Part of the fibrinogen protein family, FGL1 is expressed at low levels in the liver under usual conditions. By contrast, this protein is highly expressed in various types of cancers such as melanoma and prostate cancer.
According to a recent study, FGL1 protein is a hot immune inhibitory ligand of LAG-3 products. Therefore, inhibiting the interaction between FGL1 and LAG-3 would not only improve the body’s immunity but would also slow down the growth of tumors.
ACROBiosystems has developed HEK293-expressed FGL1 protein with a wide range of tags (His, Fc) and species (Mouse, Human, Cyno). The company has also developed AviTagTM biotinylated FGL1 protein that can help in developing drugs. Moreover, ACROBiosystems has validated the activity and purity of FGL1 protein and also offers protocols.
Application
Product List
| Molecule |
Cat. No. |
Host |
Product Description |
Product Status |
FGL1
(HEK293 expressed) |
FG1-H5253 |
Human |
Human FGL1 Protein, Fc Tag |
Launched |
| FG1-H82F3 |
Human |
Biotinylated Human FGL1 Protein, Fc Tag, Avi Tag (Avitag™) |
| FG1-M5255 |
Mouse |
Mouse FGL1 Protein, Fc Tag |
| FG1-C5253 |
Cynomolgus / Rhesus macaque |
Cynomolgus / Rhesus macaque FGL1 Protein, Fc Tag |
| FG1-H52H7 |
Human |
Human FGL1 Protein, His Tag |
Coming soon |
| FG1-H82E5 |
Human |
Biotinylated Human FGL1 Protein, His Tag, Avi Tag (Avitag™) |
| FG1-M5253 |
Mouse |
Mouse FGL1 Protein, Mouse IgG2a Fc Tag |
| FG1-C5256 |
Cynomolgus / Rhesus macaque |
Cynomolgus / Rhesus macaque FGL1 Protein, Mouse IgG2a Fc Tag |
As cited above, FGL1 protein has been recognized as a hot immune inhibitory ligand of LAG-3 products.
Bioactivity
Bioactivity of FGL1 was Validated by ELISA
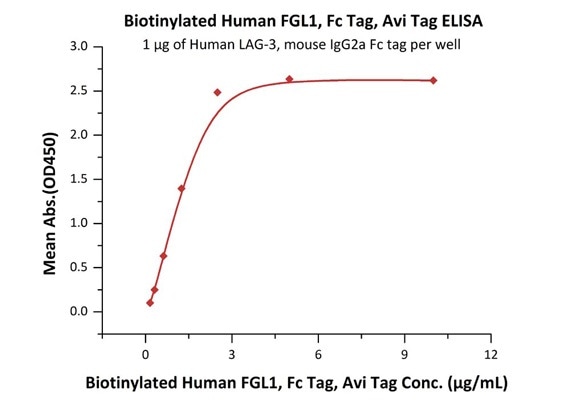
Immobilized Human LAG-3, mouse IgG2a Fc tag (Cat. No. LA3-H52Aa) at 10 μg/mL (100 μL/well) can bind Biotinylated Human FGL1, Fc Tag, Avi Tag (Cat. No. FG1-H82F3) with a linear range of 0.156–1.25 μg/mL.
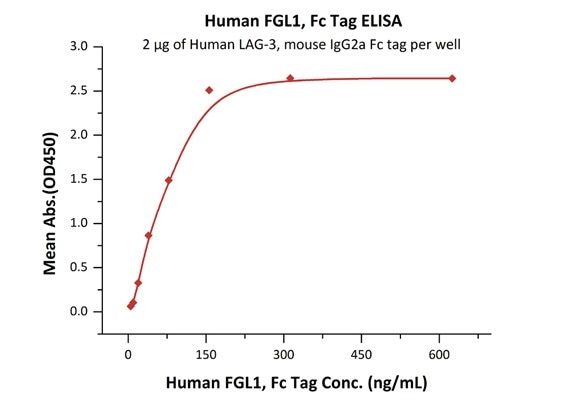
Immobilized Human LAG-3, mouse IgG2a Fc tag (Cat. No. LA3-H52Aa) at 20 μg/mL (100 μL/well) can bind Human FGL1, Fc Tag (Cat. No. FG1-H5253) with a linear range of 5–78 ng/mL.
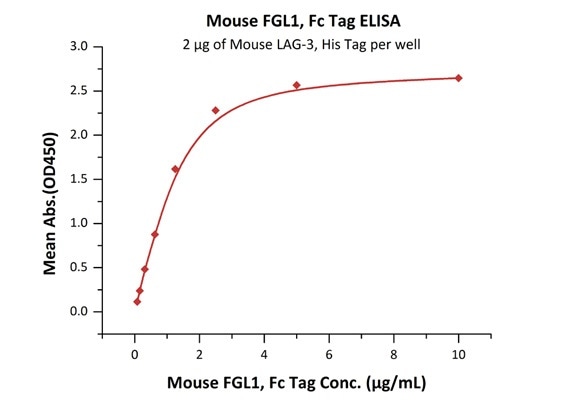
Immobilized Mouse LAG-3, His Tag (Cat. No. LA3-M52H5) at 20 μg/mL (100 μL/well) can bind Mouse FGL1, Fc Tag (Cat. No. FG1-M5255) with a linear range of 0.078–1.25 μg/mL.
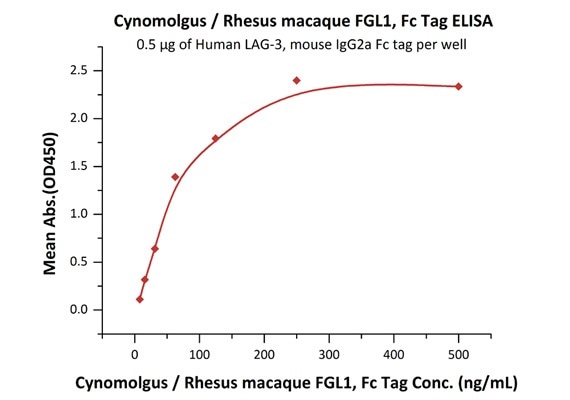
Immobilized Human LAG-3, mouse IgG2a Fc tag (Cat. No. LA3-H52Aa) at 5 μg/mL (100 μL/well) can bind Cynomolgus / Rhesus macaque FGL1, Fc Tag (Cat. No. FG1-C5253) with a linear range of 8–125 ng/mL.
*Customers can contact ACROBiosystems if they wish to add further experimental design and application data of FGL1 protein. If they have any custom-made product or more suggestion for FGL1 protein, they can explore the development suggestion section.
About ACROBiosystems
ACROBiosystems is a cornerstone enterprise of the pharmaceutical and biotechnology industries. Their mission is to help overcome challenges with innovative tools and solutions from discovery to the clinic. They supply life science tools designed to be used in discovery research and scalable to the clinical phase and beyond. By consistently adapting to new regulatory challenges and guidelines, ACROBiosystems delivers solutions, whether it comes through recombinant proteins, antibodies, assay kits, GMP-grade reagents, or custom services. ACROBiosystems empower scientists and engineers dedicated towards innovation to simplify and accelerate the development of new, better, and more affordable medicine.
Sponsored Content Policy: News-Medical.net publishes articles and related content that may be derived from sources where we have existing commercial relationships, provided such content adds value to the core editorial ethos of News-Medical.Net which is to educate and inform site visitors interested in medical research, science, medical devices and treatments.