COVID-19 infections are once again on the rise in several states just weeks after parts of the U.S. began reopening. As the pandemic continues, researchers and manufacturers are driving prospective therapeutics into clinical trials at an accelerated rate. Recently, Eli Lilly and Regeneron announced their successful clinical trials of therapeutic antibody against COVID-19.
While the development cycle of therapeutic antibodies is fairly short many experts consider the efforts of the companies advancing antibody drugs to be crucial. In comparison with vaccines or antiviral drugs, the therapeutic antibody’s capacity to both treat and protect against viral infections makes them special in some regards. Due to the benefit of high specificity and is easy to scale up, neutralizing antibody development is attracting attention globally.
From the outset of the declaration of the global SARS-CoV-2 pandemic, ACROBiosystems has been dedicated to advancing SARS-CoV-2 related protein reagents and kit products to assist the development of vaccines, therapeutics, and diagnostics. Simultaneously, ACROBiosystems is actively engaged in the detection and characterization of neutralizing antibodies effective against COVID-19.
In collaboration with East China Normal University, SymRay Biopharma Inc., and the First Affiliated Hospital of Zhejiang University, School of Medicine, ACROBiosystems recently released an article titled, ‘Cross-neutralization antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 and RBD mutations from convalescent patient antibody libraries’.
1. The binding affinity of plasma to SARS-CoV-2 RBD
An examination of the capacity of the binding ability of plasma from 18 recovered COVID-19 patients to SARS-CoV-2 RBD by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) was carried out. Moreover, it was discovered that a majority of these convalescent patients could generate high titer of SARS-CoV-2 RBD-specific antibodies in contrast to healthy donors (Fig. 1).
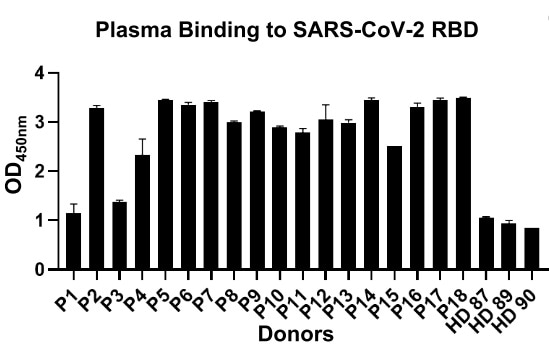
Figure 1. The binding affinity of plasma from each patient to RBD by ELISA. (P1-18, Patients with COVID-19 recovered. HD87-90, healthy donors).
2. Generation of patient-derived antibody library
The PBMC from 18 patients that had recovered from COVID-19 were isolated to produce phage-displayed scFv libraries for panning the neutralizing antibodies. Using solid-phase-bound RBD, affinity selection of the patient-derived antibody library was performed. Following three rounds of panning, 456 positive clones were detected showing the potential bind with RBD specifically. Selectively, 19 of them were then expressed for the following steps.
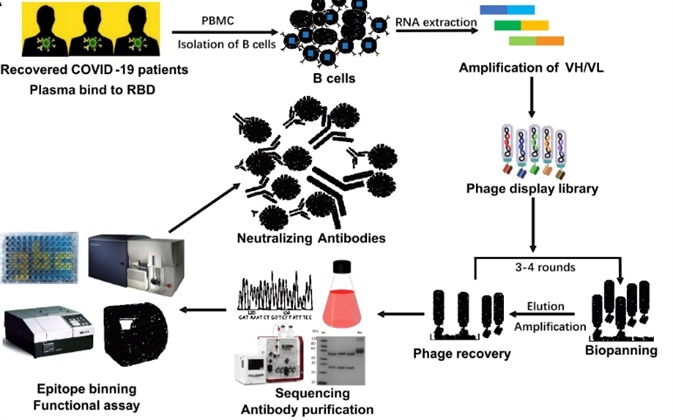
Figure 2. The flow chart of construction and panning of patient-derived scFv libraries.
3. Epitope binning assay
19 IgG can be separated into six different Bins via the Octet method. This includes Bin1 and Bin2 as the groups with the greatest number of clones, indicating that these two epitopes on RBD are vital for recognition by the humoral immune system.
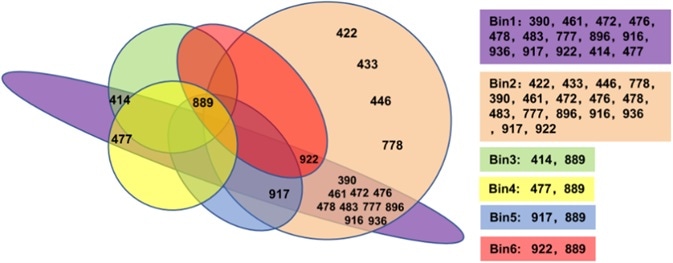
Figure 3. The 19 antibodies were divided into 6 bins by epitope binning assay.
4. Cross-neutralization against SARS-CoV-2 RBD mutations
Based on the in vitro binding assay, some IgG in Bin2 demonstrate superior bioactivity in the blockade of RBD binding to human ACE2 cells. Choosing four antibodies from Bin2 to promote characterization of the neutralizing activity against SARS-CoV-2 RBD mutants – as illustrated in Fig. 4 – HTS0483 can bind with all the RBD mutants and successfully impede the binding between ACE2 and all RBD mutants. This is suggestive of the potentiality of that HTS0483 has the capacity for development into the therapeutics for COVID-19.
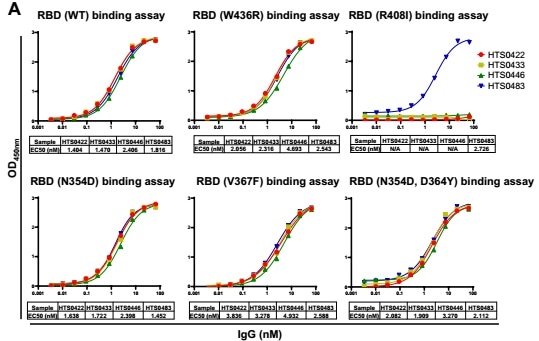
Figure 4. Cross-neutralization against SARS-CoV-2 RBD mutations by different antibodies. (A) The binding affinity of 4 positive antibodies from Bin2 to different SARS-CoV-2 RBD mutations. (B) The blocking ability of 4 positive antibodies from Bin2 to different SARS-CoV-2 RBD mutations.
5. Antiviral properties of human antibodies
All four antibodies from Bin2 demonstrated excellent neutralizing activities in the antiviral studies. The IC50 is between 12.5 nM to 50 nM.
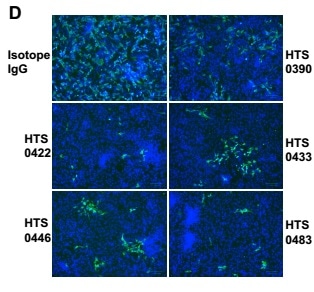
Figure 5. Antiviral properties of human IgG antibodies. The authentic infection of SARS-CoV-2 to Vero-E6 cells was neutralized by Anti-RBD antibodies. Image Credit: AcroBiosystems
ACROBiosystems has advanced anti-SARS-CoV-2 S protein RBD neutralizing antibody and Nucleocapsid antibody. Furthermore, kit products for neutralizing antibody screening and antibody titer assay, and recombination proteins are offered to accelerate the anti-SARS-CoV-2 drugs and vaccines R&D.
References and Further Reading
1. Cross-neutralization antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 and RBD mutations from convalescent patient antibody libraries. doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.06.06.137513
About ACROBiosystems
ACROBiosystems is a cornerstone enterprise of the pharmaceutical and biotechnology industries. Their mission is to help overcome challenges with innovative tools and solutions from discovery to the clinic. They supply life science tools designed to be used in discovery research and scalable to the clinical phase and beyond. By consistently adapting to new regulatory challenges and guidelines, ACROBiosystems delivers solutions, whether it comes through recombinant proteins, antibodies, assay kits, GMP-grade reagents, or custom services. ACROBiosystems empower scientists and engineers dedicated towards innovation to simplify and accelerate the development of new, better, and more affordable medicine.
Sponsored Content Policy: News-Medical.net publishes articles and related content that may be derived from sources where we have existing commercial relationships, provided such content adds value to the core editorial ethos of News-Medical.Net which is to educate and inform site visitors interested in medical research, science, medical devices and treatments.