos of News-Medical.Net which is to educate and inform site visitors interested in medical research, science, medical devices and treatments.