CAS and ACROBiosystems recently published new research in the Nature journal focussed on the COVID-19 Omicron variant. The paper is titled “Memory B cell repertoire from triple vaccines against diverse SARS-CoV-2 variants.”
This research outlines the identification of a potent broad-spectrum neutralizing antibody (NAb) for all VOC mutants. This NAb was detected in serological samples taken from three-dose inactivated vaccine recipients, representing a potential option for protecting against Omicron and future mutants.
Working in partnership with IBP, ACROBiosystems took responsibility for the BLI assay and the provision of core research tools such as recombinant antigens of VOCs and WT and the inhibitor screening kit.
The study began by testing neutralizing antibody titers of serum samples from patients that had received Sinovac‘s vaccine. These were tested against WT, Delta and Omicron using live virus assays.
After two vaccine doses, the GMT NT50 of serum samples was only 33 for WT, 6 for Delta (5.5-fold decrease) and virtually zero for Omicron. These outcomes confirm that serum antibodies are ineffective against Omicron following two doses of vaccination of inactivated vaccines.
It was noted, however, that three vaccine doses boosted the level of neutralization against WT, Delta and Omicron to a higher level. The Omicron response remained the weakest (Figure 1).
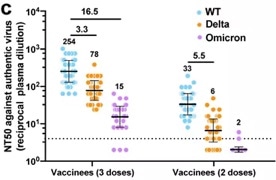
Figure 1. Neutralization of serological antibodies (post 2-dose vs. 3-dose) against WT, Delta and Omicron. Image Credit: ACROBiosystems
The researchers continued their study by isolating memory B cells from human peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) taken from the individuals provided three doses of inactivated vaccines.
They also used gene sequencing to obtain the sequences of variable regions of the heavy and light antibody chains.
The antibodies were recombinantly expressed in vitro before being analyzed for binding epitopes. It was determined that 163 of these antibodies were able to bind viral RBD, 100 to NTD and 51 to S2 subunit.
Of the 163 RBD-binding antibodies, it was determined that 31 could potently neutralize WT and all VOC variants (Alpha, Beta, Gamma, Delta, Omicron) in both pseudovirus and live virus assays, while 30 of these were able to effectively block the ACE2-RBD interaction (Figure 2).
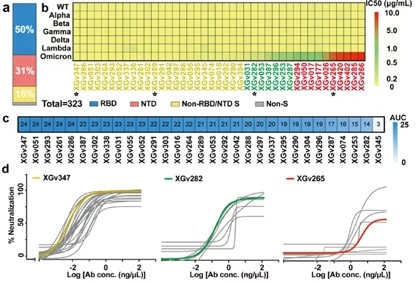
Figure 2. Isolation of potent neutralizing antibodies from PBMCs in 3-dose inactivated vaccine recipients. Image Credit: ACROBiosystems
A minimal number of antibodies were found to maintain neutralization against Omicron. Previous studies had shown that half inhibitory concentrations (IC50) of GSK/Vir’s VIR-7831 and Singlomics’ DXP-604 were 0.27 μg/ml and 0.16 μg/ml, respectively, against an Omicron pseudovirus.
Of the 31 broad-spectrum antibodies acquired as part of this study, 13 exhibited an IC50 of fewer than 0.02 μg/ml against Omicron - 10-40 times the neutralizing activity of VIR-7831 and DXP-604.
These findings suggest that these antibodies have strong neutralization potential against Omicron, representing promising tools for the prevention and treatment of infection from this VOC.
The team’s previous structural research had developed a means of dividing neutralizing antibodies into classes I-VI according to differential binding epitopes. It is possible to classify the broad-spectrum neutralizing antibodies identified here into classes I, II and IV after testing via competitive ELISA.
Four representative antibodies were selected for structural analysis. This analysis revealed that:
- The Class II antibody XGv347 and the Class IV antibody XGv289 exhibited strong neutralizing activity against all VOCs.
- The Class IV antibody XGv282 exhibited an extreme neutralizing activity against VOCs other than Omicron, though it did display a somewhat compromised ability to neutralize Omicron.
- The Class IV antibody XGv265 exhibited an extreme neutralizing activity against VOCs other than Omicron while also displaying a significantly reduced neutralizing activity against Omicron.
Cryo-election microscopy was used to investigate the three-dimensional structure of the complex formed between the antibody’s Fab region and the Omicron spike trimer protein.
This analysis revealed that the Fab region of XGv347 tended to bind to the antigen in three states:
- 3 Fabs simultaneously bind to 3 RBDs in the “down” configuration.
- 2 Fabs simultaneously bind to 2 RBDs in the “up” configuration.
- 2 Fabs bind to 2 RBDs, with one in an “up” and the other in a “down” configuration, respectively.
Unlike that of XGv347, the Fab regions of XGv289, XGv282 and XGv265 were each found to bind to the antigen in just one state (Figure 3):
- 3 XGv289 Fabs bind to 2 “up” and 1 “down” RBDs
- 3 XGv282 Fabs bind to 1 “up” and 2 “down” RBDs
- 2 XGv265 Fabs bind to 1 “up” and 1 “down” RBD
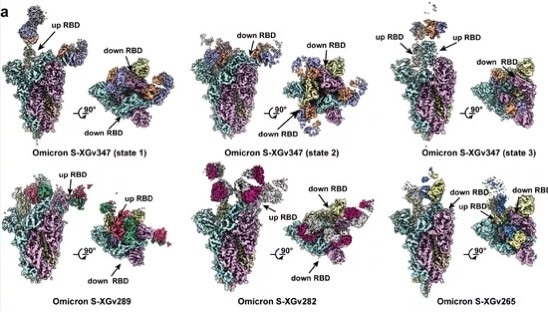
Figure 3. Different RBD binding patterns of the four selected neutralizing antibodies from different classes. Image Credit: ACROBiosystems
A significant overlap was shown between XGv347 binding sites and the ACE2 binding sites on RBD.
The binding pattern of XGv347 was also found to exhibit a degree of similarity with the pan-coronavirus neutralizing antibodies A23-58.1 and S2K146, suggesting the potential for this class of antibodies to be used to neutralize Omicron and other potentially emerging mutants.
An investigation into XGv289, XGv282, and XGv265 revealed binding sites that are similar to REGN10987, DH1047, REG-812. Their shared reduction in neutralization potential could be affected by the N440K and G446S mutations prevalent in Omicron (Figure 4).
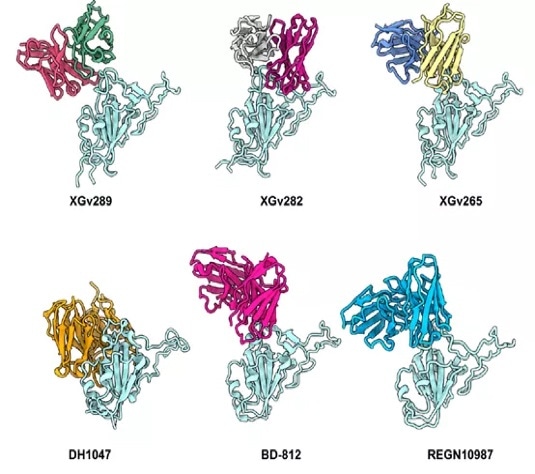
Figure 4. Binding epitopes of the four selected antibodies in comparison with licensed mAbs. Image Credit: ACROBiosystems
It should also be noted that the binding affinity between XGv282 and Omicron RBD decreased 5-fold, but its neutralizing effect was observed to decrease almost 40-fold.
XGv347, in contrast, exhibited a 40-fold decrease in affinity with Omicron RBD despite maintaining a strong level of neutralization. These findings indicate that binding epitope is more critical than binding affinity in terms of antibody neutralization.
When utilized with BALB/c mice, it was observed that a single injection of the XGv282 antibody could reduce viral RNA load in the host lung tissues around 1000-fold.
A single injection of XGv347, XGv289, XGv282, XGv265, XGv052, and combinatorial injection of XGv052/XGv289, XGv282/XGv347 were found to almost eliminate the virus, with no notable damage seen in histopathological sections (Figure 5).
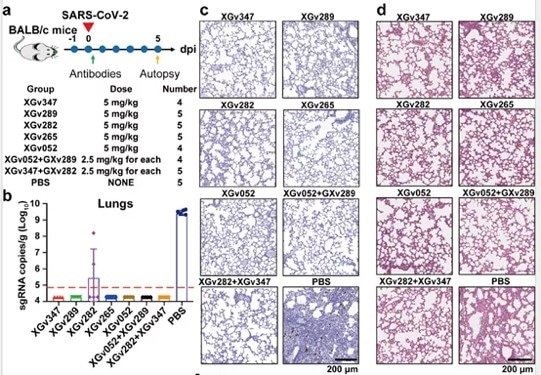
Figure 5. Neutralizing antibodies provide strong protection against viral infection in BALB/c mice. Image Credit: ACROBiosystems
It was also found that when utilized with human ACE2 transgenic mice, one injection of XGv347 could eliminate the viral RNA load caused by Omicron infection in lungs with no observable damage in histopathological sections (Figure 6).
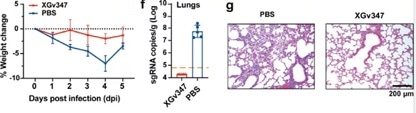
Figure 6. XGv347 provides strong protection against Omicron infection in human ACE2 transgenic mice. Image Credit: ACROBiosystems
Conclusion
This study saw a number of neutralizing antibodies screened and identified. It was determined that all of these could broadly neutralize WT and all VOC strains, demonstrating a robust protective effect in mice infected with the Beta and Omicron variants of COVID-19.
Antibodies able to recognize epitopes in the same region were characterized via structural analysis.
The study also confirmed that different classes of antibodies could be employed as a combined therapy in the prevention and treatment of currently circulating and potentially emerging strains of COVID-19.
The analysis of antigenic epitopes that are recognized by broad-spectrum potent neutralizing antibodies also supported the development of a theoretical basis to underpin the design of a new generation of vaccines.
Core reagents in this research
Source: ACROBiosystems
| Lineage |
Cat.No. |
Molecule |
Product description |
| Wild Type |
SPD-C52H3 |
Spike RBD |
SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) S protein RBD, His Tag (MALS verified) |
| Alpha |
SPD-C52Hn |
Spike RBD |
SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) S protein RBD (N501Y), His Tag (MALS verified) |
| Beta |
SPD-C52Hp |
Spike RBD |
SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) S protein RBD (K417N, E484K, N501Y), His Tag (MALS verified) |
| Gamma |
SPD-C52Hr |
Spike RBD |
SARS-CoV-2 S protein RBD (K417T, E484K, N501Y), His Tag (MALS verified) |
| Delta |
SPD-C52Hh |
Spike RBD |
SARS-CoV-2 Spike RBD (L452R, T478K), His Tag (MALS verified) |
| Omicron |
SPD-C522e |
Spike RBD |
SARS-CoV-2 Spike RBD, His Tag (B.1.1.529/Omicron) |
| Omicron |
EP-115 |
Inhibitor Screening Kit |
SARS-CoV-2 (B.1.1.529) Inhibitor Screening Kit (Spike RBD) |
Assay data
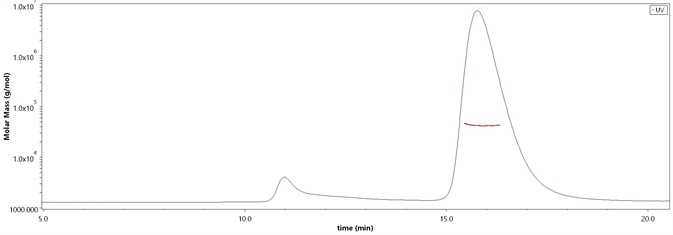
The purity of SARS-CoV-2 Spike RBD, His Tag (B.1.1.529/Omicron) (Cat. No. SPD-C522e) is more than 90% and the molecular weight of this protein is around 33-48 kDa verified by SEC-MALS. Image Credit: ACROBiosystems
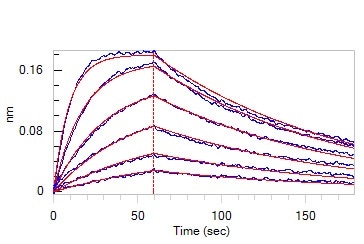
Loaded Human ACE2, Fc Tag (Cat. No. AC2-H5257) on Protein A Biosensor, can bind SARS-CoV-2 Spike RBD, His Tag (B.1.1.529/Omicron) (MALS verified) (Cat. No. SPD-C522e) with an affinity constant of 11.4 nM as determined in BLI assay (ForteBio Octet Red96e). Image Credit: ACROBiosystems
About ACROBiosystems
ACROBiosystems is a cornerstone enterprise of the pharmaceutical and biotechnology industries. Their mission is to help overcome challenges with innovative tools and solutions from discovery to the clinic. They supply life science tools designed to be used in discovery research and scalable to the clinical phase and beyond. By consistently adapting to new regulatory challenges and guidelines, ACROBiosystems delivers solutions, whether it comes through recombinant proteins, antibodies, assay kits, GMP-grade reagents, or custom services. ACROBiosystems empower scientists and engineers dedicated towards innovation to simplify and accelerate the development of new, better, and more affordable medicine.
Sponsored Content Policy: News-Medical.net publishes articles and related content that may be derived from sources where we have existing commercial relationships, provided such content adds value to the core editorial ethos of News-Medical.Net which is to educate and inform site visitors interested in medical research, science, medical devices and treatments.