Leading recombinant protein producer ACROBiosystems has produced an antibody product line called “mAb matrix” to aid in the development of target therapeutics, immunizations, and diagnostics.
The mAb matrix contains a variety of antibodies, such as antibodies against biological targets, biomarkers, receptors, cytokines antibodies (antibodies against interleukin and chemokines), viruses, antibodies against small-molecule inhibitors, antibodies for diagnostic purposes, and antibodies for process engineering, etc.
A family of "antibody matrix" for diagnostic and full-process approaches in biopharmaceutical R&D that help accelerate drug development and commercialization and offer the advantages of high specificity and sensitivity.

Image Credit: ACROBiosystems
TNF-α and signaling
The pleiotropic cytokine of the tumor necrosis factor superfamily with the most attention is TNF-α. TNF-α is a crucial cytokine in the innate immune response that aids in direct host defense against pathogens before the adaptive immune system is activated.
It is mainly generated in the search for common bacterial cell surface components of macrophage activated membrane-bound pattern recognition molecules (e.g. toll-like receptors).
Other pro-inflammatory cells, such as structural cells (i.e., fibroblasts, epithelial cells, and smooth muscle cells), monocytes, dendritic cells, B cells, CD4+ cells, neutrophils, mast cells, and eosinophils also generate TNF-α.
Initially, TNF-α is a physiologically active, membrane-anchored precursor protein (mTNF-α) of 26 KD, which TNF-α converting enzyme (TACE) then cleaves to produce a 17 KD free protein. These proteins interact with the widely expressed TNF-α receptors 1 and 2 to create biologically active homotrimers.
Without assimilating the complex, this receptor–ligand interaction causes intracellular signaling and the phosphorylation of IkBa, which activates the nuclear factor-kB (p50–p65) heterodimer and further engages with DNA chromatin structure to increase the transcription of pro-inflammatory genes like IL-1B, IL-6, IL-8, and TNF-α.
The extracellular domain of the TNF-α receptor is shed to counteract TNF- α’s activating action.
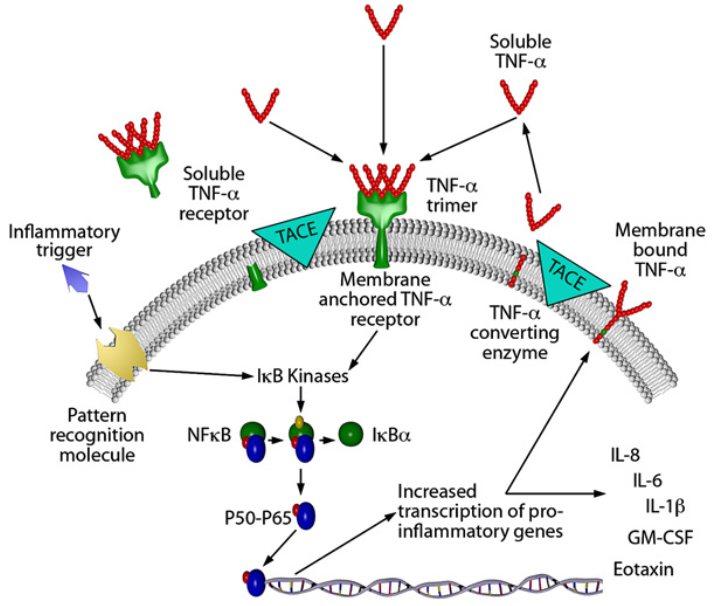
The biological mechanism and signal transduction of TNF-α. Image Credit: ACROBiosystems
Source: ACROBiosystems
| Molecule |
Cat. No. |
Species |
Product Description |
| TNF-alpha |
TNA-H4211 |
Human |
ActiveMax® Human TNF-alpha Protein, Tag Free, low endotoxin (active trimer) (MALS verified) |
| TNA-H5228 |
Human |
Human TNF-alpha Protein, His Tag (active trimer) (MALS verified) |
| TNA-H82E3 |
Human |
Biotinylated Human TNF-alpha Protein, His, Avitag™ (active trimer) (MALS verified) |
| TNA-H8211 |
Human |
Biotinylated Human TNF-alpha Protein, epitope tag free, ultra sensitivity (primary amine labeling) (active trimer) (MALS verified) |
| TNA-M82E9 |
Mouse |
Biotinylated Mouse TNF-alpha Protein, His, Avitag™ (active trimer) (MALS verified) |
| TNA-C52H3 |
Canine |
Canine TNF-alpha Protein, His Tag, active trimer (MALS verified) |
| TNFR1 |
TN1-H5222 |
Human |
Human TNFR1 / CD120a / TNFRSF1A Protein, His Tag |
| TN1-H5251 |
Human |
Human TNFR1 / CD120a / TNFRSF1A Protein, Fc Tag (MALS verified) |
| TNFR2 |
TN2-H5227 |
Human |
Human TNFR2 / CD120b / TNFRSF1B Protein, His Tag |
| TN2-H82E3 |
Human |
Biotinylated Human TNFR2 / CD120b / TNFRSF1B Protein, His, Avitag™ |
| TN2-M52H8 |
Mouse |
Mouse TNFR2 / CD120b / TNFRSF1B Protein, His Tag |
| TN2-C52H7 |
Cynomolgus / Rhesus macaque |
Cynomolgus / Rhesus macaque TNFR2 / CD120b / TNFRSF1B Protein, His Tag |
TNF-α and CRS
The production of various chemokines and cytokines is stimulated by TNF-α, a key pleiotropic mediator of both acute and chronic systemic inflammatory reactions. TNF-α also controls apoptosis and proliferation.
A variety of physiological functions, including antitumor responses, inflammation regulation, and immune system homeostasis, are also affected by it. One of the most significant cytokines that promote inflammation in the innate immune response is TNF-α.
Cytokine release storm (CRS) is primarily caused by the TNF-α signaling pathway, and TNF-α signaling dysregulation can cause CRS. Increased TNF-α may speed up viral infection, cause organ damage, and obstruct inflammatory cell death signaling pathways, which may be advantageous for COVID-19 patients or those with other infectious disorders and prevent tissue damage.
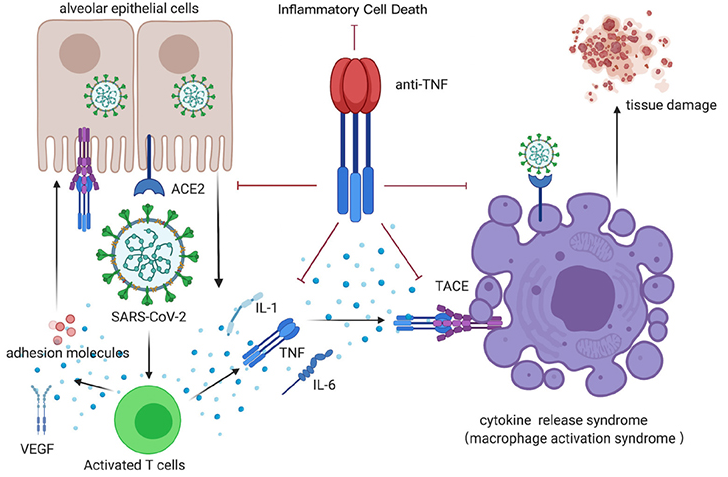
Anti-TNF-α therapy for CRS following COVID-19 infection. Image Credit: ACROBiosystems
The adoption of anti-TNF therapy could be constrained by its possible negative effects, according to certain studies. To reduce possible hazards associated with immunosuppression, it is crucial to differentiate between patients who have a bad prognosis and those who can recover on their own, as well as to discover the right treatment period for COVID-19 patients.
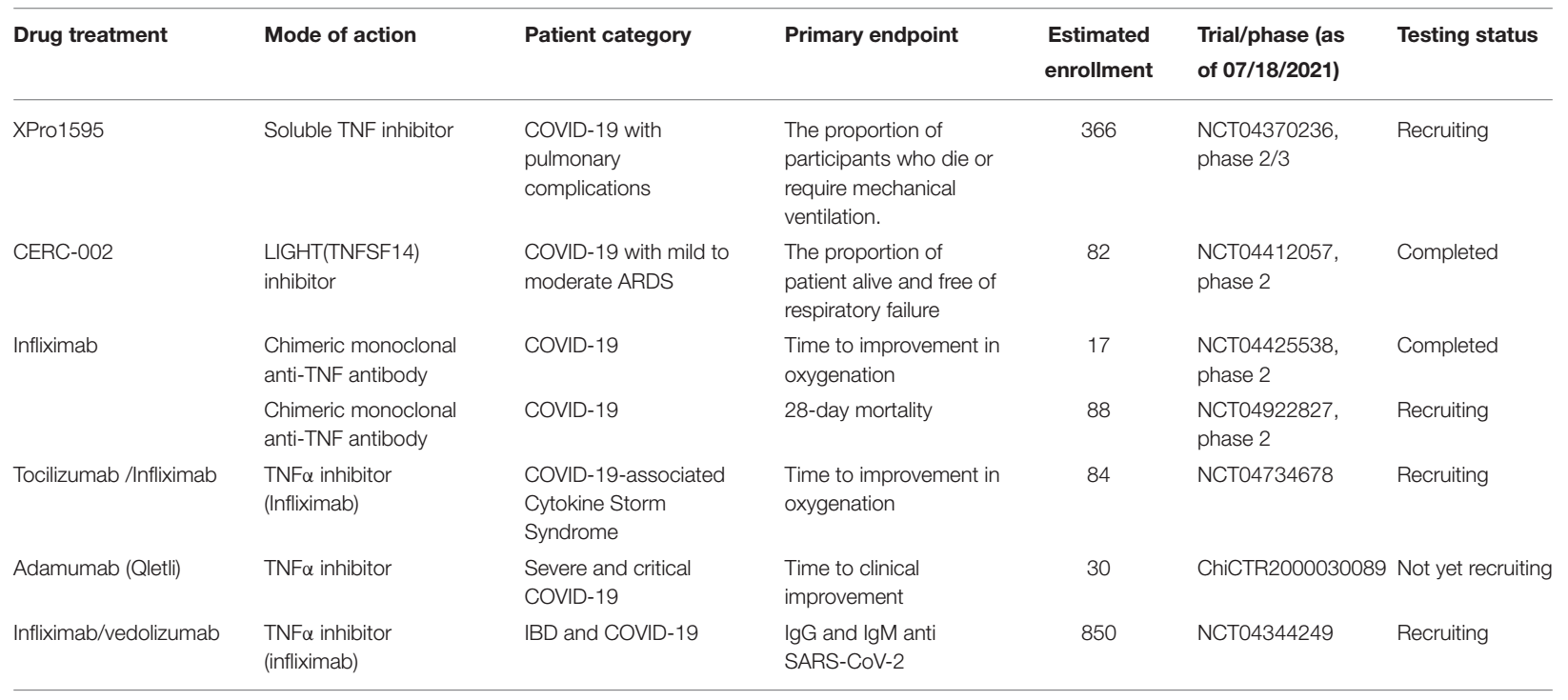
Drugs targeting TNF or its receptors in clinical studies of COVID-19 patients. Source: ACROBiosystems
TNF-α antibodies
TNF-α is a potent pro-inflammatory cytokine that, as previously noted, has pleiotropic effects on a variety of cell types. It also plays a significant role in the development of chronic inflammatory conditions like rheumatoid arthritis (RA).
Numerous anti-TNF medicines have been effective in treating chronic inflammatory conditions like psoriasis, ankylosing spondylitis (AS), Crohn’s disease, and RA. Varied anti-TNF medicines could have various effects on transmembrane TNF-α cells, which might account for differences in clinical effectiveness.
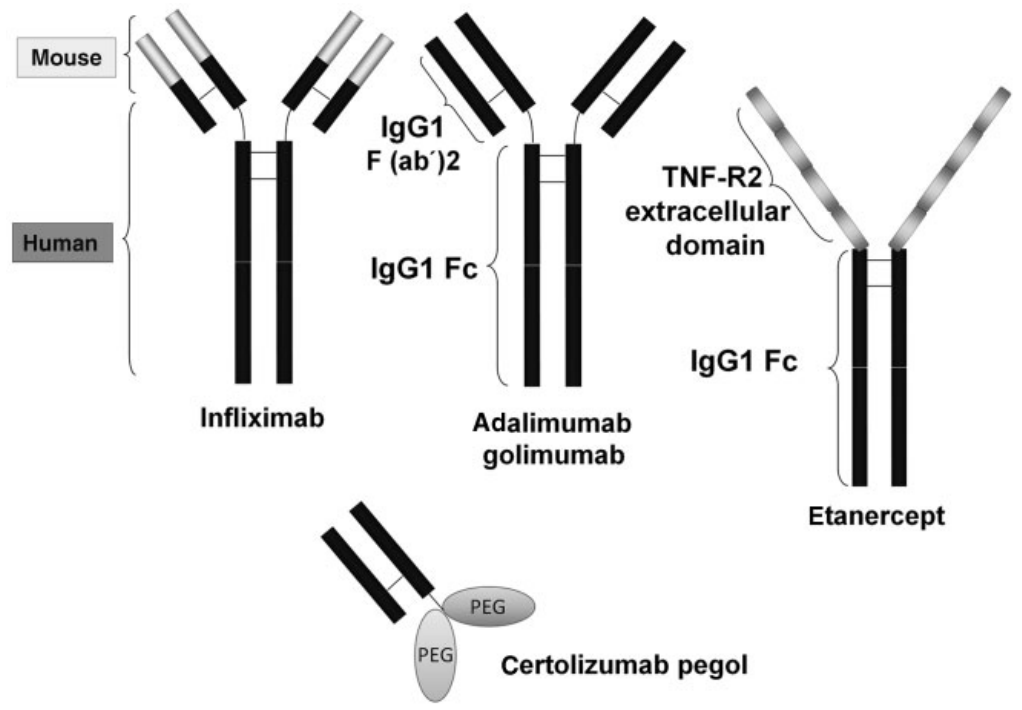
Different anti-TNF-α monoclonal antibodies. Image Credit: ACROBiosystems
Monoclonal antibodies against human TNF-α are what Infliximab, Adalimumab, and Golimumab are structurally known as. A monoclonal anti-TNF-α antibody with a murine variable region and a human variable region IgG1 constant region is called infliximab. Monoclonal anti-TNF-α antibodies with complete humanization include adalimumab and golimumab.
Human TNF-R2 (p75 TNF receptor) and human IgG1’s CH2 and CH3 domains make up the two extracellular components of etanercept. The hinge region of the IgG1 mAb anti-TNF-α Fab fragment, certolizumab, is covalently connected to two 20 KDa polyethylene glycol cross-linked chains and is devoid of the Fc fragment.
Infliximab and Etanercept have distinct binding characteristics; the former can bind soluble TNF-α in both monomeric and trimeric forms, whereas the latter can only bind the trimer. Etanercept creates somewhat unstable complexes with soluble TNF-α, whereas Infliximab generates stable complexes.
Two TNF-α molecules can attach to one Infliximab molecule, while the TNF-α homotrimer can bind to three Infliximab molecules. Etanercept, on the other hand, is believed to form a 1:1 complex with TNF-α trimers.
Two TNF-α antibodies produced by two distinct clones have been made available by ACROBiosystems:
- Human TNF-alpha Protein, His Tag (active trimer) (MALS confirmed) is the immunogen (Cat. No. TNA-H5228)
- TNF-α antibody can selectively bind to Human TNF-α homotrimeric protein, as identified by ELISA and BLI tests
- Suitable for the sandwich approach of antibodies for TNF-α detection
Product List. Source: ACROBiosystems
| Molecule |
Cat. No. |
Species |
Product Description |
| Anti-TNFα Antibody |
TNA-Y58 |
Mouse |
Monoclonal Anti-TNF-alpha antibody, Mouse IgG1 (13B8) |
| TNA-Y59 |
Mouse |
Monoclonal Anti-TNF-alpha antibody, Mouse IgG1 (16H5) |
| TNA-BLY59 |
Mouse |
Biotinylated Monoclonal Anti-TNF-alpha antibody, Mouse IgG1 (16H5)Under developmet |
Verification data
Monoclonal Anti-TNF-alpha antibody, Mouse IgG1 (13B8) Cat. No. TNA-Y58
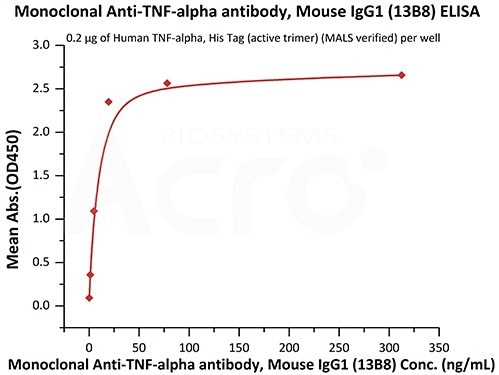
Immobilized Human TNF-alpha, His Tag (active trimer) (Cat. No. TNA-H5228) at 2 μg/mL (100 μL/well) can bind Monoclonal Anti-TNF-alpha antibody, Mouse IgG1 (13B8) (Cat. No. TNA-Y58) with a linear range of 0.3–20 ng/mL (QC tested). Image Credit: ACROBiosystems
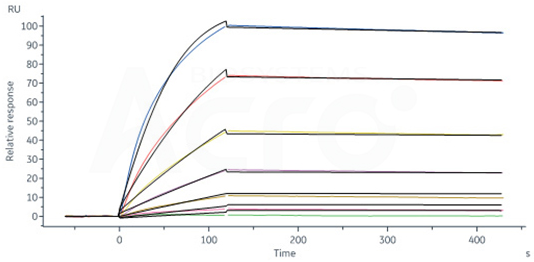
Monoclonal Anti-TNF-alpha antibody, Mouse IgG1 (13B8) (Cat. No. TNA-Y58) captured on CM5 chip via anti-mouse antibodies surface can bind Human TNF-alpha, His Tag (active trimer) (Cat. No. TNA-H5228) with an affinity constant of 0.323 nM as determined in a SPR assay (Biacore 8K). Image Credit: ACROBiosystems
Monoclonal Anti-TNF-alpha antibody, Mouse IgG1 (16H5) Cat. No. TNA-Y59
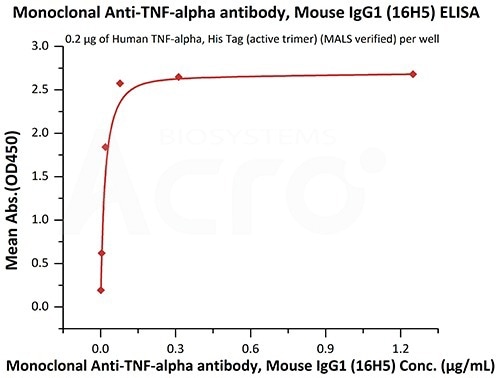
Immobilized Human TNF-alpha, His Tag (active trimer) (Cat. No. TNA-H5228) at 2 μg/mL (100 μL/well) can bind Monoclonal Anti-TNF-alpha antibody, Mouse IgG1 (16H5) (Cat. No. TNA-Y59) with a linear range of 0.001-0.078 μg/mL (QC tested). Image Credit: ACROBiosystems
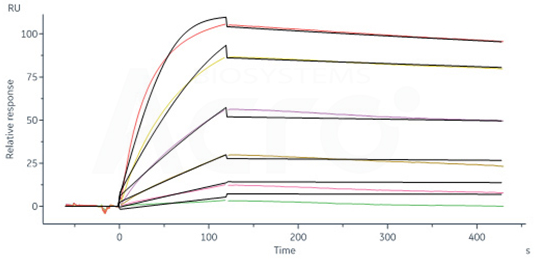
Monoclonal Anti-TNF-alpha antibody, Mouse IgG1 (16H5) (Cat. No. TNA-Y59) captured on CM5 chip via anti-mouse antibodies surface can bind Human TNF-alpha, His Tag (active trimer) (Cat. No. TNA-H5228) with an affinity constant of 0.274 nM as determined in a SPR assay (Biacore 8K). Image Credit: ACROBiosystems
References
- Brightling, C., et al. (2008) Targeting TNF-α: A novel therapeutic approach for asthma. Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2007.10.028
- Guo, Y., et al. (2022). Targeting TNF-α for COVID-19: Recent Advanced and Controversies. Frontiers Public Health. doi:10.3389/fpubh.2022.833967
- Horiuchi, T., et al. (2010). Transmembrane TNF-α: structure, function and interaction with anti-TNF agents. Rheumatology. doi:10.1093/rheumatology/keq031
About ACROBiosystems
ACROBiosystems is a cornerstone enterprise of the pharmaceutical and biotechnology industries. Their mission is to help overcome challenges with innovative tools and solutions from discovery to the clinic. They supply life science tools designed to be used in discovery research and scalable to the clinical phase and beyond. By consistently adapting to new regulatory challenges and guidelines, ACROBiosystems delivers solutions, whether it comes through recombinant proteins, antibodies, assay kits, GMP-grade reagents, or custom services. ACROBiosystems empower scientists and engineers dedicated towards innovation to simplify and accelerate the development of new, better, and more affordable medicine.
Sponsored Content Policy: News-Medical.net publishes articles and related content that may be derived from sources where we have existing commercial relationships, provided such content adds value to the core editorial ethos of News-Medical.Net which is to educate and inform site visitors interested in medical research, science, medical devices and treatments.