October 18th, 2021, saw Innovent reveal that the combination of TYVYT® Sintilimab injection, Avastin® Bevacizumab injection and chemotherapy in patients with EGFR-mutated non-squamous, non-small cell lung cancer with previous EGFR-TKI treatment had achieved its primary endpoint.
This represented the world’s first prospective, multi-center, double-blind trial and Phase 3 study to establish that when combined with chemotherapy and anti-vascular drugs, PD-1 inhibitors substantially increased PFS in EGFR-mutated non-squamous NSCLC populations with EGFR-TKI treatment progress.
The growing interest in PD-1 inhibitors as a treatment option
The utilization of immunotherapy has resulted in exceptional therapeutic outcomes in a range of tumor therapies, including melanoma and non-small cell lung cancer treatments.
Recent advances in cancer immunotherapy include the use of antibodies against programmed death 1 (PD-1) and programmed death ligand 1 (PD-L1).
PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors are the most effective class of drugs in the new drugs sector. Initial preclinical evidence indicated that activation of PD-1 and PD-L1 inhibited the activation and proliferation of tumor antigen-specific T cells.
Promotion of tumorigenesis, which negatively regulates the immune function of T cells, was also observed. Preventing this interaction triggered the immune system to attack cancerous cells.
A number of pharmaceutical companies have carried out nearly 500 clinical studies on a range of antibodies, containing up to 20 entities and hematological malignancies.
The Federal Drugs Administration (FDA) has authorized five antibodies for PD-1 PD-1 /PD-L1 signal blocking for use in the treatment of several categories of cancer, while there are a number of antibodies currently in clinical trials which will be utilized in blocking the PD-1 /PD-L1 pathway.
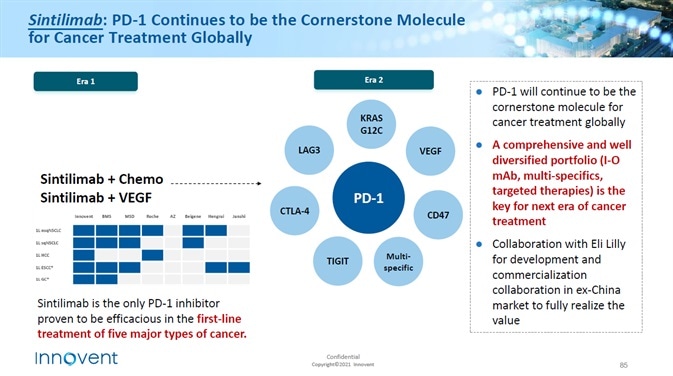
Image Credit: ACROBiosystems
Combining PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors to overcome weaknesses in tumor immunotherapy
PD-1 inhibitors have attained unparalleled success when compared to similar drugs, but not every patient has responded to PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitor treatment when utilized as a monotherapy.
Resistance has also occurred due to complex immune regulatory signaling pathways occurring after treatment.
Given the clinical limitations of anti-PD-1/PD-L1 monotherapy, it is necessary to investigate novel alternative strategies and personalized immunotherapy strategies. This can be achieved by means of a combination of chemotherapy, radiotherapy and PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors with small molecular targets.
The goal of this work is to enhance sensitivity to activated anti-tumor immune response and the response rate of patients in order to address the chokepoint in drug resistance.
Image Credit: ACROBiosystems
Combination therapy consisting of PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors, chemotherapy and radiotherapy
Chemotherapy typically destroys cancer cells by targeting their DNA synthesis and replication processes. It also has a range of other effects:
- It eliminates bone marrow-derived immunosuppressive cells
- It facilitates DCs maturation
- It stimulates Type I interferon response
- It encourages the presentation of tumor antigens after cancer cell death occurs
- It activates tumor-specific T cells
It is important to note that the correct combination of PD-1 inhibitors and chemotherapy drugs will increase the efficacy of PD-1 inhibitors, particularly where the chemotherapy-sensitive tumor possesses low immunogenicity.
Immune checkpoint inhibitors in combination with chemotherapy treatments have been effectively utilized in the following areas:
- Triple-negative breast cancer (KEYNOTES-355, Impassion13)
- Non-small cell lung cancer (KEYNOTE-189, Impower130)
- Small-cell lung cancer (KEYNOTES-407, Impower133)
It is thought that radiotherapy changes the function and differentiation of T cells and promotes PD-L1 expression. This means that the efficacy of anti-PD-L1 treatments can be enhanced when used in combination with increased radiotherapy.
Preclinical models and clinical trials indicated that radiotherapy displayed synergy with a variety of immunotherapies. Preclinical studies, in particular, suggested that combining PD-1 inhibitors and radiotherapy can reduce myelogenous inhibitory cells and activate CTL.
Combining PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors and other immune checkpoint inhibitors
PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors can be utilized in combination with other immune checkpoint inhibitors. The standard combination therapy that blocks PD-1+CTLA-4 also improves efficacy.
Combining PD-1 (nivolumab) and CTLA-4 (ipilimumab) antibodies can result in survival gains in patients diagnosed with melanoma or renal cell carcinoma. It should be noted that the prevalence of adverse reactions is greater than that of monotherapy alone.
Clinical trials involving the combination of PD-1 inhibitors and other inhibitory-receptors - for example, Tim3 and Lag-3 - are already in progress.
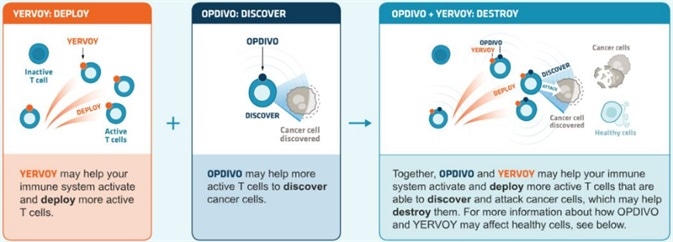
Image Credit: BMS official Website, Zhongkang Industrial Capital Research Center.
Combining PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors and immuno-agonist therapy
Agonists can augment the anti-tumor immune response facilitated by PD-1 blocking.
Agonist antibodies against co-stimulating molecules such as CD40, CD134 (OX40), CD137 (4-1BB) and CD357 (glucocorticoid-induced TNFR; GITR) have supplied lasting response tests in preclinical and clinical studies of mouse tumor models.
Various research results indicate that the application of a PD-1 blocker and a 4-1BB agonist in combination produces synergistic effects in preclinical studies. Phase I/Ib clinical trials of PDR001 (an anti-PD-1 monoclonal antibody) and GWN323 (a combined anti-GITR monoclonal antibody) are currently in progress.
Clinical trials involving the combination of the anti-PD-L1 antibody MEDI4736 and the OX40 agonist MEDI6469 are also under development.
Combining PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors and cell therapy
Chimeric antigen receptor-T (CAR-T) cell therapy and immune checkpoint blockade therapy are cell-based therapies and antibody-based therapies, respectively, and perform a vital role in combatting cancer.
Combining PD-1 blockers and CAR-T cell therapy has been shown to enhance the therapeutic effect in preclinical models and clinical trials.
One study, in particular, showed that a patient with primary mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma recovered to CD19 CAR-T cells after treatment with pembrolizumab.
Combining PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors and T-cell recruitment bispecific antibodies
The T-cell recruitment bispecific antibody (TCB) uses half of the bispecific antibody channel. But, if the T-cell itself is exhausted, it cannot carry out the role of killing tumors.
Combining PD-1 antibodies to restore T-cell activity can, in theory, improve anti-tumor activity. TCB can improve the redirect of T cells to tumors, overcoming instances where the tumors are not sensitive to PD-1 antibodies.
Other combination strategies
Other treatments utilized in combination with PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors include cytokine therapy, vaccines and chemokine inhibition. Cancer vaccines introduce antigens to the immune system, producing an anti-tumor immune response.
Given that the role of PD-1 blockers is to begin a natural immune response, combining them with cancer vaccines could be a viable option for treating tumors displaying low immunogenicity.
In the case of cytokine-related combinations, the majority of research is focused on the combination of VEGF(R) and PD-(L)1. Bevacizumab targeting VEGF itself has an anti-angiogenic effect, which has a direct impact on tumor angiogenesis and cancer cell proliferation. It also enhances T cell infiltration and tumor immunogenicity.
The combination of anti-PD-(L)1 monoclonal antibody and bevacizumab may enhance activated T cells’ response to tumor antigens and additionally enhance their capacity for killing cancer cells.
As part of the above research, ACRO Biosystems developed a sequence of high-quality immune checkpoint proteins based on the company’s technology platform - including PD-1 and PD-L1 - that can be widely utilized in a wide range of applications, including antibody screening, immunition, cell-based assays and PK.
ACRO Biosystems’ product range is rich and diverse, covering numerous labels and species. The range has been verified by MALS for high purity (purity over 90%) and has obtained ELISA/SPR/FACS verification of high bioactivity.
The antibody binding activity has been verified in line with the marketed antibody drug (Nivolumab), while ACROBiosystems has provided a succession of CAR-T and bispecific antibody target proteins.
Popular target protein for CAR-T
Image Credit: ACROBiosystems
Popular target protein with bispecific antibodies
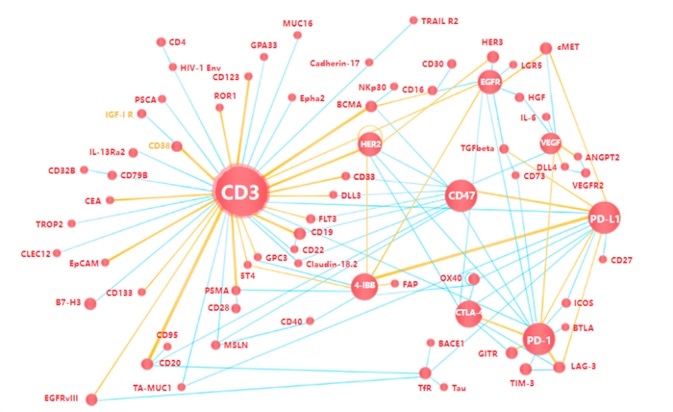
Image Credit: ACROBiosystems
Product list
Source: ACROBiosystems
| Cat. No. |
Speices |
Product Description |
Preorder/Order |
| PD1-H82E4 |
Biotinylated Human PD-1 / PDCD1 Protein, Avitag™,His Tag (recommended for biopanning) (MALS verified) |
Human |
Order |
| PD1-H5221 |
Human PD-1 / PDCD1 Protein, His Tag (MALS Verified) |
Human |
Order |
| PD1-H5257 |
Human PD-1 / PDCD1 Protein, Fc Tag, low endotoxin (MALS Verified) |
Human |
Order |
Click here to learn more about the product list.
Assay data
High purity verified by MALS(>90%)
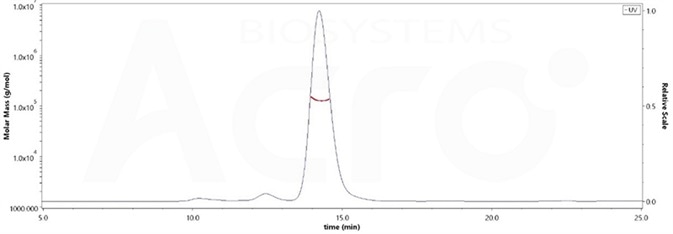
The purity of Human PD-1, Fc Tag, low endotoxin (Cat. No. PD1-H5257) was more than 90% and the molecular weight of this protein is around 105-145 kDa verified by SEC-MALS. Image Credit: ACROBiosystems
Antibody binding assay
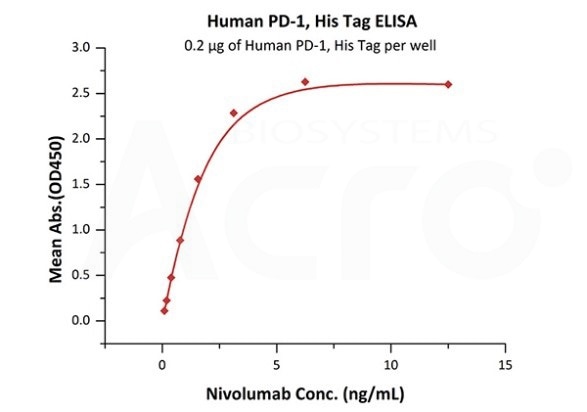
Immobilized Human PD-1, His Tag (Cat. No. PD1-H5221 ) at 2 μg/mL (100 μL/well) can bind. Image Credit: ACROBiosystems
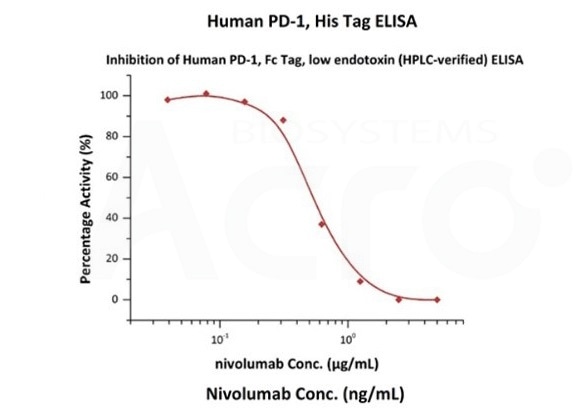
Nivolumab with a linear range of 0.1-3 ng/mL. Serial dilutions of nivolumab were added into Human PD-1, Fc Tag, low endotoxin (Cat. No. PD1-H5257): Biotinylated Human PD-L1, Fc, Avitag, His Tag (Cat. No. PD1-H82F3) binding reactions. The half maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) is 0.5381 μg/mL (Routinely tested). Image Credit: ACROBiosystems
High bioactivity verified by SPR
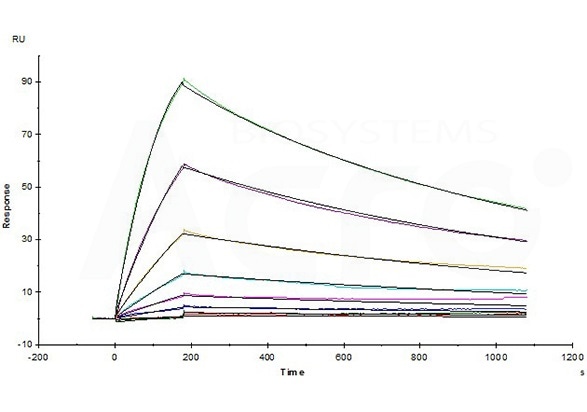
Opdivo (Nivolumab) captured on CM5 chip via anti-human IgG Fc antibodies surface, can bind Human PD-1, His Tag (Cat. No. PD1-H5221) with an affinity constant of 4.94 nM as determined in an SPR assay (Biacore T200) (Routinely tested). Image Credit: ACROBiosystems
References
- Chowdhury P S, Chamoto K, Honjo T . Combination therapy strategies for improving PD-1 blockade efficacy: A new era in cancer immunotherapy[J]. Journal of Internal Medicine, 2017.
- Xu J, Wang Y, Shi J, et al. Combination therapy: A feasibility strategy for CAR-T cell therapy in the treatment of solid tumors:[J]. Oncology Letters, 2018, 16(2):2063-2070.
About ACROBiosystems
ACROBiosystems is a cornerstone enterprise of the pharmaceutical and biotechnology industries. Their mission is to help overcome challenges with innovative tools and solutions from discovery to the clinic. They supply life science tools designed to be used in discovery research and scalable to the clinical phase and beyond. By consistently adapting to new regulatory challenges and guidelines, ACROBiosystems delivers solutions, whether it comes through recombinant proteins, antibodies, assay kits, GMP-grade reagents, or custom services. ACROBiosystems empower scientists and engineers dedicated towards innovation to simplify and accelerate the development of new, better, and more affordable medicine.
Sponsored Content Policy: News-Medical.net publishes articles and related content that may be derived from sources where we have existing commercial relationships, provided such content adds value to the core editorial ethos of News-Medical.Net which is to educate and inform site visitors interested in medical research, science, medical devices and treatments.