Since the start of the outbreak, around 13 million people have been diagnosed with SARS-CoV-2 globally, and the pandemic is ongoing with little signs of easing. Developing a vaccine against COVID-19 could be the most effective weapon to overcome this disease. Based on the information held by the World Health Organization, there are 17 vaccines in the clinical stage worldwide.
On July 1st, 2020, Pfizer and BioNTech declared the Phase 1/2 results of their jointly developed mRNA vaccine against COVID-19 to be successful. Preliminary data provided an early signal that BNT162b1 targeting the RBD SARS-CoV-2 can generate neutralizing antibody responses in humans at or beyond the levels seen in convalescent sera, and it does so at comparatively low dose levels. More details concerning these results are available on the preprint website medRxiv.1
The mRNA vaccine, BNT162b1, targets and encodes the receptor-binding domain (RBD) of the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein, a crucial focus point of virus-neutralizing antibodies. By adding a Foldon trimerization motif to the end of the RBD sequence, researchers reassured the trimeric structure, which will greater improve the immunogenicity effect. An additional modification was supplemented to the mRNA sequence to improve the effectiveness of in vivo translation (Figure 1).

Figure 1. Molecule design of BNT162b1.
At the same time, a phase 1/2 clinical trial was performed in the United States and Europe. Around 45 randomly assigned participants aged between 18 and 55 were vaccinated. Of these, 12 participants per dose level (10 ug and 30 ug) were vaccinated on Day 1 and 21, and 12 participants received a 100 μg dose on Day 1. 9 of the participants received a placebo during the trial.
Strong immunogenicity was seen and noted after vaccination with BNT162b1. RBD-binding IgG concentrations were determined at 21 days subsequent to the first dose and considerably increased 7 days after the second dose initiated on Day 21.
Following the first dose, the RBD-binding IgG GMCs (10 µg dose recipients) were akin to those witnessed in a panel of 38 convalescent, human serology samples procured at least 14 days after PCR-confirmed following SARS-CoV-2 infection/COVID-19 asymptomatic donors. Dose 2 with 10 µg or 30 µg BNT162b1, the RBD-binding IgG GMCs had been about 8-fold to 50-fold that of the convalescent serum panel geometric mean concentrations (GMC).
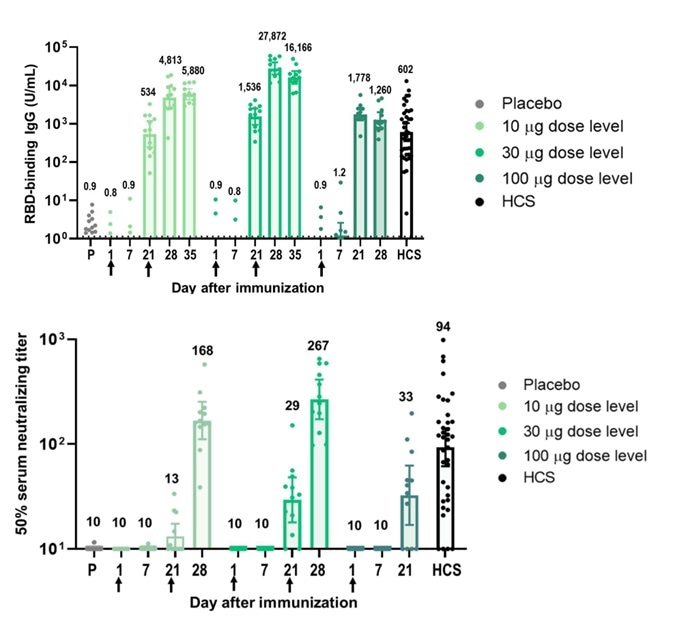
Figure 2. Immunogenicity of BNT162b1.
Negative and adverse effects included pain at the site of injection, headaches, fatigue, muscle pain, chills, joint pain, and fever. Most local reactions and systemic events peaked by the day following vaccination and resolved by Day 7.
This study had several restrictions imposed. While utilizing convalescent sera as a comparator, the type of immunity (T cells versus B cells or both) and the level of immunity required to defend against COVID19 are not known. Furthermore, an examination of available data did not evaluate the safety or immune responses beyond 2 weeks subsequent to the second administration of vaccine.
Both of these factors are important to accurately notify the public health use of this vaccine. Monitoring of all participants will continue and include the collection of serious/adverse events for 6 months, and COVID-19 infection/reinfection, and several additional immunogenicity measurements for up to two years.
If the existing studies are in effect successful and the vaccine candidate acquires regulatory approval, it is expected that the companies will manufacture up to 100 million doses by late 2020 and in excess of 1.2 billion doses by the end of 2021. In that case, BioNTech and Pfizer would collaborate to distribute the potential COVID-19 vaccine across the globe.
The biotinylated S protein RBD from ACROBiosystems (Cat.No. SPD-C82E9) was bound to streptavidin-coated Luminex microspheres in the RBD-binding IgG assay.
By engaging the unique Avitag™ technology, ACROBiosystems produced a series of SARS-CoV-2 related biotinylated recombinant proteins which are in high purity and activity and perform superior affinity. These biotinylated proteins are appropriate in different applications of SARS-CoV-2 vaccines, relative drugs, and diagnostic test development.
Additionally, ACROBiosystems has also developed a series of antibody titer assay kits to accelerate the drug and vaccine research and development.
References and Further Reading
- Mulligan et al., (2020). Phase 1/2 Study to Describe the Safety and Immunogenicity of a COVID-19 RNA Vaccine Candidate (BNT162b1) in Adults 18 to 55 Years of Age: Interim Report. medRxiv, doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.06.30.20142570
About ACROBiosystems
ACROBiosystems is a cornerstone enterprise of the pharmaceutical and biotechnology industries. Their mission is to help overcome challenges with innovative tools and solutions from discovery to the clinic. They supply life science tools designed to be used in discovery research and scalable to the clinical phase and beyond. By consistently adapting to new regulatory challenges and guidelines, ACROBiosystems delivers solutions, whether it comes through recombinant proteins, antibodies, assay kits, GMP-grade reagents, or custom services. ACROBiosystems empower scientists and engineers dedicated towards innovation to simplify and accelerate the development of new, better, and more affordable medicine.
Sponsored Content Policy: News-Medical.net publishes articles and related content that may be derived from sources where we have existing commercial relationships, provided such content adds value to the core editorial ethos of News-Medical.Net which is to educate and inform site visitors interested in medical research, science, medical devices and treatments.