Pharmacokinetics (PK) is a branch of science committed to the quantitative analysis of absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion of drug molecules within the body of a living organism. In all clinical and pre-clinical studies, serum drug concentrations are measured at different points following drug administration, both in human patients and in animals. The outcome is a significant indicator of the pharmacokinetic properties of the drug and is pertinently relevant to dosing recommendations.
Case Study
Driven by a flurry of success with monoclonal antibodies, the flourishing market of biologic drugs now requires standard high throughput assays to assess the content of mAbs in serum samples. Various types of assay designs, based on different principles, are available. The three most common ELISA setups for the detection of serum antibodies, and their general benefits and drawbacks are listed in the following table. To assess their performance in real applications, ACROBiosystems tested the setups in the following case studies measuring the concentration of anti-PD1 mAb in serum samples.
| Method |
Coating |
Sample |
Secondary Antibody |
Advantage |
Disadvantage |
Case Studies |
| Indirect assay |
Antigen |
Serum |
Goat anti-human IgG |
Simple |
High background |
Case I |
| Antibody-directed competitive assay |
Antigen |
Serum with labeled competition antibody |
SA-HRP |
Low background |
Additional reagent/labeling required |
Case II |
| Ligand-directed competitive assay |
Natural ligand for the antigen |
Serum with labeled PD-1 |
SA-HRP |
Low background |
Narrow detection range |
Case III |
Case I: Indirect ELISA
Equipment:
BMG CLARIOstar microplate reader
Sample:
Serum samples containing a monoclonal PD-1 antibody
Main Reagents:
Peroxidase AffiniPure Goat Anti-Human IgG, Fcγ Fragment Specific (Cat. No. 109-035-098, Jackson Lab, Bar Harbor, ME, USA)
Recombinant Human PD-1 protein (Cat. No. PD1-H5221, ACROBiosystems, Newark, DE, USA)
Protocol:
- Coat the microplate with 0.1 µg/well rhPD-1 for 16 hours
- Prepare serial sample dilutions (1:2)
- Wash the plate
- Add 100 µl of samples onto the plate
- Wash the plate
- Add HRP-conjugated Goat Anti-Human IgG 0.05 µg/ml
- Add TMB for colorimetric detection
Protocol:
To prevent unspecific binding, all serum samples were diluted by a factor of 1000 prior to assays. The sensitivity is 0.19 µg/mL, and the detection range is 0.19–6.25 µg/mL (Figure 1).
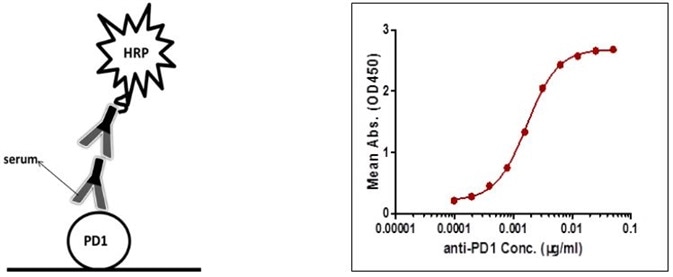
Figure 1. Detection of PD-1 antibody by indirect ELISA.
Case II: Antibody-Directed Competitive ELISA
Equipment:
BMG CLARIOstar microplate reader
Sample:
Serum samples containing a monoclonal PD-1 antibody
Main Reagents:
ELISA Assay Kit for Anti-PD-1 h-mAb in Human Serum (Cat. No. EPH-V1, ACROBiosystems, Newark, DE, USA)
Protocol:
- Coat the microplate with 0.1 µg/well rhPD-1 for 16 hours
- Prepare serial sample dilutions (1:2)
- Mix the samples with the biotinylated PD-1 antibody provided in the kit and bring them to a final concentration of 10%
- Add 100 µl of the mixed samples from step 2 to the wells after washing
- After washing, add HRP conjugated Streptavidin 0.1 µg/ml
- Add TMB for colorimetric detection
Result:
The sensitivity is 0.78 µg/mL and the detection range is 0.78–25 µg/mL (Figure 2).
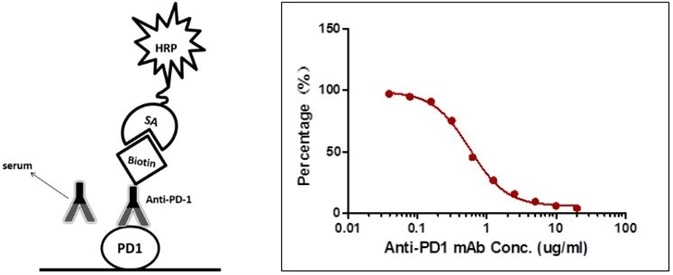
Figure 2. Detection of PD-1 antibody by antibody-directed competitive ELISA.
Related Products:
ELISA Assay Kit for Anti-PD-1 h-mAb in Human Serum (Cat. No. EPH-V1 )
Case III: Ligand-Directed Competitive ELISA
Equipment:
BMG CLARIOstar microplate reader
Sample:
Serum samples containing a monoclonal PD-1 antibody
Main Reagents:
HRP-conjugated Streptavidin Protein (Cat. No. 21126, Thermo Fisher Scientific)
Biotinylated human PD-1 (Cat. No.PD1-H82F2, ACROBiosystems, Newark, DE, USA)
Recombinant human PD-L1-Fc protein (Cat. No.PD1-H5258, ACROBiosystems, Newark, DE, USA)
Simplified Protocol:
- Coat the microplate with 0.2 µg/well rhPD-L1 for 16 hours
- Prepare serial sample dilutions (1:2), and mix with biotinylated PD-1 to a final concentration of 10%
- Add 100 µl of samples from step 2 to the wells after washing
- After washing, add HRP conjugated Streptavidin 0.1 µg/ml
- Add TMB for colorimetric detection
Result:
The sensitivity is 1.565 µg/mL and the detection range is 1.565–6.25 µg/mL (Figure 3).
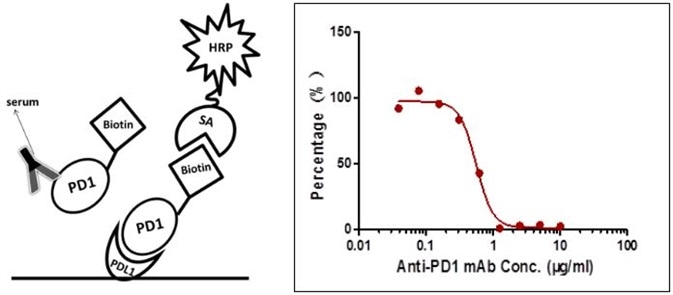
Figure 3. Detection of PD-1 antibody by ligand-directed competitive ELISA.
Methods Comparison
| Case |
Detection Range (µg/mL) |
Sensitivity (µg/mL) |
Specificity |
| Case I:Indirect ELISA |
0.19-6.25 |
0.19 |
High background |
| Case II:Antibody-directed competitive ELISA |
0.78-25 |
0.78 |
Very low background |
| Case III:Ligand-directed competitive ELISA |
1.565-6.25 |
1.565 |
Very low background |
Among the three assay designs, the ligand-directed competitive ELISA (Case III) has the lowest sensitivity and narrowest detection range, which suggests it may not the best solution for the application.
The sensitivity for the indirect ELISA is the best, but the use of a goat anti-human IgG as a secondary antibody gives rise to a high background due to unspecific binding, and therefore needs pre-dilution before analyses (Figure. 4A). However, the antibody-directed competitive ELISA uses HRP-conjugated Streptavidin for secondary detection, which reduces the background interference (Figure. 4B). Additionally, it also has the broadest detection range among the group, even though the sensitivity is lower than the indirect method.
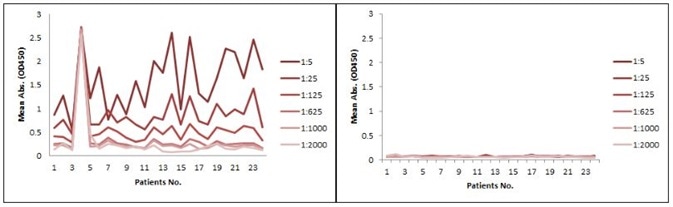
Figure 4. Comparison between Indirect ELISA and antibody-directed competitive ELISA for PD1 mAb detection in patient samples. A: Indirect ELISA; B: antibody-directed competitive ELISA.
In most applications, the background interference is more of a concern than detection sensitivity, as a detection sensitivity of lower than 1 µg/ml is already sufficient. Hence, ACROBiosystems preferred to employ the antibody-directed competitive ELISA for the PK kits.
ACROBiosystems have introduced kits for the analyses of PD-1, HER-2, and CTLA-4, respectively, in common experimental animals as well as in humans.
ACROBiosystems
ACROBiosystems is a cornerstone enterprise of the pharmaceutical and biotechnology industries. Their mission is to help overcome challenges with innovative tools and solutions from discovery to the clinic. They supply life science tools designed to be used in discovery research and scalable to the clinical phase and beyond. By consistently adapting to new regulatory challenges and guidelines, ACROBiosystems delivers solutions, whether it comes through recombinant proteins, antibodies, assay kits, GMP-grade reagents, or custom services. ACROBiosystems empower scientists and engineers dedicated towards innovation to simplify and accelerate the development of new, better, and more affordable medicine.
Sponsored Content Policy: News-Medical.net publishes articles and related content that may be derived from sources where we have existing commercial relationships, provided such content adds value to the core editorial ethos of News-Medical.Net which is to educate and inform site visitors interested in medical research, science, medical devices and treatments.