Antibodies, also known as immunoglobulins (Ig), are components of the humoral immune response — a part of the adaptive branch of the immune system.
There are five different types (IgA, IgD, IgE, IgG and IgM) of antibodies, and they have varying:
- Half-life, ranging from three days for IgA and IgD to 23 days for IgG (excluding IgG3)
- Molecular weights range from ~150 kDa (IgG) to ~900 kDa (IgM)
- The immune functions include immune cell binding affinity, complement binding ability and action sites
The constant region of the antibody heavy chain determines that IgA has an α heavy chain, IgM has a μ heavy chain, IgG has a γ heavy chain, IgE has an ε heavy chain, and IgD has a δ heavy chain.
The Fab region of the antibody is flexible and is responsible for binding to the antigen, while the Fc region is responsible for binding to the cellular receptors present on the cells’ surface, imparting the effector function.
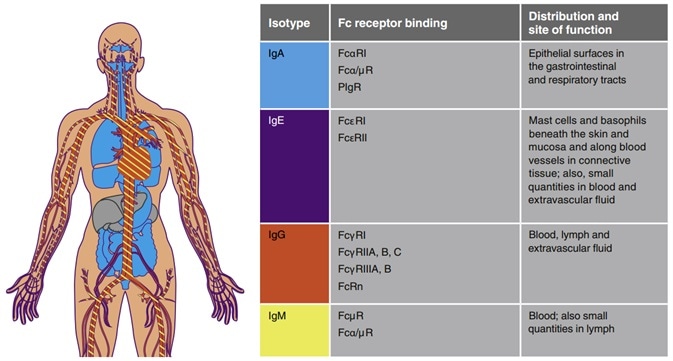
Distribution and function of different immunoglobulins. Image Credit: ACROBiosystems
FcRn is a receptor that binds specifically to IgG and mediates a pH-dependent recycling mechanism for IgG transport. FcRn-mediated mechanisms are used in two therapeutic strategies:
- Decrease in the half-life of pathological IgG antibody to treat autoimmune diseases
- Increase in the half-life of therapeutic antibody drugs to extend the therapeutic benefits
Decrease in the half-life of pathological IgG antibody to treat autoimmune diseases
IgG autoantibodies play a role in autoimmune diseases like chronic inflammatory demyelinating multiple radiculopathy (CIDP), myasthenia gravis (MG), primary immune thrombocytopenia and pemphigus.
These antibodies, for example, play a pathogenic role in MG, resulting in the failure of neuromuscular signal transduction by receptors and proteins at neuromuscular junctions. Experts in the field have investigated FcRn inhibitors to reduce IgG pathogenesis and create targeted therapies to address this mechanism of autoimmunity.
By leveraging the difference in FcRn affinity, this approach can potentially reduce endogenous pathogenic IgG concentrations, resulting in competitive binding with endogenous IgG that causes autoimmune disease.
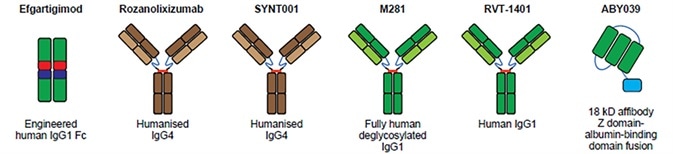
Structure of FcRn targeted drugs. Image Credit: ACROBiosystems
The first and only FcRn antagonist approved by FDA is Efgartigimod. Efgartigimod is a fragment of human IgG1 Fc, which is modified and attaches to FcRn with greater affinity. Efgartigimod is also the first approved therapy aimed specifically at decreasing pathogenic IgG, opening up a new therapeutic approach in the treatment of gMG. IgG levels were decreased by 50–75% with no effect on albumin levels, in a Phase I trial. The research advanced into a Phase II trial, where 75% of patients showed betterment in a timely manner with minimal to no relapse. Phase III trial studies revealed improvement in MG patients’ daily activities.
Rozanolixizuma is a humanized monoclonal antibody derived from UCB Biopharma, a Brussels-based biotechnology company. Rozanolixizuma binds specifically to human FcRn, hinders the interaction between IgG and FcRn, inhibits the IgG cycle and induces the clearance of pathogenic IgG autoantibodies. Rozanolixizuma is in phase III trials.
Johnson & Johnson developed Nipocalimab, an IgG1 anti-FcRn monoclonal antibody. This therapeutic lowers IgG levels by up to 90% showing a slight decrease in serum albumin and total protein levels. However, side effects such as headaches and fever suggested that Nipocalimab’s tolerability needs to be improved.
Harbour BioMed’s Batoclimab (RVT-1401) is a complete human monoclonal antibody. Batoclimab attaches to FcRn and obstructs FcRn–IgG interaction, thus accelerating the degradation of autoantibodies and treating numerous pathogenic IgG-mediated autoimmune diseases.
In China, this product has been included as a breakthrough therapy, and it is currently being tested in clinical trials for different indications.
Increase in the half-life of therapeutic antibody drugs to extend the therapeutic benefits
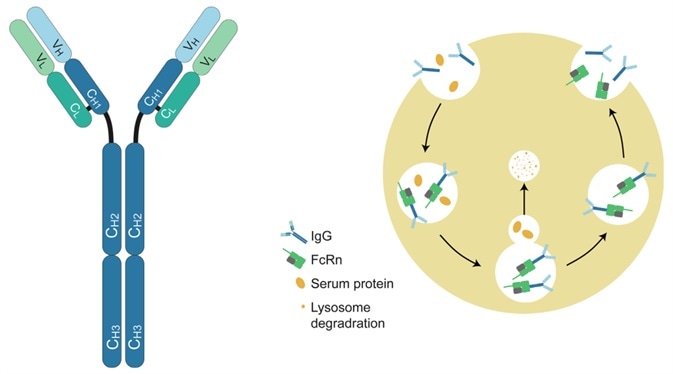
Structure of IgG antibody and FcRn-mediated recycling mechanism. Image Credit: ACROBiosystems
Therapeutic antibodies’ half-lives can be enhanced using the FcRn pathway. Biomolecular engineering, fusing Fc fragments and exchanging amino acids in specific binding bags can all help improve antibody binding to FcRn.
Etanercept, approved for rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and other autoimmune diseases, is a treatment comprising of a TNF receptor and an IgG1 Fc fragment. Etanercept can be used in combination to freely utilize TNFα and β, thus lowering the levels of these inflammatory factors. TNF can be broken down during degradation, while Fc fragments can pass through the FcRn pathway, leading to lower levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines and a longer half-life for therapeutic drugs.
VRC01, widely used for HIV-1 prevention, is a neutralizing monoclonal antibody (bnMAb) IgG1. VRC01LS extends the serum half-life by inducing two amino acid mutations (M428L and N434S) in the Fc region of VRC01. IgG–FcRn binding is enhanced by LS mutations, but FcRs binding is unaffected. VRC01 thus has no effect on Fc-mediated effector functions such as antibody-dependent cytotoxicity (ADCC).
The first drug therapy approved to treat life-threatening thrombotic microangiopathy (TMA) in patients with atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome (aHUS) is Eculizumab, a monoclonal antibody that inhibits the complement protein, C5. It helps improve outcomes in patients with aHUS and TMA. Eculizumab requires intravenous infusion every 2–3 weeks, which increases the infusion burden and the risk of associated adverse events. A highly effective anti-C5 monoclonal antibody (Ravulizumab, Ultomiris®) engineered on the basis of Eculizumab provides a significant treatment option. Ravulizumab is a combination of Eculizumab with two structural changes designed to increase its terminal elimination half-life. The two histidine substitutions in the complementary determinate region enhanced the dissociation rate of the monoclonal antibody C5 complex at pH 6.0, preventing targeted mediated antibody clearance. Two amino acid substitutions in the Fc region improved the antibody’s affinity for human FcRn. Ravulizumab addresses TMA and is tolerated well in pediatric and adult aHUS patients. Ravulizumab’s mechanism of action is similar to Eculizumab except for a four-fold increase in action time, thus, reducing the maintenance dose frequency.
Satralizumab is an IL-6R-targeting humanized monoclonal antibody that employs a novel “antibody recycling technique”. Tocilizumab is injected subcutaneously at 162 mg/week, while Satralizumab modifies the amino acid sequence in the Fc region — mutating a tyrosine residue to a histidine residue — enabling a longer antibody cycle time, and thus decreasing the frequency of administration, at 120 mg/month subcutaneously.
ACROBiosystems offers a variety of high-quality FcRn proteins to aid affinity validation of antibody drugs and the development of FcRn-targeted antibody drugs for the treatment of autoimmune diseases.
FcRn: Product features
- Various species: Mouse, Rat, Cynomolgus/Rhesus macaque, Rabbit, Porcine, Feline, Bovine and Human can be fully applied to various cross-species experiments
- Expressed by HEK293 cells: To attain post-translational modification and proper protein folding
- High purity: More than 95% as verified by SDS-PAGE and more than 90% as verified by SEC-MALS
- Low endotoxin: <1.0 EU/µg
- Biotinylated FcRn proteins labeled with AvitagTM offered: High labeling efficiency, specificity and clarity. Appropriate for ELISA/SPR/BLI detection based on binding to streptavidin for drug development and optimization process
- Affinity verified by SPR & BLI: Bioactivity is tested and guaranteed, and protocols followed are offered free of charge
Product list
Table 1. Source: ACROBiosystems
| Molecule |
Cat. No. |
Host |
Product Description |
Structure |
| FcRn (FCGRT & B2M) |
FCM-H5286 |
HEK293 |
Human FcRn / FCGRT&B2M Heterodimer Protein, His Tag&Strep II Tag (SPR & BLI & MALS verified)Hot |
|
| FCM-H8286 |
HEK293 |
Biotinylated Human FcRn / FCGRT&B2M Heterodimer Protein, His Tag&Strep II Tag, ultra sensitivity (primary amine labeling) (SPR verified) |
 |
| FCM-H82W4 |
HEK293 |
Biotinylated Human FcRn / FCGRT&B2M Heterodimer Protein,Avitag™,His Tag&Strep II Tag (SPR & BLI & MALS verified)Hot |
 |
Click here to learn more about product list.

Image Credit: ACROBiosystems
ACROBiosystems has been working on a series of IgG Fc proteins that consists of the hinge region alone, CH2 and CH3 sequences, and devoid of the Fab sequences, in addition to the previous work.
Monoclonal antibodies, IgG-like bispecific antibodies, ADCs and IgG Fc-fusion drugs can all benefit from these IgG Fc proteins as isotype controls. This product can be used for drug screening, functional verification and other purposes.
Furthermore, the IgG Fc proteins can be used as endogenous IgG for competitive validation of FcRn binding to FcRn targeted antibody drugs.
IgG Fc: Product features
- Expressed by HEK293 cells: For post-translational glycosylation, modifications and correct protein folding
- Various species and subclasses: Mouse—IgG1 Fc, IgG2a Fc, IgG2b Fc; Rabbit IgG Fc; Llama—IgG2b Fc; Human—IgG1 Fc, IgG2 Fc, IgG3 Fc, IgG4 Fc
- Low endotoxin: Less than 1.0 EU/μg by the LAL method
- Various tags: Tag Free, AvitagTM, His Tag, gD Tag, Flag Tag, AvitagTM and His tag
- High bioactivity: Substantiated by ELISA and SPR with free protocols
- High purity: More than 95% as substantiated by SDS-PAGE, more than 90% as verified by SEC-MALS
IgG Fc: Product list
Table 2. Source: ACROBiosystems
| Molecule |
Cat. No. |
Species |
Product description |
Preorder/Order |
| IgG1 Fc |
FCC-H5214 |
Human |
Human IgG1 Fc Protein, Tag Free (MALS verified) |
Order |
| IgG1 Fc |
IG1-H8213 |
Human |
Biotinylated Human IgG1 Fc protein, Avitag™ (MALS verified) |
Order |
| IgG1 Fc |
IG1-H5225 |
Human |
Human IgG1 Fc Protein, His Tag (MALS verified) |
Order |
Click here to learn more about IgG Fc:product list.

Image Credit: ACROBiosystems
References
- Hans-Hartmut Peter, Hans D. Ochs, Charlotte Cunningham-Rundles, et al. Targeting FcRn for immunomodulation: Benefits, risks, and practical considerations. Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology. 2020, 146(3): 479–491. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaci.2020.07.016.
- Adrian W. Zuercher, Rolf Spirig, Adriana Baz Morelli et al. Next-generation Fc receptor–targeting biologics for autoimmune diseases, Autoimmunity Reviews, 2019,18(10). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.autrev.2019.102366
- Yahiya Y. Syed. Ravulizumab: A Review in Atypical Haemolytic Uraemic SyndromeDrugs. 2021, 81: 587–594. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40265-021-01481-6
- Gil I. Wolfe, E. Sally Ward, Hans de Haard et al. IgG regulation through FcRn blocking: A novel mechanism for the treatment of myasthenia gravis, Journal of the Neurological Sciences, 2021, 430. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jns.2021.118074
- Johann Sellner, Harald H. Sitte, Paulus S. Rommer. Targeting interleukin-6 to treat neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorders: Implications from immunology, the FcRn pathway and clinical experience, Drug Discovery Today, 2021, 26(7):1591–1601, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.drudis.2021.03.018
About ACROBiosystems
ACROBiosystems is a cornerstone enterprise of the pharmaceutical and biotechnology industries. Their mission is to help overcome challenges with innovative tools and solutions from discovery to the clinic. They supply life science tools designed to be used in discovery research and scalable to the clinical phase and beyond. By consistently adapting to new regulatory challenges and guidelines, ACROBiosystems delivers solutions, whether it comes through recombinant proteins, antibodies, assay kits, GMP-grade reagents, or custom services. ACROBiosystems empower scientists and engineers dedicated towards innovation to simplify and accelerate the development of new, better, and more affordable medicine.
Sponsored Content Policy: News-Medical.net publishes articles and related content that may be derived from sources where we have existing commercial relationships, provided such content adds value to the core editorial ethos of News-Medical.Net which is to educate and inform site visitors interested in medical research, science, medical devices and treatments.