The quality of the reagents and materials employed in Cell and Gene Therapy (CGT) production processes is crucial in defining the final product quality and therapeutic safety.
Ensuring protection against exogenous contamination is especially vital – which encompasses the unintentional introduction of elements like bacteria, fungi, mycoplasma, and viruses into raw materials, cell substrates, and production items.
Sponsors must ensure suitable quality control of reagents and materials to reduce unnecessary risks to patients or subjects by applying measures like sterility testing or sterilization to guarantee the absence of viral and microbial contaminants.
Rigorous quality control of raw materials in CGT production is essential for decreasing the risk of exogenous factor contamination in the final CGT products and ensuring the efficacy and safety of CGT items.
To secure the safety of upcoming therapeutics, global regulatory agencies have established requirements regarding the safety of raw materials utilized in CGT production.
Specifically, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) advocates the use of readily available and feasible reagents and materials of the highest quality for CGT production, often identified as "Good Manufacturing Practices-Grade” (“GMP-grade") or declared for utilization in cell therapy production. Crucial regulatory documents include:
(1) The "Content and Review of Chemistry, Manufacturing, and Controls (CMC) Information for Human Somatic Cell Therapy Investigational New Drug Applications," issued in April 2008 by the FDA.
(2) USP<1043>"Ancillary Materials for Cell, Gene, and Tissue-Engineered Products."
(3) EP 5.2.12 "Raw Materials of Biological Origin for the Production of Cell and Gene Therapy Medicinal Products."
All three regulatory documents address and emphasize the importance of the safety of raw materials.
ACROBiosystems' GMP-grade products are designed and developed with safety in mind, including the control of exogenous contamination during the whole production and quality control procedure. The important aspects are:
1. The cell line utilized for production is well-documented and traceable to the European Collection of Authenticated Cell Cultures as the source.
2. The generation of host cells, HEK293, following domestication and establishment, undertake extensive testing (26 parameters).
An internationally established third-party testing organization carries out the testing in compliance with the following regulations:
- ICH Q5 Part III: Cell Line Characterization: viral testing.
- FDA's "Points to Consider in the Characterization of Cell Lines Used to Produce Biologicals" (1993), particularly the "V. QUALITY CONTROL TESTING" segment.
- FDA's "Characterization and Qualification of Cell Substrates and Other Biological Materials Used in the Production of Viral Vaccines for Infectious Disease Indications" (2010).
3. The modified cells undergo additional testing following the construction of the cell bank. A well-known domestic third-party testing organization conducts this testing, which includes sterility, cell morphology, mycoplasma, various indicator cell inoculation methods in vitro, retrovirus, and exogenous virus detection, among others.
4. The upstream cell culture phase employs a chemically defined medium (CDM) as a well-defined culture medium. All materials utilized in the upstream production procedure are animal-origin-free (AOF) and serum-free (SF).
Cell recovery and amplification are conducted in a Class C clean area biosafety cabinet (BSC). The reactor production phase uses aseptic welding technology and disposable closed systems. The various production stages are divided to reduce contamination and cross-contamination risks.
5. In the downstream purification process design, virus removal/inactivation phases (such as nanofiltration and low pH treatment) are introduced. Validation of viral removal processes is additionally conducted (in progress) for critical steps.
The purification process uses project-specific separation columns and chromatographic media to prevent cross-contamination risks between the various production phases. The following regulations offer guidance on viral safety:
- Viral Safety Evaluation of Biotechnology Products Derived from Cell Lines of Human or Animal Origin. 1999. International Conference on Harmonization(ICH)Q5A(R1).
- Guideline on Virus Safety Evaluation of Biotechnological Investigational Medicinal Products. EMEA /CHMP / BWP / 398498 / 2005. European Medicines Agency (EMA). 2009.
- Viral Safety Evaluation of Biotechnology Products Derived from Cell Lines of Human or Animal. USP General Chapters:<1050>.
6. The formulation production is conducted in a stringent Grade B+A production setting. Following sterilization filtration, automated equipment, and a one-time-use sterile filling system are employed for processing the semi-finished product.
Aseptic component assembly, filling, stoppering, automatic infeed, outfeed, and lyophilization are operations conducted in a clean B+A-grade environment (examined utilizing the PMS continuous environmental monitoring system).
Post-lyophilization vials are sealed within a Grade C+A environment. Following successful quality inspection, manual inspection, labeling, and other procedures are undertaken before the final products are released.
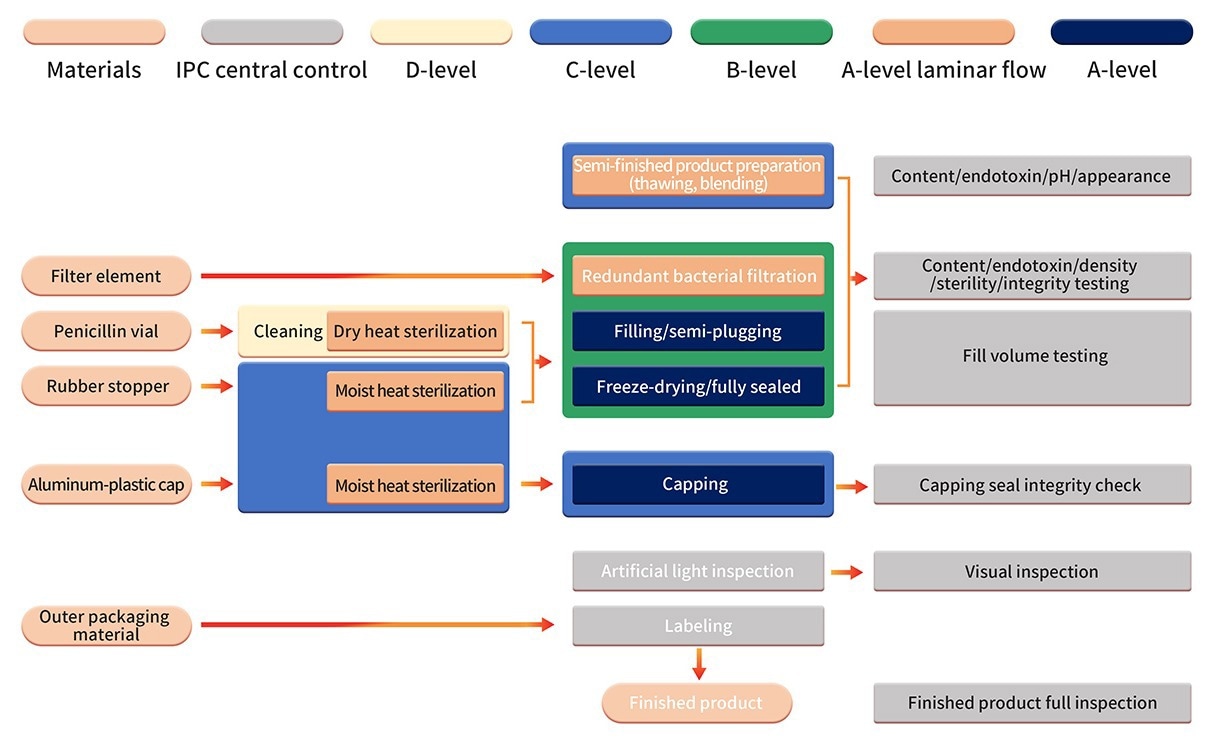
Image Credit: ACROBiosystems
7. Rigorous aseptic process validation involves consistent confirmation of aseptic process control. This includes utilizing aseptic nutrient media and/or product substitutes in APS (media simulation containers).
APS assesses every aseptic operation, spanning from the sterilization and cleaning of process materials to the sealing of containers. Various aseptic operations and interventions are considered under both standard production and worst-case conditions.
- Reference regulation: EU GMP Annex 1.
8. Raw materials and packaging materials employed in production are carefully chosen from pharmaceutical-grade sources. Materials utilized in GMP product production undergo joint assessment and classification by production, research, and quality teams.
Key materials adhere to relevant regulations and pharmacopeias, and their quality standards are determined through critical characterization analysis. Image 2 illustrates the material management process.
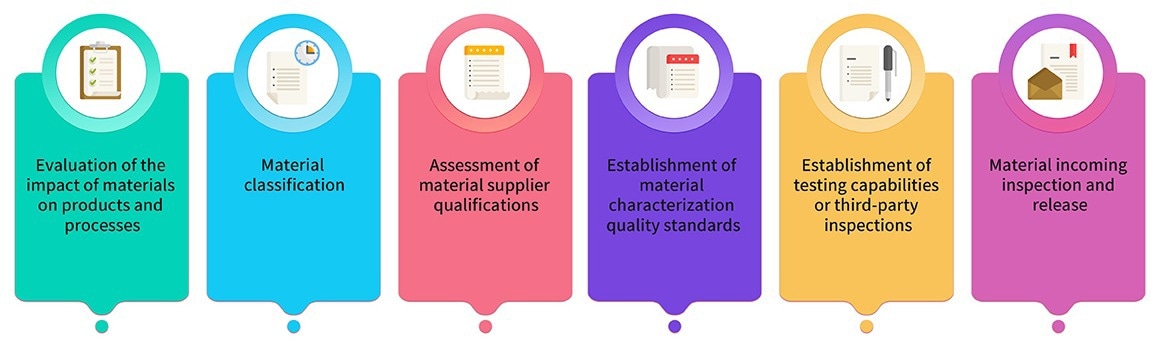
Image Credit: ACROBiosystems
9. ACROBiosystems' GMP-grade products are not solely manufactured under a pharmaceutical-grade facility but are also designed and controlled under appropriate domestic and international CGT regulations. Using GMP-grade IL-15 as an example, the final product quality control release encompasses the following:
- SDS-PAGE > 95 %
- Endotoxin levels under 10 EU/mg
- Residual Host Cell DNA content under 0.02 ng/μg
- Residual Host Cell Protein content under 0.5 ng/ug
- Biological activity > 0.8 x 107 IU/mg (Reference the WHO Human IL-15 (National Institute for Biological Standards and Control code: 90/530) as standard)
- Microbial testing
- Mycoplasma testing
- In vitro virus assay
- Batch-to-batch consistency
- Comprehensive stability data support (accelerated, freeze-thaw, long-term, shipping stability verification)
ACROBiosystems rigorously manages potential external factors during the whole procedure of development, production, quality testing, and quality system - guaranteeing the safety of its products.
ACROBiosystems’ commitment lies in creating high-quality reagents for clinical applications in cell and gene therapy and merging drug production standards with more stringent quality control and release testing standards. This ensures customers receive superior and safer GMP-grade products.
About ACROBiosystems
ACROBiosystems is a cornerstone enterprise of the pharmaceutical and biotechnology industries. Their mission is to help overcome challenges with innovative tools and solutions from discovery to the clinic. They supply life science tools designed to be used in discovery research and scalable to the clinical phase and beyond. By consistently adapting to new regulatory challenges and guidelines, ACROBiosystems delivers solutions, whether it comes through recombinant proteins, antibodies, assay kits, GMP-grade reagents, or custom services. ACROBiosystems empower scientists and engineers dedicated towards innovation to simplify and accelerate the development of new, better, and more affordable medicine.
Sponsored Content Policy: News-Medical.net publishes articles and related content that may be derived from sources where we have existing commercial relationships, provided such content adds value to the core editorial ethos of News-Medical.Net which is to educate and inform site visitors interested in medical research, science, medical devices and treatments.