ACROBiosystems — the leading producer of recombinant proteins and other vital reagents to encourage the development of target therapeutics, diagnostics, and vaccines — has established an antibody product line called “mAb matrix.”
Biological target antibodies, receptor antibodies, biomarker antibodies, cytokine antibodies (chemokine antibodies, interleukin antibodies), small molecular inhibitors antibodies, virus antibodies, process engineering antibodies, diagnostic antibodies, and so on are all included in the mAb matrix.
The products in the “antibody matrix” series are characterized by high specificity and sensitivity, and they are appropriate for the methodology construction of both diagnosis and the overall process in biopharmaceutical R&D, assisting in the acceleration of medicine R&D and commercialization.

Image Credit: ACROBiosystems
The functions of IFN-γ
The immune system has evolved according to two basic rules: “destroy foreign objects when in danger,” and “do not seriously harm the host.”
Selectively treating normal cells while avoiding immune lesions is a difficult task. As a result, inflammation activates the regulatory system and initiates tissue repair, restoring physiological functions and internal stability. Interferon plays a major role between immune and non-immune cells.
IFN-γ is a soluble cytokine that belongs to the type II interferon family. IFN-γ is a multi-effect cytokine that has antiviral, antitumor, and immune-regulatory properties. As a result, IFN-γ plays a crucial role in the coordination of congenital and adaptive immune responses.
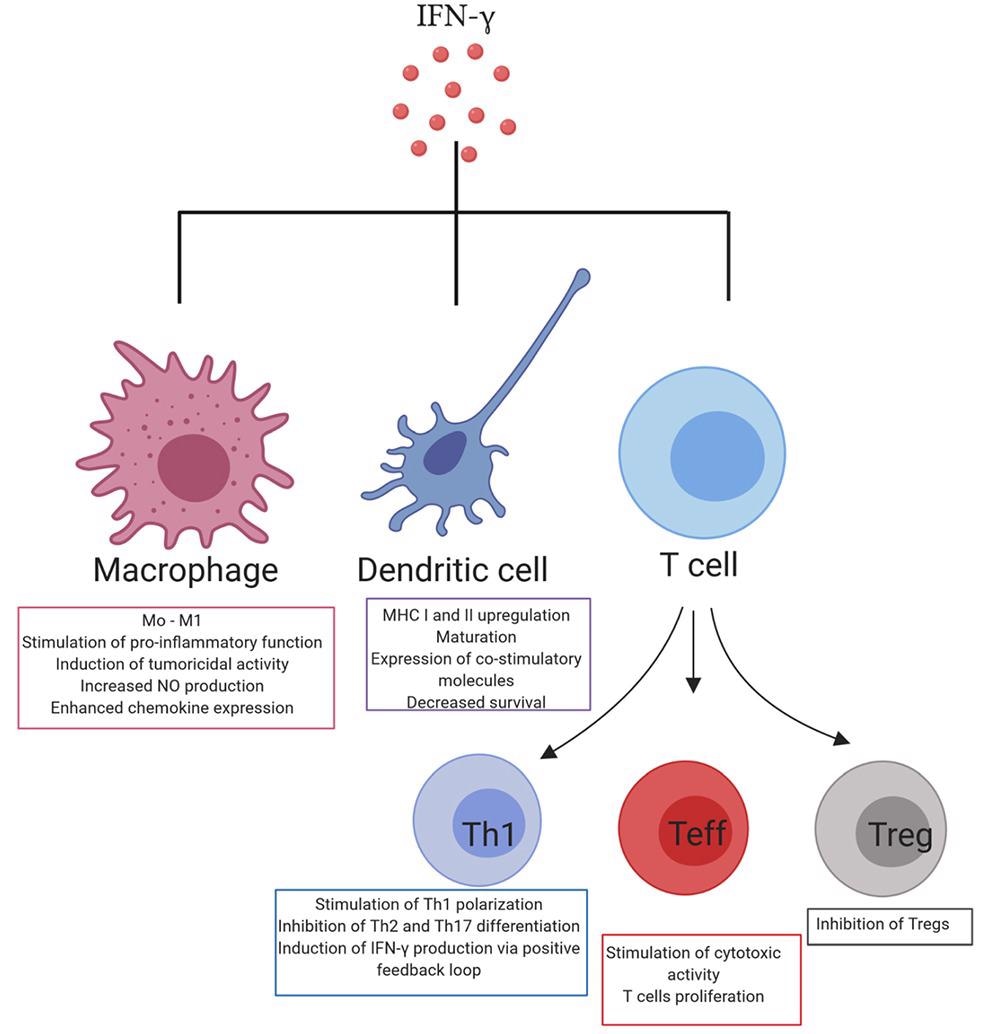
The interaction of IFN-γ with immune cells. Image from reference
In an inflammatory environment, IFN-γ activates an immune response that promotes pathogen removal while also preventing overactivation of the immune system and tissue damage, though the complex mechanisms that keep this balance in place are unknown.
IFN-γ performs a cohesive anti-tumor and pro-tumor immune function in the tumor microenvironment (TME). IFN-γ, along with granzyme B and perforin, acts as a cytotoxic cytokine that causes tumor cells to die.
IFN-γ can also produce immune checkpoint inhibitory molecules and indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO), which stimulates immune suppression in other ways. Although IFN-γ is an important part of antitumor immunity, it can also start an alternate program in tumor cells, giving them the ability to respond better to immune responses.
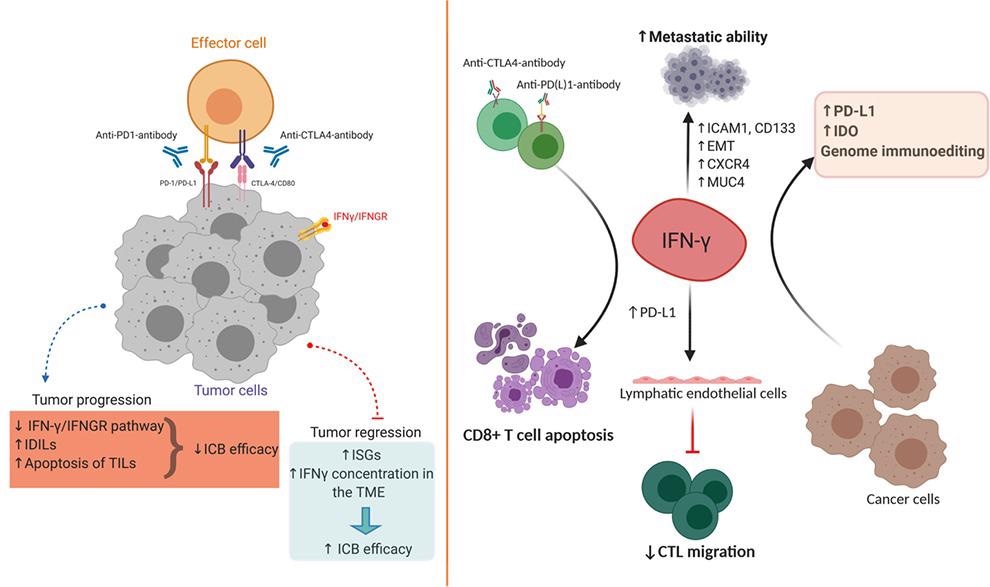
Pro-tumor and anti-tumor effects of IFN-γ. Image from reference
The structure of IFN-γ
IFN-γ is a protein encoded by the IFNG gene and has two antiparallel polypeptide chains. Fully synthetic IFN-γ is glycosylated at the amino terminus and the level of glycosylation determines the actual weight of the defined moiety. It has been observed that glycosylation itself does not affect the activity of interferon; however, it prevents its degradation by proteases.
As a result of this chemical modification, IFN-γ has a longer half-life in the blood, extending its mediated effects.
Table 1. Product list: IFN-γ and IFN-γ R1. Source: ACROBiosystems
| Molecule |
Cat. No. |
Species |
Product Description |
| IFN-γ |
IFG-H4211 |
Human |
ActiveMax® Human IFN-gamma / IFNG Protein, Tag Free |
| IFN-γ R1 |
IF1-H5223 |
Human |
Human IFN-gamma R1 /IFNGR1 Protein, His Tag |
| IFN-γ R1 |
IF1-H5254 |
Human |
Human IFNGR1 / CD119 Protein, With C-Fc Tag |
The detection of IFN-γ
IFN-γ-mediated host-pathogen interactions are important for understanding disease mechanisms and have a lot of therapeutic potential for treating infections and autoimmune diseases. T cells which are capable of identifying and eradicating cancer cells were pinpointed based on IFN-γ positivity during CAR-T cell therapy.
Furthermore, effector T cell clones are typically chosen based on their ability to produce interferon. However, the expression of IFN-γ and the efficacy of CAR-T cell therapy in vivo are not always correlated, implying that IFN-γ has a different role in cancer immunoediting. Despite this, IFN-γ remains one of the most important parameters for predicting clinical response.
CAR-T cells produce IFN-γ and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF). These can improve cell adhesion, antigen presentation, and Th1 cell recruitment, boosting host antitumor immunity. Furthermore, tumor-infiltrating macrophages must be regulated by IFN-γ to enhance the success rate of CAR-T cell therapy or inhibit tumor recurrence.
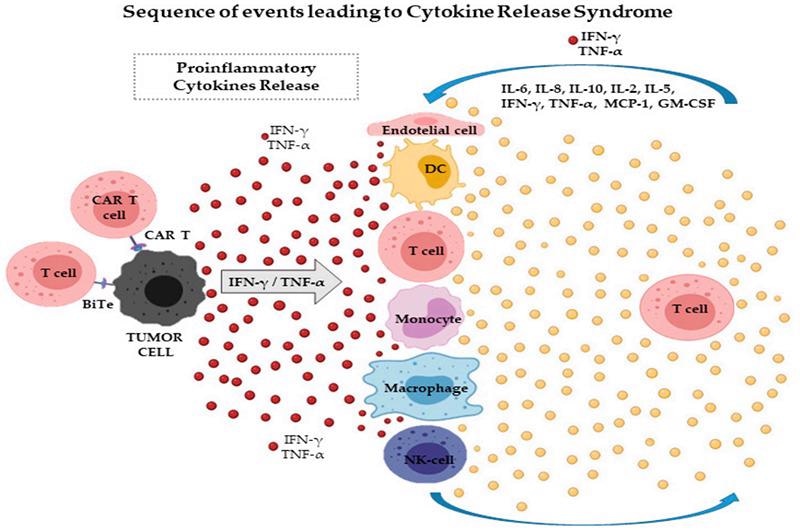
CAR-T cells target tumor cells and induce the release of cytokines such as IFN-γ. Image from reference
The immunopathological consequences of adoptive T cell therapy, including CAR-T, encompass cytokine release syndrome (CRS) and macrophage activation syndrome (MAS). In these syndromes, IFN-γ is assumed to be a common player. In addition to increased IFN-γ levels, mediators like IL-6, IL-10, IFN-γ-induced chemokines, and TNF-α play a role in potentially fatal toxicity and other negative effects.
Macrophages differentiate into hemophagocytic cells and aggravate the disease when chronically exposed to IFN-γ, suggesting that MAS has an IFN-γ dependent-physiopathology.
As a result, IFN-γ detection and monitoring are extremely important in clinical practice.
At the moment, antigen–antibody specific binding is the most common method for detecting IFN-γ. Three human–mouse chimeric anti-IFN γ antibodies derived from different clones have been launched by ACROBiosystems. They can bind specifically to Human IFN-γ and have been verified to be suitable for IFN-γ detection using the antibodies sandwich method.
Table 2. Product List. Source: ACROBiosystems
| Molecule |
Cat. No. |
Species |
Product Description |
| Anti-IFNγ antibody |
IFN-M411 |
Human |
Monoclonal Anti-IFNγ antibody, Human IgG1 (13E6H4) |
| IFN-M412 |
Human |
Monoclonal Anti-IFNγ antibody, Human IgG1 (8C5F8) |
| IFN-M414 |
Human |
Monoclonal Anti-IFNγ antibody, Human IgG1 (13E6H6) |
Product features
- High purity: greater than 95% as verified by SDS-PAGE
- High biological activity: the binding activity and affinity to IFN-γ are confirmed by SPR, ELISA, and BLI
- High sensitivity: appropriate for detecting IFN-γ and developing detection methods, with a sensitivity of pg grade
- High specificity: binds specifically to IFN-γ, and not to other cytokines (IL-2, IL-4, IL-6, IL-10, GM-CSF, TNF-alpha)
Verification data
Monoclonal Anti-IFNγ antibody, Human IgG1 (13E6H4) (Cat. No. IFN-M411)

Human IgG1 (13E6H4) monoclonal anti-IFNγ antibody on SDS-PAGE under reducing (R) conditions. Coomassie Blue was used to stain the gel overnight. The protein is more than 95% pure. Image Credit: ACROBiosystems
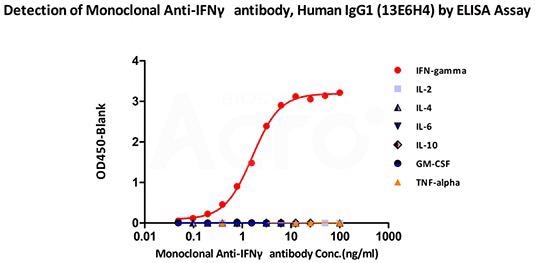
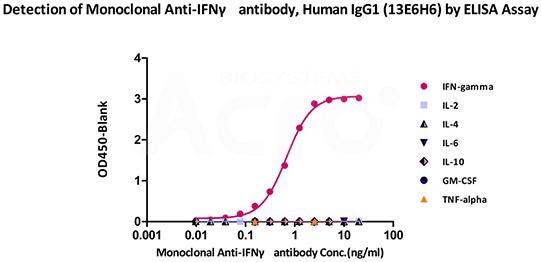
Immobilized ActiveMax® Human IFN-gamma, Tag Free (Cat. No. IFG-H4211) can attach to Monoclonal Anti-IFNγ antibody, Human IgG1 (13E6H4) (Cat. No. IFN-M411) with a linear range of 0.09–1.56 ng/mL (QC tested). Cross-reactivity was not observed with other human cytokines like IL-2, IL-4, IL-6, IL-10, GM-CSF, and TNF-alpha. Image Credit: ACROBiosystems
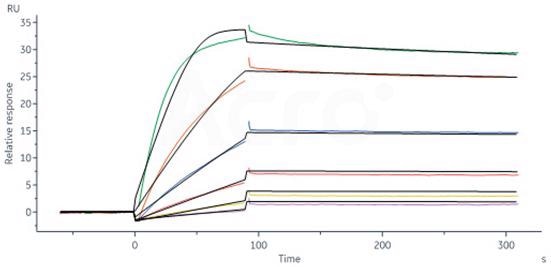
Monoclonal Anti-IFNγ antibody, Human IgG1 (Cat. No. IFN-M411) captured on CM5 chip via Anti-human IgG Fc antibodies surface can attach ActiveMax® Human IFN-gamma, Tag Free (Cat. No. IFG-H4211) with an affinity constant of 0.158 nM as quantified in an SPR assay (Biacore 8K). Image Credit: ACROBiosystems
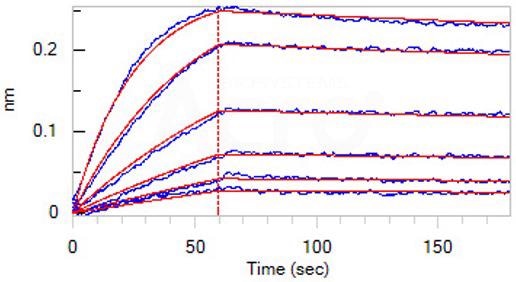
As quantified in BLI assay (ForteBio Octet Red96e), loaded Monoclonal Anti-IFNγ antibody, Human IgG1 (Cat. No. IFN-M411) on AHC Biosensor, can attach ActiveMax® Human IFN-gamma, Tag Free (Cat. No. IFG-H4211) with an affinity constant of 0.653 nM. Image Credit: ACROBiosystems
Monoclonal Anti-IFNγ antibody, Human IgG1 (8C5F8), (Cat. No. IFN-M412)

Monoclonal Anti-IFNγ antibody, Human IgG1 (8C5F8) on SDS-PAGE under reducing (R) condition. Coomassie Blue was used to stain the gel overnight. The protein is more than 95% pure. Image Credit: ACROBiosystems
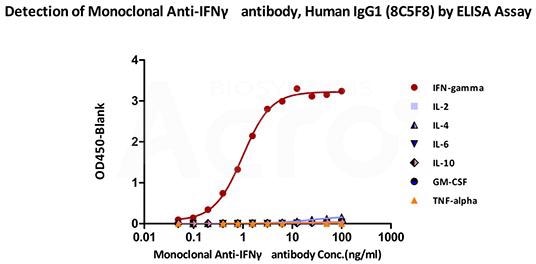
Immobilized ActiveMax® Human IFN-gamma, Tag Free (Cat. No. IFG-H4211) can bind Monoclonal Anti-IFNγ antibody, Human IgG1 (8C5F8) (Cat. No. IFN-M412) with a linear range of 0.09–1.56 ng/mL (QC tested). Cross-reactivity was not observed with other human cytokines like IL-2, IL-4, IL-6, IL-10, GM-CSF, and TNF-alpha. Image Credit: ACROBiosystems
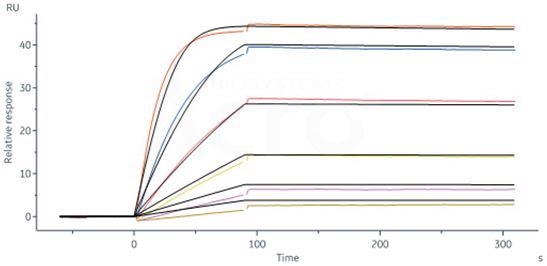
Monoclonal Anti-IFNγ antibody, Human IgG1 (8C5F8) (Cat. No. IFN-M412) captured on CM5 chip via Anti-human IgG Fc antibodies surface can bind ActiveMax® Human IFN-gamma, Tag Free (Cat. No. IFG-H4211) with an affinity constant of 41.1 pM as evaluated by SPR assay (Biacore 8K). Image Credit: ACROBiosystems
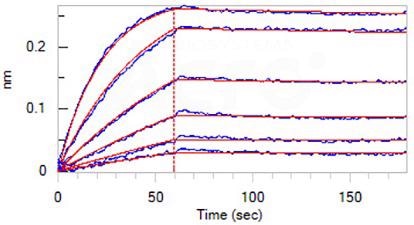
Loaded Monoclonal Anti-IFNγ antibody, Human IgG1 (Cat. No. IFN-M412) on AHC Biosensor, can bind ActiveMax® Human IFN-gamma, Tag Free (Cat. No. IFG-H4211) with an affinity constant of 0.545 nM as identified with the BLI assay (ForteBio Octet Red96e). Image Credit: ACROBiosystems
Monoclonal Anti-IFNγ antibody, Human IgG1 (13E6H6) (Cat. No. IFN-M414)
e
Monoclonal Anti-IFNγ antibody, Human IgG1 (13E6H6) on SDS-PAGE under reducing (R) condition. Coomassie Blue was used to stain the gel overnight. The protein is more than 95% pure. Image Credit: ACROBiosystems
Immobilized ActiveMax® Human IFN-gamma, Tag Free (Cat. No. IFG-H4211) can bind Monoclonal Anti-IFNγ antibody, Human IgG1 (13E6H6) (Cat. No. IFN-M414) with a linear range of 0.07–0.63 ng/mL (QC tested). Cross-reactivity was not observed with other human cytokines like IL-2, IL-4, IL-6, IL-10, GM-CSF, and TNF-alpha. Image Credit: ACROBiosystems
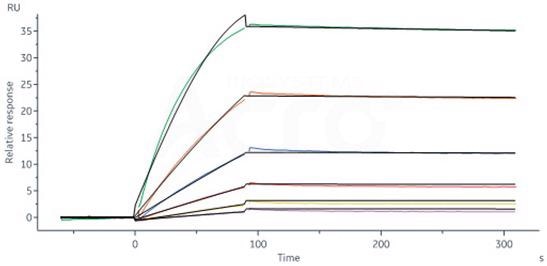
Monoclonal Anti-IFNγ antibody, Human IgG1 (13E6H6) (Cat. No. IFN-M414) captured on CM5 chip via Anti-human IgG Fc antibodies surface can bind ActiveMax® Human IFN-gamma, Tag Free (Cat. No. IFG-H4211) with an affinity constant of 0.11 nM as evaluated by an SPR assay (Biacore 8K). Image Credit: ACROBiosystems
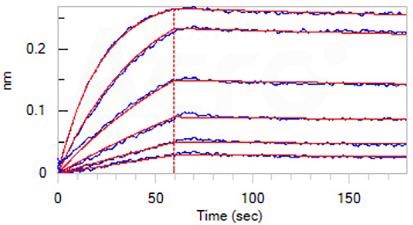
Loaded Monoclonal Anti-IFNγ antibody, Human IgG1 (Cat. No. IFN-M414) on AHC Biosensor, can bind ActiveMax® Human IFN-gamma, Tag Free (Cat. No. IFG-H4211) with an affinity constant of 0.718 nM as quantified in BLI assay (ForteBio Octet Red96e). Image Credit: ACROBiosystems
References
- M. Alper Kursunel, Gunes Esendagli. The untold story of IFN-γ in cancer biology, Cytokine & Growth Factor Reviews (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cytogfr.2016.07.005.
- Jorgovanovic, D., Song, M., Wang, L. et al. Roles of IFN-γ in tumor progression and regression: a review. Biomarker Research (2020). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40364-020-00228-x
- Maria Cosenza, Stefano Sacchi, Samantha Pozzi. Cytokine Release Syndrome Associated with T-Cell-Based Therapies for Hematological Malignancies: Pathophysiology, Clinical Presentation, and Treatment. J. Mol. Sci. (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22147652.
About ACROBiosystems
ACROBiosystems is a cornerstone enterprise of the pharmaceutical and biotechnology industries. Their mission is to help overcome challenges with innovative tools and solutions from discovery to the clinic. They supply life science tools designed to be used in discovery research and scalable to the clinical phase and beyond. By consistently adapting to new regulatory challenges and guidelines, ACROBiosystems delivers solutions, whether it comes through recombinant proteins, antibodies, assay kits, GMP-grade reagents, or custom services. ACROBiosystems empower scientists and engineers dedicated towards innovation to simplify and accelerate the development of new, better, and more affordable medicine.
Sponsored Content Policy: News-Medical.net publishes articles and related content that may be derived from sources where we have existing commercial relationships, provided such content adds value to the core editorial ethos of News-Medical.Net which is to educate and inform site visitors interested in medical research, science, medical devices and treatments.