Conventional monoclonal antibodies specifically bind mono to certain cells or proteins and exercise biological activities. However, it is crucial to block multiple signaling pathways to prevent compensatory effects, particularly for cancer and autoimmune treatments. Viruses can routinely mutate and so easily develop resistance.
Therefore, to avoid the emergence of resistance, it is commonplace to utilize multi-targeting therapies. Under these circumstances, monoclonal antibodies have reduced efficacy.
Recent technological progress has led to the development of bispecific antibodies (BsAb). Bispecific antibodies can produce a synergy effect, which makes them a preferred choice in drug research areas. As of now, there are hundreds of BsAb in clinical trials, a number that will continue to grow in the coming years.
There are multiple formats of BsAb such as IgG-like and non-IgG-like, asymmetric and symmetric. For these newer molecules, pharmacokinetic (PK)/PD assessment and characterization are crucial. Quality attributes including antigen specificity; avidity (for bispecific antibodies that target two molecules on the same cell); affinity and on- and off-rates; process-related impurities such as aggregates, fragments, and homodimers; potency; stability; and half-life may impact pharmacology and should be examined carefully.[2]
As bispecific antibodies may present as a combination of active and inactive biological forms, it is key to determine the bispecific antibody form(s) that is most pharmacologically appropriate to PK/PD assessment and to then develop validated assays that measure the suitable form(s) accordingly. Due to the synergetic effect BsAb presents, the dosage is comparatively low. It, therefore, necessitates a more sensitive assay for analysis.
Case study
Antigen-antibody affinity
Case 1 antigen-antibody affinity
It is crucial to select the building blocks of BsAb with the greatest binding affinity, functionality, and stability based on the kinetics and binding affinities. Especially true when the effector cell and the target cell are subjected to dual-targeting.
Over-activation of T cells or other immune cells is a potential issue when targeting CD3, which can lead to uncurbed cytokines release and result in biosafety issues. Therefore, it becomes a key step to limit the binding of the Fc fragment of CD3-targeting antibodies and Fc gamma receptors, and as a result, decrease any side effects.
To support the potential applications, ACROBiosystems developed a 1:1 heterodimer CD3E&CD3D recombinant protein. This was completed by verifying the purity and bioactivity of the CD3E&CD3D protein utilizing the bispecific antibody (AMG420) through SPR, ELISA, and SDS-PAGE.
MALS verification
Human CD3E&CD3D Heterodimer Protein, His Tag&Tag Free (Cat. No. CDD-H52W1) on SDS-PAGE under reducing (R) and non-reducing (NR) condition. The purity of the protein was more than 85% and around 35-43 kDa verified by SEC-MALS. Image Credit: ACROBiosystems
SPR verification
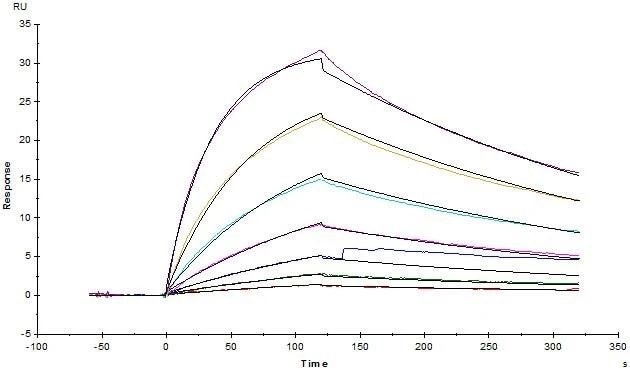
Human CD3E&CD3D Heterodimer Protein, His Tag&Tag Free (Cat. No. CDD-H52W1) on SDS-PAGE under reducing (R) and non-reducing (NR) condition. The purity of the protein was more than 85% and around 35-43 kDa verified by SEC-MALS. Image Credit: ACROBiosystems
ELISA assay verification
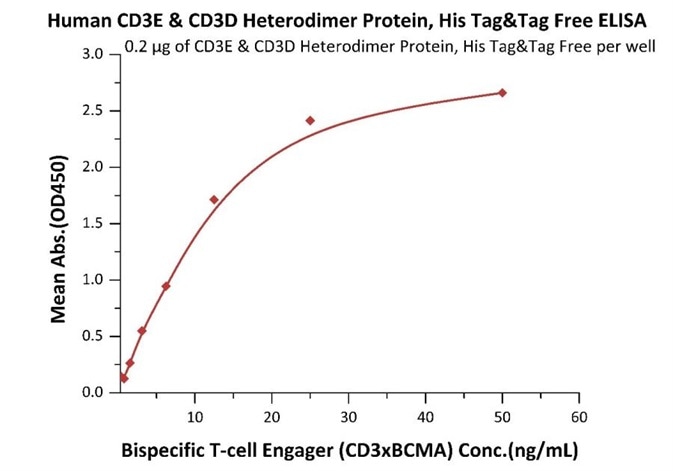
Immobilized Human CD3E&CD3D Heterodimer Protein, His Tag&Tag Free (Cat. No. CDD-H52W1) at 2 μg/mL, add increasing concentrations of Bispecific T cell Engager (CD3 X BCMA) and then add Biotinylated BCMA Fc, Avitag (Cat. No. BC7-H82F0) at 0.2 μg/mL. Detection was performed using HRP-conjugated streptavidin with sensitivity of 4 ng/mL. Image Credit: ACROBiosystems
Case 2 FcRn-antibody affinity
Like BsAb, IgG sustains the same bioactivity and PK/PD attributes as the conventional IgG monoclonal antibody. ACROBiosystems verified the affinity between IgG like BsAb and Fc gamma receptors with the use of Biacore.
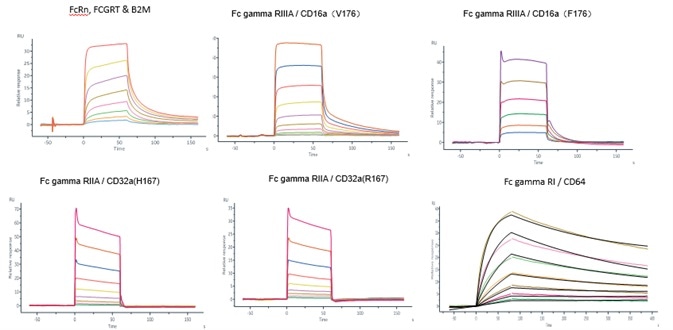
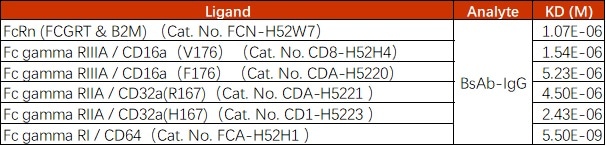
Image Credit: ACROBiosystems
Table 1. Source: ACROBiosystems
PK assessment
The clinical and preclinical pharmacology studies for a BsAb, including the PK assessment, are generally complex because of the interference of anti-drug antibodies and free target proteins present in biological samples.
Intact assay
For the intact BsAb molecule, all functional domains are not inhibited by ADA or free target proteins. Development of the intact assay is carried out to assess the intact BsAb molecule. For this type of assay development, recombinant protein targets or competitive anti-idiotypic antibodies can be used. Some of the benefits of the intact assay include high specificity, small matrix effect, and high sensitivity.
Free A/B assay
Free A/B assay can be developed to examine the functional domains. This technique can be used to assess the activity and exposure of the distinct functional domain as well as analyzing the interference of ADA and free target proteins. Using the particular target protein and the detection antibody is suitable for assay development. The sensitivity is comparatively low because of the matrix effect and steric hindrance in clinical PK study.
Total assay
The complete assay will not be impeded by ADA and free target proteins. Development of the process can be based on the structural domain of the BsAb molecule utilizing non-competitive ADA and detection antibodies, which is useful for evaluation of toxicity.
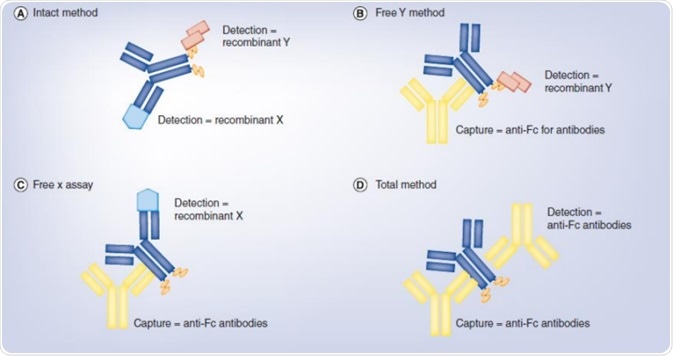
Image Credit: ACROBiosystems
Case 3
An ELISA method, based on the intact assay method, was determined for free CTLA-4 x OX40 BsAb measurement utilizing MALS verified OX40 protein and biotin-labeled CTLA-4 protein.
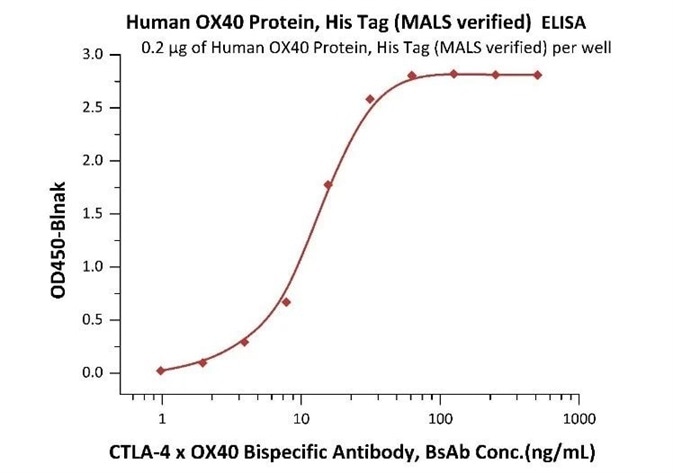
Immobilized Human OX40 Protein, His Tag (MALS verified) (Cat. No. OX0-H5224) at 2 μg/mL, add increasing concentrations of CTLA-4 x OX40 bispecific antibody in 50% Human serum and then add Biotinylated Human CTLA-4, Fc, Avitag (Cat. No. CT4-H82F3) at 0.2 μg/mL. Detection was performed using HRP-conjugated streptavidin with a sensitivity of 4 ng/mL (Intact assay). Image Credit: ACROBiosystems
Methodology validation
Table 2. Source: ACROBiosystems
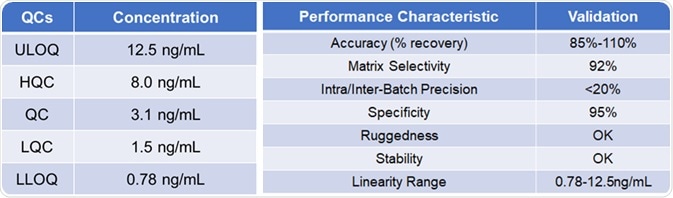
When advancing a PK method, consideration must be given to all the pros and cons of various detection methods. Based on the necessity of sensitivity, the most suitable choices are made to establish a fulfilling method through optimizations.
ACROBiosystems provides SPR /BLI analytical services to its customers based on the Biacore T200/8K platform and ForteBio Octet platform. The SPR/BLI analytical services incorporate antibody screening, kinetic analysis, antibody pairing/group, and interaction measurement.
About ACROBiosystems
ACROBiosystems is a cornerstone enterprise of the pharmaceutical and biotechnology industries. Their mission is to help overcome challenges with innovative tools and solutions from discovery to the clinic. They supply life science tools designed to be used in discovery research and scalable to the clinical phase and beyond. By consistently adapting to new regulatory challenges and guidelines, ACROBiosystems delivers solutions, whether it comes through recombinant proteins, antibodies, assay kits, GMP-grade reagents, or custom services. ACROBiosystems empower scientists and engineers dedicated towards innovation to simplify and accelerate the development of new, better, and more affordable medicine.
Sponsored Content Policy: News-Medical.net publishes articles and related content that may be derived from sources where we have existing commercial relationships, provided such content adds value to the core editorial ethos of News-Medical.Net which is to educate and inform site visitors interested in medical research, science, medical devices and treatments.